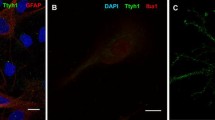
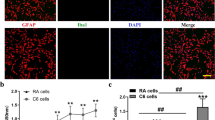
Abstract
The Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor (RhoGDI) originally downregulates Rho family GTPases by preventing nucleotide exchange and membrane association. Although RhoGDI2 functions as a metastasis regulator, little is known in glial cells under neuropathological conditions. We monitored RhoGDI2 expression in the mouse brain after administering a kainic acid(KA)-induced excitotoxic lesion. In control, RhoGDI2 immunoreactivity (IR) was evident in the neuronal layer of the hippocampus. However, RhoGDI2 IR was increased in astrocytes markedly throughout the hippocampus at day 3 post-treatment with KA. To further investigate the molecular mechanism of RhoGDI2-induced cellular migration, primary astrocytes were transfected with the flag-tagged RhoGDI2 cDNA. Cell migration assay revealed that RhoGDI2 cDNA transfection inhibits astrocyte migration. Overexpression of RhoGDI2 leads to inhibit protein kinase B (PKB) activation and cdc42 and cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) phosphorylation. In conclusion, our results suggested for the first time that RhoGDI2 is required for PKB and CREB activation and cdc42 expression in astrocyte migration after KA-mediated excitotoxic lesion in mouse brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal NK, Chen CH, Cho H, Boulbes DR, Spooner E, Sarbassov DD (2013) Rictor regulates cell migration by suppressing RhoGDI2. Oncogene 32:2521–2526
Brunet N, Morin A, Olofsson B (2002) RhoGDI-3 regulates RhoG and targets this protein to the golgi complex through its unique N-terminal domain. Traffic 3:342–357
Cho HJ, Baek KE, Park SM, Kim IK, Choi YL, Cho HJ, Nam IK, Hwang EM, Park JY, Han JY, Kang SS, Kim DC, Lee WS, Lee MN, Oh GT, Kim JW, Lee CW, Yoo J (2009) RhoGDI2 expression is associated with tumor growth and malignant progression of gastric cancer. Clini Cancer Res 15:2612–2619
Chuang TH, Xu X, Knaus UG, Hart MJ, Bokoch GM (1993) GDP dissociation inhibitor prevents intrinsic and GTPase activating protein-stimulated GTP hydrolysis by the Rac GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem 268:775–778
Dastpeyman M, Motamed N, Azadmanesh K, Mostafavi E, Kia V, Jahanian-Najafabadi A, Shokrgozar MA (2012) Inhibition of silibinin on migration and adhesion capacity of human highly metastatic breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-231, by evaluation of beta1-integrin and downstream molecules, Cdc42, Raf-1 and D4GDI. Med Oncol 29:2512–2518
DerMardirossian C, Bokoch GM (2005) GDIs: central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation. Trends Cell Biol 15:356–363
Dovas A, Couchman JR (2005) RhoGDI: multiple functions in the regulation of Rho family GTPase activities. Biochem J 390:1–9
Dubreuil CI, Winton MJ, McKerracher L (2003) Rho activation patterns after spinal cord injury and the role of activated Rho in apoptosis in the central nervous system. J Cell Biol 162:233–243
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420:629–635
Fischer I, Alliod C, Martinier N, Newcombe J, Brana C, Pouly S (2011) Sphingosine kinase 1 and sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 are functionally upregulated on astrocytes under pro-inflammatory conditions. PLoS ONE 6:e23905
Garcia-Mata R, Boulter E, Burridge K (2011) The ‘invisible hand’: regulation of RHO GTPases by RHOGDIs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:493–504
Gildea JJ, Seraj MJ, Oxford G, Harding MA, Hampton GM, Moskaluk CA, Frierson HF, Conaway MR, Theodorescu D (2002) RhoGDI2 is an invasion and metastasis suppressor gene in human cancer. Cancer Res 62:6418–6423
Hall A (1998) Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279:509–514
Hansen C, Howlin J, Tengholm A, Dyachok O, Vogel WF, Nairn AC, Greengard P, Andersson T (2009) Wnt-5a-induced phosphorylation of DARPP-32 inhibits breast cancer cell migration in a CREB-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 284:27533–27543
Hart MJ, Maru Y, Leonard D, Witte ON, Evans T, Cerione RA (1992) A GDP dissociation inhibitor that serves as a GTPase inhibitor for the Ras-like protein CDC42Hs. Science 258:812–815
Holtje M, Hoffmann A, Hofmann F, Mucke C, Grosse G, Van Rooijen N, Kettenmann H, Just I, Ahnert-Hilger G (2005) Role of Rho GTPase in astrocyte morphology and migratory response during in vitro wound healing. J Neurochem 95:1237–1248
Hsu JY, Bourguignon LY, Adams CM, Peyrollier K, Zhang H, Fandel T, Cun CL, Werb Z, Noble-Haeusslein LJ (2008) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 facilitates glial scar formation in the injured spinal cord. J Neurosci 28:13467–13477
Iden S, Collard JG (2008) Crosstalk between small GTPases and polarity proteins in cell polarization. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:846–859
Lee YS, Kang JW, Lee YH, Kim DW (2011) ID4 mediates proliferation of astrocytes after excitotoxic damage in the mouse hippocampus. Anat cell biol 44:128–134
Niu H, Li H, Xu C, He P (2010) Expression profile of RhoGDI2 in lung cancers and role of RhoGDI2 in lung cancer metastasis. Oncol Rep 24:465–471
Nobes CD, Hall A (1995) Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81:53–62
Okada S, Nakamura M, Katoh H, Miyao T, Shimazaki T, Ishii K, Yamane J, Yoshimura A, Iwamoto Y, Toyama Y, Okano H (2006) Conditional ablation of Stat3 or Socs3 discloses a dual role for reactive astrocytes after spinal cord injury. Nat Med 12:829–834
Park J, Kwon K, Kim SH, Yi MH, Zhang E, Kong G, Kim DW, Park J (2013) Astrocytic phosphorylation of PDK1 on Tyr9 following an excitotoxic lesion in the mouse hippocampus. Brain Res 1533:37–43
Penkowa M, Camats J, Hadberg H, Quintana A, Rojas S, Giralt M, Molinero A, Campbell IL, Hidalgo J (2003) Astrocyte-targeted expression of interleukin-6 protects the central nervous system during neuroglial degeneration induced by 6-aminonicotinamide. J Neurosci Res 73:481–496
Qian Y, Corum L, Meng Q, Blenis J, Zheng JZ, Shi X, Flynn DC, Jiang BH (2004) PI3 K induced actin filament remodeling through Akt and p70S6K1: implication of essential role in cell migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C153–C163
Renault-Mihara F, Beuvon F, Iturrioz X, Canton B, De Bouard S, Leonard N, Mouhamad S, Sharif A, Ramos JW, Junier MP, Chneiweiss H (2006) Phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes-15 kDa expression inhibits astrocyte migration by a protein kinase C delta-dependent mechanism. Mol Biol Cell 17:5141–5152
Scherle P, Behrens T, Staudt LM (1993) Ly-GDI, a GDP-dissociation inhibitor of the RhoA GTP-binding protein, is expressed preferentially in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7568–7572
Scita G, Tenca P, Frittoli E, Tocchetti A, Innocenti M, Giardina G, Di Fiore PP (2000) Signaling from Ras to Rac and beyond: not just a matter of GEFs. EMBO j 19:2393–2398
Sofroniew MV (2005) Reactive astrocytes in neural repair and protection. Neuroscientist 11:400–407
Stambolic V, Woodgett JR (2006) Functional distinctions of protein kinase B/Akt isoforms defined by their influence on cell migration. Trends Cell Biol 16:461–466
Takaishi K, Kikuchi A, Kuroda S, Kotani K, Sasaki T, Takai Y (1993) Involvement of rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI) in cell motility. Mol Cell Biol 13:72–79
Theodorescu D, Sapinoso LM, Conaway MR, Oxford G, Hampton GM, Frierson HF Jr (2004) Reduced expression of metastasis suppressor RhoGDI2 is associated with decreased survival for patients with bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:3800–3806
Van Aelst L, D’Souza-Schorey C (1997) Rho GTPases and signaling networks. Genes Dev 11:2295–2322
Walton MR, Dragunow I (2000) Is CREB a key to neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci 23:48–53
Yi MH, Lee YS, Kang JW, Kim SJ, Oh SH, Kim YM, Lee YH, Lee SD, Kim DW (2013) NFAT5-dependent expression of AQP4 in astrocytes. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:223–232
Zhang Y, Zhang B (2006) D4-GDI, a Rho GTPase regulator, promotes breast cancer cell invasiveness. Cancer Res 66:5592–5598
Zhong Y, Zhang B, Eum SY, Toborek M (2012) HIV-1 Tat triggers nuclear localization of ZO-1 via Rho signaling and cAMP response element-binding protein activation. J Neurosci 32:143–150
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (2013R1A1A1A05006966) and by Chungnam National University Hospital Research Fund, 2013.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest related to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Min-Hee Yi and Kisang Kwon have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, MH., Kwon, K., Zhang, E. et al. RhoGDI2 Expression in Astrocytes After an Excitotoxic Lesion in the Mouse Hippocampus. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 167–174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0108-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0108-z