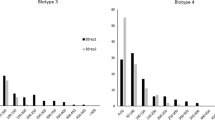
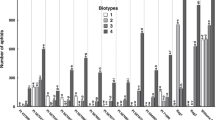
Abstract
Aphis glycines Matsumura, the soybean aphid, first arrived in North America in 2000 and has since become the most important insect pest of domestic soybean, causing significant yield loss and increasing production costs annually in many parts of the USA soybean belt. Research to identify sources of resistance to the pest began shortly after it was found and several sources were quickly identified in the USDA soybean germplasm collection. Characterization of resistance expression and mapping of resistance genes in resistant germplasm accessions resulted in the identification of six named soybean aphid resistance genes: Rag1, rag1c, Rag2, Rag3, rag4, and Rag5 (proposed). Simple sequence repeat markers flanking the resistance genes were identified, facilitating efforts to use marker-assisted selection to develop resistant commercial cultivars. Saturation or fine-mapping with single nucleotide polymorphism markers narrowed the genomic regions containing Rag1 and Rag2 genes. Two potential NBS-LRR candidate genes for Rag1 and one NBS-LRR gene for Rag2 were found within the regions. Years before the release of the first resistant soybean cultivar with Rag1 in 2009, a soybean aphid biotype, named biotype 2, was found that could overcome the resistance gene. Later in 2010, biotype 3 was characterized for its ability to colonize plants with Rag2 and other resistance genes. At present, three biotypes have been reported that can be distinguished by their virulence on Rag1 and Rag2 resistance genes. Frequency and geographic distribution of soybean aphid biotypes are unknown. Research is in progress to determine the inheritance of virulence and develop DNA markers tagging virulence genes to facilitate monitoring of biotypes. With these research findings and the availability of host lines with different resistance genes and biotypes, the soybean aphid-soybean pest-host system has become an important model system for advanced research into the interaction of an aphid with its plant host, and also the tritrophic interaction that includes aphid endosymbionts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anstead JA, Burd JD, Shufran KA (2003) Over-summering and biotypic diversity of Schizaphis graminum (Homoptera: Aphididae) populations on noncultivated grass hosts. Environ Entomol 32:662–667
Auclair JL (1989) Host plant resistance. In: Minks A, Harrewijn P (eds) Aphids: their viology, natural enemies, and control. Elsevier, New York, pp 225–265
Bai X, Zhang W, Orantes L, Jun TH, Mittapalli O, Mian MAR, Michel AP (2010) Combining next-generation sequencing strategies for rapid molecular resource development from an invasive aphid species, Aphis glycines. PLoS One 5:e11370
Basky Z (2003) Biotypic and pest status differences between Hungarian and South African populations of Russian wheat aphid, Diuraphis noxia (Kurdjumov) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Pest Manage Sci 59:1152–1158
Blackman RL, Eastop VF (2000) Aphids on the World’s crops. Wiley, Chichester
Botha A, Li Y, Lapitan N (2005) Cereal host interaction with a homopteran insect, Russian wheat aphid: a review. J Plant Insect Interact 1:211–222
Bregitzer P, Mornhinweg DW, Jones BL (2003) Resistance to Russian wheat aphid damage derived from STARS 9301B protects agronomic performance and malting quality when transferred to adapted barley germplasm. Crop Sci 43:2050–2057
Burd JD, Porter DR (2006) Biotypic diversity in greenbug (Hemiptera: Aphididae): characterizing new virulence and host associations. J Econ Entomol 99:959–965
Burd JD, Porter DR, Puterka GJ, Haley SD, Peairs FB (2006) Biotypic variation among north American Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) populations. J Econ Entomol 99:1862–1866
Caspers-Simmet J (2008) Soybean-aphid resistant varieties will come with a difference. In: Agri News. http://webstar.agrinews.com/agrinews/295310252644869.bsp
Chacón JM, Landis DA, Heimpel GE (2008) Potential for biotic interference of a classical biological control agent of the soybean aphid. Biol Control 46:216–225
Chandrasena D, DiFonzo C, Byrne A (2011) An aphid-dip bioassay to evaluate susceptibility of soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to pyrethroid, organophosphate, and neonicotinoid insecticides. J Econ Entomol 104:1357–1363
Cortada L, Sakai H, Verdejo-Lucas S, Mizukubo T (2011) Meloidogyne virulence locus molecular marker for characterization of selected Mi-virulent populations of Meloidogyne spp. is correlated with several genera of Betaproteobacteria. Phytopathology 101:410–415
Costamagna AC, Landis DA, Difonzo CD (2007) Suppression of soybean aphid by generalist predators results in a trophic cascade in soybeans. Ecol Appl 17:441–451
Diaz-Montano J, Reese JC, Schapaugh WT, Campbell LR (2006) Characterization of antibiosis and antixenosis to the soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in several soybean genotypes. J Econ Entomol 99:1884–1889
Diaz-Montano J, Reese JC, Louis J, Campbell LR, Schapaugh WT (2007) Feeding behavior by the soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on resistant and susceptible soybean genotypes. J Econ Entomol 100:984–989
Flor HH (1971) Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9:275–296
Fox TB, Landis DA, Cardoso FF, Difonzo CD (2005) Impact of predation on establishment of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines in soybean, Glycine max. BioControl 50:545–563
Francis F, Guillonneau F, Leprince P, De Pauw E, Haubruge E, Jia L, Goggin F (2010) Tritrophic interactions among Macrosiphum euphorbiae aphids, their host plants and endosymbionts: investigation by a proteomic approach. J Insect Physiol 56:575–585
Gizlice Z, Carter TE, Burton JW (1994) Genetic base for North American public soybean cultivars released between 1947 and 1988. Crop Sci 34:1143–1151
Haley SD, Peairs FB, Walker CB, Rudolph JB, Randolph TL (2004) Occurrence of a new Russian wheat aphid biotype in Colorado. Crop Sci 44:1589–1592
Hartman GL, Domier LL, Wax LM, Helm CG, Onstad DW, Shaw JT, Solter LF, Voegtlin DJ, D’Arcy CJ, Gray ME, Steffey KL, Isard SA, Orwick PL (2001) Occurrence and distrubution of Aphis glycines on soybeans in Illinois in 2000 and its potential control. Plant Health Progress. doi:10.1094/PHP-2001-0205-1001-HN
Hartman GL, West E, Herman T (2011) Crops that feed the world 2. Soybean-worldwide production, use, and constraints caused by pathogens and pests. Food Security 3:5–17
He F, Liu X, Yan F, Wang Y (1995) Soybean resistance to the soybean aphid. Liaoning Agric Sci 4:30–34
Heimpel GE, Ragsdale DW, Venette R, Hopper KR, O’Neil RJ, Rutledge CE, Wu Z (2004) Prospects for importation biological control of the soybean aphid: anticipating potential costs and benefits. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:249–258
Hesler LS, Dashiell KE (2007) Resistance to Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in various soybean lines under controlled laboratory conditions. J Econ Entomol 100:1464–1469
Hesler LS, Dashiell KE (2008) Identification and characterization of new sources of resistance to Aphis glycines Matsumura (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in soybean lines. Appl Entomol Zool 43:197–206
Hesler LS, Dashiell KE, Lundgren JG (2007) Characterization of resistance to Aphis glycines in soybean accessions. Euphytica 154:91–99
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2004a) Resistance of Glycine species and various cultivated legumes to the soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 97:1071–1077
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2004b) Resistance to the soybean aphid in soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 44:98–106
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2006a) A single dominant gene for resistance to the soybean aphid in the soybean cultivar Dowling. Crop Sci 46:1601–1605
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2006b) Soybean aphid resistance in soybean Jackson is controlled by a single dominant gene. Crop Sci 46:1606–1608
Hill CB, Kim K-S, Crull L, Diers BW, Hartman GL (2009) Inheritance of resistance to the soybean aphid in soybean PI200538. Crop Sci 49:1193–1200
Hill CB, Crull L, Herman TK, Voegtlin DJ, Hartman GL (2010) A new soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) biotype identified. J Econ Entomol 103:509–515
Hodgson EW, Venette RC, Abrahamson M, Ragsdale DW (2005) Alate production of soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Minnesota. Environ Entomol 34:1456–1463
Hogg DB, Mahr D (2007) Binodoxys communis field cage releases for control of the soybean aphid in Wisconsin. Wis Crop Manage 14:129–130
Hu Q, Zhao J, Cui D (1993) Relationship between content of secondary catabolite-lignin-in soybean and soybean resistance to the soybean aphid. Plant Prot 19:8–9
Hymowitz T, Bernard R (1991) Origin of the soybean and germplasm introduction and development in North America. In: Shands HL (ed) Use of plant introductions in cultivar development, part 1. vol 17. CSSA Special Publication, pp 149–167
Jun TH, Rouf Mian MA, Michel AP (2012) Genetic mapping revealed two loci for soybean aphid resistance in PI 567301B. Theor Appl Genet 124:13–22
Kaczorowski KAK, Diers KS, Hudson BW, Matthew E (2008) Microarray-based genetic mapping using soybean near-isogenic lines and generation of SNP markers in the Rag1 aphid-resistance interval. Plant Genome 1:89–98
Kaiser ME, Noma T, Brewer MJ, Pike KS, Vockeroth J, Gaimari SD (2007) Hymenopteran parasitoids and dipteran predators found using soybean aphid after its midwestern United States invasion. Ann Entomol Soc Am 100:196–205
Kaloshian I (2004) Gene-for-gene disease resistance: bridging insect pest and pathogen defense. J Chem Ecol 30:2419–2438
Kaloshian I, Lange WH, Williamson VM (1995) An aphid-resistance locus is tightly linked to the nematode-resistance gene, Mi, in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:622–625
Kang S-T, Rouf Mian MA, Hammond RB (2008) Soybean aphid resistance in PI 243540 is controlled by a single dominant gene. Crop Sci 48:1744–1748
Kim K-S, Diers BW (2009) The associated effects of the soybean aphid resistance locus Rag1 on soybean yield and other agronomic traits. Crop Sci 49:1726–1732
Kim C, Schaible G, Garrett L, Lubowski R, Lee D (2008a) Economic impacts of the US soybean aphid infestation: a multi-regional competitive dynamic analysis. Agri Econ Rev 37:227–242
Kim K-S, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Mian MAR, Diers BW (2008b) Discovery of soybean aphid biotypes. Crop Sci 48:923–928
Kim KS, Bellendir S, Hudson KA, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Hyten DL, Hudson ME, Diers BW (2010) Fine mapping the soybean aphid resistance gene Rag1 in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 120:1063–1071
Klingler J, Powell G, Thompson GA, Isaacs R (1998) Phloem specific aphid resistance in Cucumis melo line AR 5: effects on feeding behaviour and performance of Aphis gossypii. Entomol Exp Appl 86:79–88
Li Y, Hill CB, Hartman GL (2004) Effect of three resistant soybean genotypes on the fecundity, mortality, and maturation of soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 97:1106–1111
Li Y, Hill CB, Carlson S, Diers BW, Hartman GL (2007) Soybean aphid resistance genes in the soybean cultivars Dowling and Jackson map to linkage group. Mol Breed 19:25–34
Li Y, Zou J, Li M, Bilgin DD, Vodkin LO, Hartman GL, Clough SJ (2008) Soybean defense responses to the soybean aphid. New Phytol 179:185–195
Liu J, Wu K, Hopper KR, Zhao K (2004) Population dynamics of Aphis glycines (Homoptera: Aphididae) and its natural enemies in soybean in northern China. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:235–239
Lu LH, Chen RL (1993) Production of the soybean aphid alatae Aphis glycines. Acta Entomol Sinica 36:143–149
Luginbill JP (1969) Developing resistant plants-the ideal method of controlling insects. US Government Print Office
Luzzi BM, Boerma HR, Hussey RS (1995) Inheritance of resistance to the peanut root-knot nematode in soybean. Crop Sci 35:50–53
Matsumura S (1917) A list of the Aphididae of Japan, with description of new species and genera. J College of Ag, Sapporo, Jap 7:387–388
McCornack BP, Ragsdale DW, Venette RC (2004) Demography of soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) at summer temperatures. J Econ Entomol 97:854–861
Mensah C, DiFonzo C, Nelson RL, Wang D (2005) Resistance to soybean aphid in early maturing soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 45:2228–2233
Mensah C, DiFonzo C, Wang D (2008) Inheritance of soybean aphid resistance in PI 567541B and PI 567598B. Crop Sci 48:1759–1763
Mian MAR, Hammond RB, St. Martin SK (2008a) New plant introductions with resistance to the soybean aphid. Crop Sci 48:1055–1061
Mian RM, Kang S-T, Beil S, Hammond R (2008b) Genetic linkage mapping of the soybean aphid resistance gene in PI 243540. Theor Appl Genet 117:955–962
Michel AP, Zhang W, Kyo Jung J, Kang ST, Mian M (2009) Population genetic structure of Aphis glycines. Environ Entomol 38:1301–1311
Michel AP, Mian MAR, Davila-Olivas NH, CaÒas LA (2010) Detached leaf and whole plant assays for soybean aphid resistance: differential responses among resistance sources and biotypes. J Econ Entomol 103:949–957
Mignault MP, Roy M, Brodeur J (2006) Soybean aphid predators in Quebec and the suitability of Aphis glycines as prey for three Coccinellidae. Biocontrol 51:89–106
Nielsen C, Hajek AE (2005) Control of invasive soybean aphid, Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae), populations by existing natural enemies in New York State, with emphasis on entomopathogenic fungi. Environ Entomol 34:1036–1047
Noma T, Brewer MJ (2008) Seasonal abundance of resident parasitoids and predatory flies and corresponding soybean aphid densities, with comments on classical biological control of soybean aphid in the midwest. J Econ Entomol 101:278–287
Powell G, Tosh C, Hardie J (2006) Host plant selection by aphids: behavioral, evolutionary, and applied perspectives. Annu Rev Entomol 51:309–330
Ragsdale D, Voegtlin DJ, O’Neil RJ (2004) Soybean aphid biology in North America. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:204–208
Ragsdale DW, McCornack BP, Venette RC, Potter BD, Macrae IV, Hodgson EW, O’Neal ME, Johnson KD, O’Neil RJ, DiFonzo CD (2007) Economic threshold for soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 100:1258–1267
Ragsdale DW, Landis DA, Brodeur J, Heimpel GE, Desneux N (2011) Ecology and management of the soybean aphid in North America. Annu Rev Entomol 56:375–399
Randolph T, Peairs F, Kroening M, Armstrong J, Hammon R, Walker C, Quick J (2003) Plant damage and yield response to the Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) on susceptible and resistant winter wheats in Colorado. J Econ Entomol 96:352–360
Richardson ML, Lagos DM (2007) Effects of a juvenile hormone analogue, pyriproxyfen, on the apterous form of soybean aphid (Aphis glycines). J Appl Entomol 131:297–302
Rossi M, Goggin FL, Milligan SB, Kaloshian I, Ullman DE, Williamson VM (1998) The nematode resistance gene Mi of tomato confers resistance against the potato aphid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9750–9754
Rutledge CE, O’Neil RJ, Fox TB, Landis DA (2004) Soybean aphid predators and their use in integrated pest management. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:240–248
Schmidt NP, O’Neal ME, Dixon PM (2008) Aphidophagous predators in Iowa soybean: a community comparison across multiple years and sampling methods. Ann Entomol Soc Am 101:341–150
Smith CM (2005) Plant resistance to arthropods: molecular and conventional approaches. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Smith CM, Boyko EV (2007) The molecular bases of plant resistance and defense responses to aphid feeding: current status. Entomol Exp Appl 122:1–16
Smith CM, Belay T, Stauffer C, Stary P, Kubeckova I, Starkey S (2004) Identification of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) populations virulent to the Dn4 resistance gene. J Econ Entomol 97:1112–1117
Somers DS, Chen CY, Gu CG, Mensah CMC, Nelson RL, Wang D (2007) SSR marker diversity of soybean aphid resistance sources in North America. Genome 50:1104–1111
Tagu D, Klingler J, Moya A, Simon J (2008) Early progress in Aphid Genomics and consequences for plant-aphid interactions studies. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21:701–708
Takahashi S, Inaizumi M, Kawakami K (1993) Life cycle of the soybean aphid Aphis glycines Matsumura, in Japan. Jan J Appl Entomol Zool 37:207–207
Tilmon K, Hodgson E, O’Neal M, Ragsdale D (2011) Biology of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in the United States. J Integr Pest Manage 2. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1603/IPM10016
Tsuchida T, Koga R, Fukatsu T (2004) Host plant specialization governed by facultative symbiont. Science 303:1989
van Emden HF (2007) Host-plant resistance. In: van Emden HF, Harrington R (eds) Aphids as crop pests. CAB International, Wallingford, UK
Van Nurden A, Scott R, Hesler L, Tilmon K, Glover K, Carter C (2010) Inheritance of soybean aphid resistance from PI 71506. J Crop Improv 24:400–416
Venette RC, Ragsdale DW (2004) Assessing the invasion by soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae): where will it end? Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:219–226
Voegtlin DJ, Halbert SE, Qiao G (2004a) A guide to separating Aphis glycines Matsumura and morphologically similar species that share its hosts. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:227–232
Voegtlin DJ, O’Neil RJ, Graves WR (2004b) Tests of suitability of overwintering hosts of Aphis glycines: identification of a new host association with Rhamnus alnifolia L’Héritier. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:233–234
Voegtlin DJ, O’neil RJ, Graves WR, Lagos D, Yoo HJS (2005) Potential winter hosts of soybean aphid. Ann Entomol Soc Am 98:690–693
Walling LL (2000) The myriad plant responses to herbivores. J Plant Growth Regul 19:195–216
Wang C, Siang N, Chang G, Chu H (1962) Studies on the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura. Acta Entomol Sinica 11:31–44
Wu Z, Schenk-Hamlin D, Zhan W, Ragsdale DW, Heimpel GE (2004) The soybean aphid in China: a historical review. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:209–218
Wyckhuys KAG, Koch RL, Kula RR, Heimpel GE (2009) Potential exposure of a classical biological control agent of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines, on non-target aphids in North America. Biol Invasions 11:857–871
Yue D, Guo S, Shan Y (1989) Resistance of wild soybean Glycine soja to Aphis glycines. I. Screening for resistant varieties. Jilin Agric Sci 3:15–19
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2009) Molecular mapping of soybean aphid resistance genes in PI 567541B. Theor Appl Genet 118:473–482
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2010) A novel locus for soybean aphid resistance. Theor Appl Genet 120:1183–1191
Zhu J, Zhang A, Park K-C, Baker T, Lang B, Jyrenka R, Obrycki JJ, Graves WR, Pickett JA, Smiley D, Chauhan KR, Klun JA (2006) Sex pheromone of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura, and its potential use in semiochemical-based control. Environ Entomol 35:249–257
Acknowledgments
We thank the following funding agencies for partial support of our research program: Illinois Soybean Association, North Central Soybean Research Program, and the United Soybean Board. We also thank Dr. David Voegtlin for his editorial comments and Theresa Herman for her overall review. We also appreciate the cooperative efforts of Drs. Brian Diers and Rosanna Giordano on soybean aphid breeding and genomics research, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, C.B., Chirumamilla, A. & Hartman, G.L. Resistance and virulence in the soybean-Aphis glycines interaction. Euphytica 186, 635–646 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0695-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0695-z