Summary
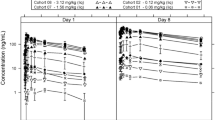
Purpose: This study was to determine the maximum tolerated dose, dose-limiting toxicities, and pharmacokinetic profile of TTI-237, a novel anti-tubulin drug, administered weekly in patients with refractory solid tumors. Patients and methods: Using an accelerated dose escalation design, patients with refractory solid tumors were enrolled in this study and treated with TTI-237 intravenously on days 1, 8 and 15 of a 28-day cycle. The starting dose was 4.5 mg/m2. Pharmacokinetic studies were performed in patients at all dose levels. Result: Twenty-eight patients were enrolled and treated with TTI-237 at dose of 4.5, 9, 15, 22.5 and 31.5 mg/m2. One dose-limiting toxicity neutropenia fever was observed at 31.5 mg/m2, and all seven patients developed grade 3 or 4 neutropenia at that dose level. TTI-237 dosage was de-escalated to 22.5 and 18 mg/m2. Six patients were treated at the 18 mg/m2 dose level without dose-limiting toxicity prior to trial termination. The mean terminal-phase elimination half-life (t1/2) for TTI-237 was 25–29 h, and the mean area under the concentration time curve at 31.5 mg/m2 was 2,768 ng•h/mL. Conclusion: A protocol defined maximum tolerated dose was not determined because of early termination of the TTI-237 trial by the sponsor. 18 mg/m2 may be a tolerable dose of TTI-237.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hahn WC, Weinberg RA (2002) Rules for making human tumor cells. N Engl J Med 347:1593–1603
Jordan MA, Wilson L (2004) Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 4:253–265
Nogales E (2001) Structural insight into microtubule function. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 30:397–420
Bhalla KN (2003) Microtubule-targeted anticancer agents and apoptosis. Oncogene 22:9075–9086
Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC (1995) Paclitaxel (taxol). N Engl J Med 332:1004–1014
Cortes JE, Pazdur R (1995) Docetaxel. J Clin Oncol 13:2643–2655
Crown J, O’Leary M, Ooi WS (2004) Docetaxel and paclitaxel in the treatment of breast cancer: a review of clinical experience. Oncologist 9(Suppl 2):24–32
Bonomi P, Kim K, Fairclough D, Cella D, Kugler J, Rowinsky E, Jiroutek M, Johnson D (2000) Comparison of survival and quality of life in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with two dose levels of paclitaxel combined with cisplatin versus etoposide with cisplatin: results of an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trial. J Clin Oncol 18:623–631
Fossella F, Pereira JR, von Pawel J, Pluzanska A, Gorbounova V, Kaukel E, Mattson KV, Ramlau R, Szczesna A, Fidias P et al (2003) Randomized, multinational, phase III study of docetaxel plus platinum combinations versus vinorelbine plus cisplatin for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the TAX 326 study group. J Clin Oncol 21:3016–3024
Thigpen JT, Blessing JA, Ball H, Hummel SJ, Barrett RJ (1994) Phase II trial of paclitaxel in patients with progressive ovarian carcinoma after platinum-based chemotherapy: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 12:1748–1753
Tannock IF, de Wit R, Berry WR, Horti J, Pluzanska A, Chi KN, Oudard S, Theodore C, James ND, Turesson I et al (2004) Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 351:1502–1512
Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, Rodrigues A, Fodor M, Chao Y, Voznyi E et al (2006) Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: a report of the V325 Study Group. J Clin Oncol 24:4991–4997
Hitt R, Lopez-Pousa A, Martinez-Trufero J, Escrig V, Carles J, Rizo A, Isla D, Vega ME, Marti JL, Lobo F et al (2005) Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus fluorouracil to paclitaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil induction chemotherapy followed by chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:8636–8645
Vermorken JB, Remenar E, van Herpen C, Gorlia T, Mesia R, Degardin M, Stewart JS, Jelic S, Betka J, Preiss JH et al (2007) Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 357:1695–1704
Beyer CF, Zhang N, Hernandez R, Vitale D, Nguyen T, Ayral-Kaloustian S, Gibbons JJ (2009) The microtubule-active antitumor compound TTI-237 has both paclitaxel-like and vincristine-like properties. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 64:681–689
Zhang N, Ayral-Kaloustian S, Nguyen T, Afragola J, Hernandez R, Lucas J, Gibbons J, Beyer C (2007) Synthesis and SAR of [1, 2, 4]triazolo[1, 5-a]pyrimidines, a class of anticancer agents with a unique mechanism of tubulin inhibition. J Med Chem 50:319–327
Beyer CF, Zhang N, Hernandez R, Vitale D, Lucas J, Nguyen T, Discafani C, Ayral-Kaloustian S, Gibbons JJ (2008) TTI-237: a novel microtubule-active compound with in vivo antitumor activity. Cancer Res 68:2292–2300
Rowinsky EK (1997) The taxanes: dosing and scheduling considerations. Oncology (Williston Park) 11:7–19
Seidman AD, Berry D, Cirrincione C, Harris L, Muss H, Marcom PK, Gipson G, Burstein H, Lake D, Shapiro CL et al (2008) Randomized phase III trial of weekly compared with every-3-weeks paclitaxel for metastatic breast cancer, with trastuzumab for all HER-2 overexpressors and random assignment to trastuzumab or not in HER-2 nonoverexpressors: final results of Cancer and Leukemia Group B protocol 9840. J Clin Oncol 26:1642–1649
Geney R, Ungureanu M, Li D, Ojima I (2002) Overcoming multidrug resistance in taxane chemotherapy. Clin Chem Lab Med 40:918–925
Orr GA, Verdier-Pinard P, McDaid H, Horwitz SB (2003) Mechanisms of Taxol resistance related to microtubules. Oncogene 22:7280–7295
Goodin S, Kane MP, Rubin EH (2004) Epothilones: mechanism of action and biologic activity. J Clin Oncol 22:2015–2025
Thomas ES, Gomez HL, Li RK, Chung HC, Fein LE, Chan VF, Jassem J, Pivot XB, Klimovsky JV, de Mendoza FH et al (2007) Ixabepilone plus capecitabine for metastatic breast cancer progressing after anthracycline and taxane treatment. J Clin Oncol 25:5210–5217
Carmena M, Earnshaw WC (2003) The cellular geography of aurora kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:842–854
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang-Gillam, A., Arnold, S.M., Bukowski, R.M. et al. A phase I dose escalation study of TTI-237 in patients with advanced malignant solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 30, 266–272 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9506-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9506-3