Abstract
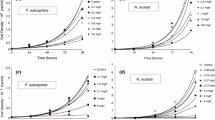
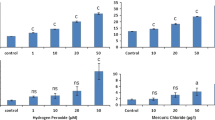
The microalga Euglena was selected as a bioindicator for determining genotoxicity potencies of organic pollutants in Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake, Jiangsu, China among seasons in 2008. Several methods, including the comet assay to determine breaks in DNA and quantification of antioxidant enzymes were applied to characterize genotoxic effects of organic extracts of water from Taihu Lake on the flagellated, microalga Euglena gracilis. Contents of photosynthetic pigments, including Chl a, Chl b and carotenoid pigments were inversely proportion to concentrations of organic extracts to which E. gracilis was exposed. Organic extracts of Taihu Lake water also affected activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) of E. gracilis. There were no statistically significant differences in SOD activities among seasons except in June but significant differences in POD activities were observed among all seasons. The metrics of DNA fragmentation in the alkaline unwinding assay (Comet assay), olive tail moment (OTM) and tail moment (TM), used as measurement endpoints during the genotoxicity assay were both greater when E. gracilis was exposed to organic of water collected from Taihu Lake among four seasons. It is indicated that the comet assay was useful for determining effects of constituents of organic extracts of water on E. gracilis and this assay was effective as an early warning to organic pollutants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera J, Bischof K, Karsten U, Hanelt D, Wiencke C (2002) Seasonal variation in ecophysiological patterns in macroalgae from an Arctic fjord. II. Pigment accumulation and biochemical defence systems against high light stress. Mar Biol 140:1087–1095
Ahmed H, Häder DP (2010) A fast algal bioassay for assessment of copper toxicity in water using Euglena gracilis. J Appl Phycol 22:785–792
Akcha F, Arzul G, Rousseau S, Bardouil M (2008) Comet assay in phytoplankton as biomarker of genotoxic effects of environmental pollution. Mar Environ Res 6:59–61
Allen RD (1995) Dissection of oxidative stress tolerance using transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 107:1049–1054
Aoyama K, Iwahori K, Miyata N (2003) Application of Euglena gracilis cells to comet assay: evaluation of DNA damage and repair. Mutat Res 538:155–162
Aust SD, Marehouse LA, Thomas CE (1985) Role of metals in oxygen radical reactions. J Free Radic Biol Med 1:3–25
Bian YM, Kang ZQ (1994) Systematic analysis for the trace non-volatile organic compounds in drinking water. J Chin Mass Spectrom Soc 15:1–8
Butow BJ, Wynne D, Tel-Or E (1997) Antioxidative protection of Peridinium gatunense in Lake Kinneret: seasonal and daily variation. J Phycol 33:780–786
Checcucci A, Colombetti G, Ferrara R, Lenci F (1976) Action spectra for photo accumulation of green and colorless Euglena: evidence for identification of receptor pigments. Photochem Photobiol 23:51–54
Chen YG, Chen HG, Wu YL, Li ZL, Sun LW, Qu MM (2007) Toxicity evaluation of Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu, China drinking water source. Hydrobiologia 581:297–303
Chen CS, Hseu YC, Liang SH, Kuo JY, Chen SC (2008) Assessment of genotoxicity of methyl-tert-butyl ether, benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene to human lymphocytes using comet assay. Hazard Mater 153:351–356
Collins AR, Dusinska M, Ma AG, Fleming I (1995) The comet assay modified to detect DNA-base oxidation and repair of DNA-damage in cellular and subcellular systems. J Cell Biochem 21A:347
Couderchet M, Vernet G (2003) Pigments as biomarkers of exposure to the vineyard herbicide flazasulfuron in freshwater algae. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 55:271–277
Danilov R, Ekelund N (2000) Applicability of growth rate, cell shape, and motility of Euglena gracilis as physiological parameters for bioassessment at lower concentrations of toxic substances: an experimental approach. Environ Toxicol 16:78–83
Danilov RA, Ekelund NGA (2001) Responses of photosynthetic efficiency, cell shape and motility in Euglena gracilis (Euglenophyceae) to short-term exposure to heavymetals and pentachlorophenol. Water Air Soil Pollut 132:61–73
De Coen WM, Janssen CR, Giesy JP (2000) Biomarker applications in ecotoxicology: bridging the gap between toxicology and ecology, new microbiotests for routine toxicity screening and biomonitoring. In: Persoone G, Jenssen C, De Coen W (eds) New microbiotests for routine toxicity screening and biomonitoring klewer. Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, pp 13–25
Desai SR, Verlecar XN, Nagarajappa, Goswami U (2006) Genotxicity of cadmium in marine diatiom Chaetoceros tenuissimus using the alkaline comet assay. Ecotoxicology 15:359–363
Djomo JE, Dauta A, Ferrier V, Narbonne JF, Monkiedje A, Njine T, Garrigues P (2004) Toxic effects of some major polyaromatic hydrocarbons found in crude oil and aquatic sediments on Scenedesmus subspicatus. Water Res 38:1817–1821
Einicker-Lamas M, Mezian GA, Fernandes TB, Silva FLS, Guerra F, Miranda K, Attias M, Oliveira MM (2002) Euglena gracilis as a model for the study of Cu2+ and Zn2+ toxicity and accumulation in eukaryotic cells. Environ Pollut 120:779–786
Erbes M, Wessler A, Obst U (1997) Wild a detection of primary DNA damage in Chlamidomonas reinrardtii by means of modified microgel electrophoresis. Environ Mol Mutagen 30:448–458
Franqueira D, Orosa M, Torres E, Herrero C, Cid A (2000) Potential use of flow cytometry in toxicity studies with microalgae. Sci Total Environ 247:119–126
Fu GX, Xiao LZ, Jian T (2009) Determination of microcystin-LR in water from Lake Tai, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:230–233
Gao XY, Shi XR, Cui YB, Li M, Zhang RF, Qian X, Jiang Y (2011) Organic pollutants and ambient severity for the drinking water source of western Taihu Lake. Ecotoxicology 20:959–967
Giesy JP (2001) Hormesis—does it have relevance at the population, community or ecosystem levels of organization? Hum Exp Toxicol 20:517–520
Giesy JP, Graney RL (1989) Recent developments in and intercomparisons of acute and chronic bioassays. Hydrobiologia 188:21–60
Giesy JP, Versteeg DJ, Graney RL (1988) A review of selected clinical indicators of stress-induced changes in aquatic organisms. In: Evans MS (ed) Toxic contaminants and ecosystem health: a great lakes focus. Wiley, New York, pp 169–200
Haruhiko N, Yuko H, Masahiro K (2005) Concentrations and compositions of organochlorine contaminants in sediments, soils, crustaceans, fishes and birds collected from Lake Tai, Hangzhou Bay and Shanghai city region, China. Environ Pollution 133:415–429
Hecker M, Giesy JP (2011) Effect-directed analysis of Ah-receptor mediated toxicants, mutagens and endocrine disruptors in sediments and biota. In: Brack W (ed) Effect-directed analysis of complex environmental contamination, 15 vol of the handbook of environmental chemistry. Springer, Berlin, pp 285–313
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equation for determining chlorophyll a, b, c 1 and c 2 . Biochem Physiol Pflanz 167:194–204
Katsoyiannis A, Samara C (2005) Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the conventional activated sludge treatment process: fate and mass balance. Environ Res 97:245–257
Kelly MG, Cazaubon A, Coring E (1998) Recommendations for the routine sampling of diatoms for water quality assessments in Europe. J Appl Phycol 10:215–224
Klobuear GLV, Pavlica M, Erben R, Pape D (2003) Application of the micronucleus and comet assays to mussel Dreissena polymorpha haemocytes for genotoxicity monitoring of freshwater environments. Aquat Toxicol 64:15–23
Kohler A, Arndt U (1992) Bioindikatoren für Umweltbelastungen Neue Aspekte und Entwicklungen. Hohenheimer Umwelttagung 24:251
Li HS (2000) Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment. Beijing Higher Education Press, China, pp 134–137 (in Chinese)
Li M, Hu C, Gao X, Xu Y, Qian X, Brown MT, Cui Y (2009) Genotoxicity of organic pollutants in source of drinking water on microalga Euglena gracilis. Ecotoxicology 18:669–676
Lu G, Yan Z, Wang Y, Chen W (2011) Assessment of estrogenic contamination and biological effects in Lake Taihu. Ecotoxicology 20:974–981
Lu G, Yang X, Li Z, Zhao H, Wang C (2013) Contamination by metals and pharmaceuticals in northern Taihu Lake (China) and its relation to integrated biomarker response in fish. Ecotoxicology 22:50–59
Mazhoudi S, Chaoui A, Ghorbal MH, Ferjani EE (1997) Response of antioxidant enzymes to excess copper in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum, Mill). Plant Sci 127:129–137
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase: an enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biochem 244:6049–6055
McCormick PV, Cairns JJ (1994) Algae as indicators of environmental change. J Appl Phycol 6:509–526
Mitchelmore CL, Chipman JK (1998) DNA strand breakage in aquatic organisms and the potential value of the comet assay in environmental monitoring. Mutat Res 399:135–147
Mitter R (2002) Oxidatve stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Ohe T, Watanabe T, Wakabayashi K (2004) Mutagens in surface waters: a review. Mutat Res 567:109–149
Pellacani C, Buschini A, Furlini M, Poli P, Rossi C (2006) A battery of in vivo and in vitro tests useful for genotoxic pollutant detection in surface waters. Aquat Toxicol 77:1–10
Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao GA (2010) Drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ Manage 45:105–112
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Snyder SA, Snyder EM, Villeneuve D, Kannan K, Aillalobos A, Blankenship AL, Giesy JP (2000) Instrumental and bioanalytical measures of endocrine disruptors in water. In: Keith LH, Jones-Lepp TL, Needham Larry L (eds) Analysis of environmental endocrine disruptors: ACS symposium series 747. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 73–95
Sosak-Swiderska B, Tyrawska D, Maslikowska B (1998) Microalgal ecotoxicity test with 3,4-dichloroaniline. Chemosphere 37:2975–2982
Stebbing ARD (1982) Hormesis—the stimulation of growth by low levels of inhibitors. Sci Total Environ 22:213–234
Strickland JD, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull Fish Res Board Can 167:201–203
Sviežená B, Gálová E, Kusenda B, Slaninová M, Vlček D, Dušinská M (2004) The comet assay and troubles with its application in the green alga Chlamidomonas reinhardtii. Czech Phycol Olomouc 4:163–174
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Turgeon S, Rodriguez MJ, Thriault LP (2004) Perception of drinking water in the Quebec City region (Canada): the influence of water quality and consumer location in the distribution system. J Environ Manage 70:363–373
Watanabe M, Suzuki T (2002) Involvement of reactive oxygen stress in cadmium-induced cellular damage in Euglena gracilis. Comp Biochem Physiol C 131:491–500
Weckx J, Clijesters H (1996) Oxidative damage and defense mechanisms in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris as a result of root assimilation of toxic amounts of copper. Physiol Plantarum 96:506–512
Wu YL, Chen HG, Li ZL, Sun LW (2008) Genotoxicity evaluation of drinking water sources in human peripheral blood lymphocytes using the comet assay. J Environ Sci 20:487–491
Zhu G, Chi QQ, Qin BQ (2005) Heavy-metal contents in suspended solids of Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake and its environmental significances. J Environ Sci 17:672–675
Zhu JP, Susan P, Yong LF (2006) Phthalate esters in human milk: concentration variations over a 6-month postpartum time. Environ Sci Technol 40:5276–5281
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Major Project of Science & Technology Ministry of China (2012ZX07501-003), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2008CB418003), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21077052, 31072217) and Science and Technology Support Program of Jiangsu Province (BE2012737). The authors wish to acknowledge the support of an instrumentation grant from the Canada Foundation for Infrastructure. Prof. Giesy was supported by the program of 2012 “High Level Foreign Experts” (#GDW20123200120) funded by the State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs, the P.R. China to Nanjing University and the Einstein Professor Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He was also supported by the Canada Research Chair program, a Visiting Distinguished Professorship in the Department of Biology and Chemistry and State Key Laboratory in Marine Pollution, City University of Hong Kong.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Gao, X., Wu, B. et al. Microalga Euglena as a bioindicator for testing genotoxic potentials of organic pollutants in Taihu Lake, China. Ecotoxicology 23, 633–640 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1214-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1214-x