Abstract
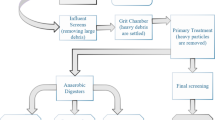
In wastewater treatment plants, predicting influent water quality is important for energy management. The influent water quality is measured by metrics such as carbonaceous biochemical oxygen demand (CBOD), potential of hydrogen, and total suspended solid. In this paper, a data-driven approach for time-ahead prediction of CBOD is presented. Due to limitations in the industrial data acquisition system, CBOD is not recorded at regular time intervals, which causes gaps in the time–series data. Numerous experiments have been performed to approximate the functional relationship between the input and output parameters and thereby fill in the missing CBOD data. Models incorporating seasonality effects are investigated. Four data-mining algorithms—multilayered perceptron, classification and regression tree, multivariate adaptive regression spline, and random forest—are employed to construct prediction models with the maximum prediction horizon of 5 days.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acha, V., Meurens, M., Naveau, H., Dochain, D., Bastin, G., & Agathos, S. N. (1999). Model-based estimation of an anaerobic reductive dechlorination process via an attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared sensor. Water Science and Technology, 40(8), 33–40.
Bernard, O., Hadj-Sadok, Z., Dochain, D., Genovesi, A., & Steyer, J. P. (2001). Dynamical model development and parameter identification for an anaerobic wastewater treatment process. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 75(4), 424–438.
Bigss, D., Ville, B., & Suen, E. (1991). A method of choosing multiway partitions for classification and decision trees. Journal of Applied Statistics, 18(1), 49–62.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32.
Breiman, L., Friedman, J. H., Olshen, R. A., & Stone, C. J. (1984). Classification and regression trees. Monterey, CA: Wadsworth Int.
Cartensen, J., Harremoes, P., & Strube, R. (1996). Software sensors based on the grey-box modeling approach. Water Science and Technology, 33(1), 117–126.
Chen, M. S., Han, J., & Yu, P. S. (1996). Data mining: an overview from a database perspective. Knowledge and Data Engineering, 8(6), 866–883.
Cheruy, A. (1997). Software sensors in bioprocess engineering. Journal of Biotechnology, 52(3), 193–199.
Choi, D. J., & Park, H. (2001). A hybrid artificial neural network as a software sensor for optimal control of a wastewater treatment process. Water Research, 35(16), 3959–3967.
Ciaccio, L. L. (1992). Instrumental determination of the energy oxygen and BOD5. Water Science and Technology, 26(5–6), 1345–1353.
Comas, J., Dzeroski, S., Gibert, K., Roda, I. R., & Marre, M. S. (2001). Knowledge discovery by means of inductive methods in wastewater treatment plant data. AI Communications, 14(1), 45–62.
Coope, I. D. (1993). Circle fitting by linear and nonlinear least squares. Journal of Optimization: Theory and Applications, 76(2), 381–388.
Dixon, M., Gallop, J. R., Lambert, S. C., & Healy, J. V. (2007). Experience with data mining for the anaerobic wastewater treatment process. Environmental Modeling & Software, 22(3), 315–322.
Gernaeya, K. V., Loosdrecht, M., Henzec, M., Lindd, M., & Jorgensen, S. B. (2004). Activated sludge wastewater treatment plant modeling and simulation: state of the art. Environmental Modeling & Software, 19(9), 763–783.
Giudici, P., & Figini, S. (2009). Applied data mining for business and industry. Chichester, UK: Wiley.
Grossman, R. L., Kamath, C., Kegelmeyer, P., Kumar, V., & Namburu, R. R. (2001). Data mining for scientific and engineering applications. The Netherlands: Kluwer.
Hall, M. A. (1998). Correlation-based feature subset selection for machine learning. New Zealand: Hamilton.
Haykin, S. (1998). Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Henze, M., Harremes, P., Jansen, J. L. C., & Arvin, E. (2001). Wastewater treatment: biological and chemical processes. New York: Springer.
Hertz, J. A., Krogh, A., & Palmer, R. G. (1999). Introduction to the theory of neural computation. Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
Holmberg, A. (1982). Modeling of the activated sludge process for microprocessor-based state estimation and control. Water Research, 16(7), 1233–1246.
Kohavi, R., & John, G. H. (1997). Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artificial Intelligence, 97(1–2), 273–324.
Koza, J. R. (1992). Genetic programming: on the programming of computers by means of natural selection. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Kudo, T., & Matsumoto, Y. (2004). A boosting algorithm for classification of semi-structured text. Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP).
Kusiak, A., & Verma, V. (2011). A data-driven approach for monitoring blade pitch faults in wind turbines. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2(1), 87–96.
Madalina, C. (2010). The pollution level analysis of a wastewater treatment plant emissary using data mining. Buletinul, LXII(1), 69–78.
Mamais, D., Jenkins, D., & Pitt, P. (1993). A rapid physical–chemical method for the determination of readily biodegradable soluble COD in municipal wastewater. Water Research, 27(1), 195–197.
Onnerth, T. B., Nielsen, M. K., & Stamer, C. (1996). Advanced computer control based on real and software sensors. Water Science and Technology, 33(1), 234–245.
Qasim, S. R. (1998). Wastewater treatment plants: planning, design, and operation. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Sànchez-Marrè, M., Gibert, K. and Rodríguez-Roda, I. (2004). GESCONDA: a tool for knowledge discovery and data mining in environmental databases. Research on Computing Science. Centro de Investigación en Computación, Instituto Politécnico Nacional, México DF, México, 11, 348–364.
Seckin, N. (2011). Modeling flood discharge at ungauged sites across Turkey using neuro-fuzzy and neural networks. Journal of hydroinformatics, 13(4), 842–849.
Spanjers, H., Olsson, G., & Klapwijk, A. (1993). Determining influent short-term biochemical oxygen demand by combined respirometry and estimation. Water Science and Technology, 28(11–12), 401–414.
Tan, P. T., Steinbach, M., & Kumar, V. (2006). Introduction to data mining. Boston: Pearson.
Yu, H. Q., & Fang, H. P. (2003). Acidogenesis of gelatin-rich wastewater in an up flow anaerobic reactor: influence of pH and temperature. Water Research, 37(1), 55–66.
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported by the Iowa Energy Center, grant no. 08-01
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusiak, A., Verma, A. & Wei, X. A data-mining approach to predict influent quality. Environ Monit Assess 185, 2197–2210 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2701-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2701-2