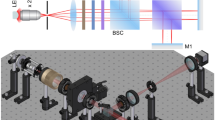
Abstract
Polarised light from astronomical targets can yield a wealth of information about their source radiation mechanisms, and about the geometry of the scattered light regions. Optical observations, of both the linear and circular polarisation components, have been impeded due to non-optimised instrumentation. The need for suitable observing conditions and the availability of luminous targets are also limiting factors. The science motivation of any instrument adds constraints to its operation such as high signal-to-noise (SNR) and detector readout speeds. These factors in particular lead to a wide range of sources that have yet to be observed. The Galway Astronomical Stokes Polarimeter (GASP) has been specifically designed to make observations of these sources. GASP uses division of amplitude polarimeter (DOAP) (Compain and Drevillon Appl. Opt. 37, 5938–5944, 1998) to measure the four components of the Stokes vector (I, Q, U and V) simultaneously, which eliminates the constraints placed upon the need for moving parts during observation, and offers a real-time complete measurement of polarisation. Results from the GASP calibration are presented in this work for both a 1D detector system, and a pixel-by-pixel analysis on a 2D detector system. Following Compain et al. (Appl. Opt. 38, 3490–3502 1999) we use the Eigenvalue Calibration Method (ECM) to measure the polarimetric limitations of the instrument for each of the two systems. Consequently, the ECM is able to compensate for systematic errors introduced by the calibration optics, and it also accounts for all optical elements of the polarimeter in the output. Initial laboratory results of the ECM are presented, using APD detectors, where errors of 0.2 % and 0.1° were measured for the degree of linear polarisation (DOLP) and polarisation angle (PA) respectively. Channel-to-channel image registration is an important aspect of 2-D polarimetry. We present our calibration results of the measured Mueller matrix of each sample, used by the ECM, when 2 Andor iXon Ultra 897 detectors were loaned to the project. A set of Zenith flat-field images were recorded during an observing campaign at the Palomar 200 inch telescope in November 2012. From these we show the polarimetric errors from the spatial polarimetry indicating both the stability and absolute accuracy of GASP.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Errors quoted are based on the Poissonian statistics for the 3 × 3 pixel area
References
Aben, I., Helderman, F., Stam, D.M., Stammes, P.: Spectral fine-structure in the polarisation of skylight. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 591–594 (1999)
Aben, I., Stam, D.M., Helderman, F.: The ring effect in skylight polarisation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 519–522 (2001)
Azzam, R., Bashara, N.: Ellipsometry and Polarized Light. North Holland (1988)
Azzam, R.M.A., Lopez, A.G.: Accurate calibration of the four-detector photopolarimeter with imperfect polarizing optical elements. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 6(10), 1513–1521 (1989)
Boesche, E., Stammes, P., Ruhtz, T., Preusker, R., Fischer, J.: Effect of aerosol microphysical properties on polarization of skylight: sensitivity study and measurements. Appl. Opt. 45, 8790–8805 (2006)
Collins, P., Kyne, G., Lara, D., Redfern, M., Shearer, A., Sheehan, B.: The Galway astronomical Stokes polarimeter: an all-Stokes optical polarimeter with ultra-high time resolution. Experimental Astronomy (2013)
Collins, P., Sheehan, B., Redfern, M., Shearer, A.: GASP - Galway Astronomical Stokes Polarimeter. ArXiv e-prints (2009)
Compain, E., Drevillon, B.: Broadband division-of-amplitude polarimeter based on uncoated prisms. Appl. Opt. 37, 5938–5944 (1998)
Compain, E., Poirier, S., Drevillon, B.: General and self-consistent method for the calibration of polarization modulators, polarimeters, and mueller-matrix ellipsometers. Appl. Opt. 38, 3490–3502 (1999)
Cronin, T.W., Warrant, E.J., Greiner, B.: Celestial polarization patterns during twilight. Appl. Opt. 45, 5582–5589 (2006)
Dahlberg, A.R., Pust, N.J., Shaw, J.A.: All-sky imaging polarimeter measurements of visible and NIR skylight at Mauna Loa, Hawaii. In: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, vol. 7461, p 7 (2009)
de Martino, A.: General methods for optimized design and calibration of Mueller polarimeters. Thin Solid Films 455, 112–119 (2004)
Drevillon, B.: Progress in crystal growth and characterization of materials (1993)
Harrington, D.M., Kuhn, J.R., Hall, S.: Deriving telescope mueller matrices using daytime sky polarization observations. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 123, 799–811 (2011)
Hauge, P.S.: Mueller matrix ellipsometry with imperfect compensators. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 68(11), 1519–1528 (1978)
Horváth, G., Barta, A., Gaĺ, J., Suhai, B., Haiman, O.: Ground-based full-sky imaging polarimetry of rapidly changing skies and its use for polarimetric cloud detection. Appl. Opt. 41, 543–559 (2002)
Kisselev, V., Bulgarelli, B.: Reflection of light from a rough water surface in numerical methods for solving the radiative transfer equation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 85, 419–435 (2004)
Kyne, G.: The optical development and calibration of the Galway Astronomical Stokes Polarimeter (GASP) as a multi-detector system for the polarimetric observations of variable optical sources. PhD thesis, The National University of Ireland, Galway. http://hdl.handle.net/10379/4572 (2014)
Lara Saucedo, D.: Three-dimensional complete polarisation sensitive imaging using a confocal Mueller matrix polarimeter. PhD thesis, Imperial College London (2005)
Litvinov, P., Hasekamp, O., Cairns, B., Mishchenko, M.: Reflection models for soil and vegetation surfaces from multiple-viewing angle photopolarimetric measurements. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 111, 529–539 (2010)
Peltoniemi, J., Hakala, T., Suomalainen, J., Puttonen, E.: Polarised bidirectional reflectance factor measurements from soil, stones, and snow. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 110, 1940–1953 (2009)
Pust, N.J., Shaw, J.A.: Dual-field imaging polarimeter for studying the effect of clouds on sky and target polarization. In: Shaw, J.A., Tyo, J.S. (eds.) Polarization Science and Remote Sensing II, volume 5888 of Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, pp 295–303 (2005)
Pust, N.J., Shaw, J.A.: Dual-field imaging polarimeter using liquid crystal variable retarders. Appl. Opt. 45, 5470–5478 (2006)
Pust, N.J., Shaw, J.A.: All-sky polarization imaging. In: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, vol. 6682, p 4 (2007)
Pust, N.J., Shaw, J.A.: Digital all-sky polarization imaging of partly cloudy skies. Appl. Opt. 47, 190 (2008)
Pust, N.J., Shaw, J.A.: How good is a single-scattering model of visible-NIR atmospheric skylight polarization?. In: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, vol. 7461 (2009)
Shaw, J.A., Pust, N.J., Staal, B., Johnson, J., Dahlberg, A.R.: Continuous outdoor operation of an all-sky polarization imager. In: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, vol. 7672 (2010)
Shukurov, A.K., Shukurov, K.A.: Field studies of the correlation between the atmospheric aerosol content and the light polarization at the zenith of the daytime sky. Izv. Atmos. Oceanic Phys. 42, 68–73 (2006)
Smith, M.H., Woodruff, J.B., Howe, J.D.: Beam wander considerations in imaging polarimetry. In: Goldstein, D.H., Chenault, D.B. (eds.) Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, vol. 3754, pp 50–54 (1999)
Suhai, B., Horváth, G.: How well does the Rayleigh model describe the E-vector distribution of skylight in clear and cloudy conditions? A full-sky polarimetric study. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 21(9), 1669–1676 (2004)
Thompson, R.C., Bottiger, J.R., Fry, E.S.: Measurement of polarized light interactions via the mueller matrix. Appl. Opt. 19(8), 1323–1332 (1980)
Tyo, J.S., Goldstein, D.L., Chenault, D.B., Shaw, J.A.: Review of passive imaging polarimetry for remote sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 45(22), 5453–5469 (2006)
Ugolnikov, O., Maslov, I.: Quadrantids 2008 and 2009: detection of dust in the atmosphere by polarization twilight sky measurements. In: Proceedings of the International Meteor Conference, 27th IMC, Sachticka, 2008, pp 98–101 (2010)
Ugolnikov, O.S., Postylyakov, O.V., Maslov, I.A.: Effects of multiple scattering and atmospheric aerosol on the polarization of the twilight sky. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 88, 233–241 (2004)
Vermeulen, A., Devaux, C., Herman, M.: Retrieval of the scattering and microphysical properties of aerosols from ground-based optical measurements including polarization. I. Method. Appl. Opt. 39, 6207–6220 (2000)
Zeng, J., Han, Q., Wang, J.: High-spectral resolution simulation of polarization of skylight: sensitivity to aerosol vertical profile. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, 20801 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyne, G., Lara, D., Hallinan, G. et al. An investigation of the Eigenvalue Calibration Method (ECM) using GASP for non-imaging and imaging detectors. Exp Astron 41, 43–66 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-015-9464-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-015-9464-z