Abstract
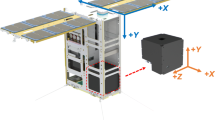
The next generation of instrumentation for nuclear astrophysics will have to achieve a factor of 10–100 improvement in sensitivity over present technologies. With the focusing gamma-ray telescope MAX we take up this challenge: combining unprecedented sensitivity with high spectral and angular resolution, and the capability of measuring the polarization of the incident photons. The feasibility of such a crystal diffraction gamma-ray lens has recently been demonstrated with the prototype lens CLAIRE. MAX is a proposed mission which will make use of satellite formation flight to achieve 86 m focal length, with the Laue lens being carried by one satellite and the detector by the other. In the current design, the Laue diffraction lens of MAX will consist of 13740 copper and germanium (Ge1−x Si x , x ∼ 0.02) crystal tiles arranged on 36 concentric rings. It simultaneously focuses in two energy bands, each centred on one of the main scientific objectives of the mission: the 800–900 keV band is dedicated to the study of nuclear gamma-ray lines from type Ia supernovae (e.g. 56 Co decay line at 847 keV) while the 450–530 keV band focuses on electron-positron annihilation (511 keV emission) from the Galactic centre region with the aim of resolving potential point sources. MAX promises a breakthrough in the study of point sources at gamma-ray energies by combining high narrow-line sensitivity (better than 10−6 cm−2 s−1) and high energy resolution (E/dE ∼ 500). The mission has successfully undergone a pre-phase A study with the French Space Agency CNES, and continues to evolve: new diffracting materials such as bent or composite crystals seem very promising.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrosimov, N. et al.: J. Crystal Growth 275, e495–e500 (2005)
Abrosimov, N.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9036-3 (2006)
Authier, A.: Dynamical theory of X-ray diffraction. Oxford Science Publications (2001)
Boggs, S.E. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9051-4 (2006b)
Bastie, P. et al.: ESRF User report, http://ftp.esrf.fr/pub/UserReports/32513_A.pdf (2006)
Halloin, H., Bastie, P. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9064-z (2006)
Caroli, E. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9048-z (2006)
Courtois, P. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-005-9018-x (2006)
Cosmic Vision, ESA, BR-247
Duchon, P. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9070-1 (2006)
Halloin, H.: Phd Thesis, University Toulouse III, (2003) http://www.cesr.fr/∼pvb/MAX/publis/Diss_Halloin_03.pdf
Hernanz, M. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9036-3 (2006)
Hinglais, E. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-005-9020-3 (2006)
Jean, P. et al.: A&A 445, 579–589 (2006)
Knödlseder, J. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9031-8 (2006)
Leising, M.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9052-3 (2006)
Limousin, O. et al.: NIM A 504, 24–37 (2003)
Lund, N.: Exp Astron 2, 259 (1992)
Prantzos, N.: In Proc 5th INTEGRAL Science Workshop (ESA SP-552), 15 (2005)
Smither, R. et al.: RSI 76, 123107 (2005)
Smither, R. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-005-90919-9 (2006)
Takahashi, T.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9059-9 (2006)
von Ballmoos, P. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9071-0 (2006)
Weidenspointner, G. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9035-4 (2006)
Wunderer, C. et al.: Exp. Astron. 20, DOI 10.1007/s10686-006-9034-5 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS: 95.55.Ka, 29.30.Kv, 61.10.-i
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrière, N., Ballmoos, P.v., Halloin, H. et al. MAX, a Laue diffraction lens for nuclear astrophysics. Exp Astron 20, 269–278 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-006-9058-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-006-9058-x