Abstract
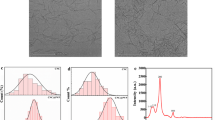
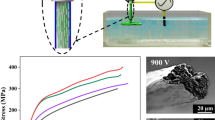
The development of nonwoven meshes based on cellulose acetate (CA) reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) is reported. The meshes were electrospun from 15 wt% CA (Mn = 30,000) in dimethylacetamide/acetone (1:2, w/w) solutions with various concentrations of CNC dispersions. The investigated six levels of CNC dispersions in CA solutions were: 0, 0.075, 0.147, 0.225, 0.300 and 0.382 wt%, which corresponded to 0, 0.50, 1.00, 1.50, 1.99 and 2.55 wt% of CNC in solid fibers. The basis of the impact of CNC nano-particles on fiber diameter and morphology was explored by assessing their contributions to the viscosity, conductivity and homogeneity of CA/CNC solutions. CA/CNC nonwoven meshes spun from suspensions with 0.075 wt% CNC had best results in morphology and fiber uniformity. Additionally, mechanical properties of CA nonwoven meshes with five levels of CNC loading (0, 0.50, 1.00, 1.50 and 1.99 wt%) were examined. The CA nonwoven mesh with 0.50 wt% CNC showed best mechanical properties, and its elastic modulus (E) was improved to an average value of 1.68 GPa from 1.17 GPa of neat CA nanofiber nonwoven mesh. These improved meshes would have applications such as separation membranes, supports for catalysts and sensors, engineered tissues and other smart materials.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki D, Teramoto Y, Nishio Y (2007) SH-containing cellulose acetate derivatives: preparation and characterization as a shape memory-recovery material. Biomacromolecules 8:3749–3757
Boluk Y, Danumah C (2014) Analysis of cellulose nanocrystal rod lengths by dynamic light scattering and electron microscopy. J Nanoparticle Res 16:1–7
Boluk Y, Zhao L, Incani V (2012) Dispersions of nanocrystalline cellulose in aqueous polymer solutions: structure formation of colloidal rods. Langmuir 28:6114–6123
Brinkert L, Abidine N, Aptel P (1993) On the relation between compaction and mechanical properties for ultrafiltration hollow fibers. J Membr Sci 77:123–131
Chen Z, Wei B, Mo X, Lim C, Ramakrishna S, Cui F (2009) Mechanical properties of electrospun collagen–chitosan complex single fibers and membrane. Mater Sci Eng C 29:2428–2435
Chen C, Zhao Y, Liu W (2013) Electrospun polyethylene glycol/cellulose acetate phase change fibers with core–sheath structure for thermal energy storage. Renew Energy 60:222–225
Chew SY, Hufnagel TC, Lim CT, Leong KW (2006) Mechanical properties of single electrospun drug-encapsulated nanofibres. Nanotechnology 17:3880
De Vrieze S, Van Camp T, Nelvig A, Hagström B, Westbroek P, De Clerck K (2009) The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J Mater Sci 44:1357–1362
Dong H, Strawhecker KE, Snyder JF, Orlicki JA, Reiner RS, Rudie AW (2012) Cellulose nanocrystals as a reinforcing material for electrospun poly (methyl methacrylate) fibers: formation, properties and nanomechanical characterization. Carbohydr Polym 87:2488–2495
Ferrarezi MMF, Rodrigues GV, Felisberti MI, Gonçalves MdC (2013) Investigation of cellulose acetate viscoelastic properties in different solvents and microstructure. Eur Polym J 49:2730–2737
Gu SY, Wu QL, Ren J, Vancso GJ (2005) Mechanical properties of a single electrospun fiber and its structures. Macromol Rapid Commun 26:716–720
Guo J, Barbari TA (2010) A dual mode interpretation of the kinetics of penetrant-induced swelling and deswelling in a glassy polymer. Polymer 51:5145–5150
Gupta P, Elkins C, Long TE, Wilkes GL (2005) Electrospinning of linear homopolymers of poly(methyl methacrylate): exploring relationships between fiber formation, viscosity, molecular weight and concentration in a good solvent. Polymer 46:4799–4810
Halaui R, Moldavsky A, Cohen Y, Semiat R, Zussman E (2011) Development of micro-scale hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 379:370–377
Han SO, Youk JH, Min KD, Kang YO, Park WH (2008) Electrospinning of cellulose acetate nanofibers using a mixed solvent of acetic acid/water: effects of solvent composition on the fiber diameter. Mater Lett 62:759–762
Haward R, Thackray G (1968) The use of a mathematical model to describe isothermal stress-strain curves in glassy thermoplastics. Proc R Soc Lond A 302:453–472
Huang L, Arena JT, Manickam SS, Jiang X, Willis BG, McCutcheon JR (2014) Improved mechanical properties and hydrophilicity of electrospun nanofiber membranes for filtration applications by dopamine modification. J Membr Sci 460:241–249
Inai R, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2005) Structure and properties of electrospun PLLA single nanofibres. Nanotechnology 16:208
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink H-P, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:3358–3393
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S, Lindström T, Ankerfors M, Gray D, Dorris A (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5438–5466
Konwarh R, Karak N, Misra M (2013) Electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers: the present status and gamut of biotechnological applications. Biotechnol Adv 31:421–437
Lalia BS, Guillen E, Arafat HA, Hashaikeh R (2014) Nanocrystalline cellulose reinforced PVDF-HFP membranes for membrane distillation application. Desalination 332:134–141
Lim C, Tan E, Ng S (2008) Effects of crystalline morphology on the tensile properties of electrospun polymer nanofibers. Appl Phys Lett 92:141908
Lisunova M, Hildmann A, Hatting B, Datsyuk V, Reich S (2010) Nanofibres of CA/PAN with high amount of carbon nanotubes by core–shell electrospinning. Compos Sci Technol 70:1584–1588
Liu H, Hsieh YL (2002) Ultrafine fibrous cellulose membranes from electrospinning of cellulose acetate. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 40:2119–2129
Liu H, Tang C (2006) Electrospinning of cellulose acetate in solvent mixture N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc)/acetone. Polym J 39:65–72
Lu P, Hsieh Y-L (2009) Cellulose nanocrystal-filled poly (acrylic acid) nanocomposite fibrous membranes. Nanotechnology 20:415604
Lu P, Hsieh Y-L (2010) Multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) reinforced cellulose fibers by electrospinning. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:2413–2420
Ma Z, Ramakrishna S (2008) Electrospun regenerated cellulose nanofiber affinity membrane functionalized with protein A/G for IgG purification. J Membr Sci 319:23–28
Ma Z, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2005) Electrospun cellulose nanofiber as affinity membrane. J Membr Sci 265:115–123
McKee MG, Wilkes GL, Colby RH, Long TE (2004) Correlations of solution rheology with electrospun fiber formation of linear and branched polyesters. Macromolecules 37:1760–1767
Nista SVG, Peres L, D’Ávila MA, Schmidt FL, Mei I, Lucia H (2012) Nanostructured membranes based on cellulose acetate obtained by electrospinning, part 1: study of the best solvents and conditions by design of experiments. J Appl Polym Sci 126:E70–E78
Park WI, Kang M, Kim HS, Jin HJ (2007) Electrospinning of poly(ethylene oxide) with bacterial cellulose whiskers. In: Kim BC, Ahn KD (eds) Macromolecular symposia, vol 1. Wiley, Weinheim, pp 289–294
Peresin MS, Habibi Y, Vesterinen A-H, Rojas OJ, Pawlak JJ, Seppälä JV (2010) Effect of moisture on electrospun nanofiber composites of poly(vinyl alcohol) and cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 11:2471–2477
Ramires EC, Dufresne A (2011) A review of cellulose nanocrystals and nanocomposites. Tappi J 10:9–16
Reneker D, Yarin A, Zussman E, Xu H (2007) Electrospinning of nanofibers from polymer solutions and melts. Adv Appl Mech 41:43–346
Rodríguez K, Gatenholm P, Renneckar S (2012) Electrospinning cellulosic nanofibers for biomedical applications: structure and in vitro biocompatibility. Cellulose 19:1583–1598
Tan E, Ng S, Lim C (2005) Tensile testing of a single ultrafine polymeric fiber. Biomaterials 26:1453–1456
Tashiro K, Kobayashi M (1991) Theoretical evaluation of three-dimensional elastic constants of native and regenerated celluloses: role of hydrogen bonds. Polymer 32:1516–1526
Tungprapa S et al (2007) Electrospun cellulose acetate fibers: effect of solvent system on morphology and fiber diameter. Cellulose 14:563–575
Vallejos ME, Peresin MS, Rojas OJ (2012) All-cellulose composite fibers obtained by electrospinning dispersions of cellulose acetate and cellulose nanocrystals. J Polym Environ 20:1075–1083
Viet D, Beck-Candanedo S, Gray DG (2007) Dispersion of cellulose nanocrystals in polar organic solvents. Cellulose 14:109–113
Wang M, Jin H-J, Kaplan DL, Rutledge GC (2004) Mechanical properties of electrospun silk fibers. Macromolecules 37:6856–6864
Wang C, Hsu C-H, Lin J-H (2006) Scaling laws in electrospinning of polystyrene solutions. Macromolecules 39:7662–7672
Wei X, Xia Z, Wong S-C, Baji A (2009) Modelling of mechanical properties of electrospun nanofibre network. Int J Exp Comput Biomech 1:45–57
Wierenga AM, Philipse AP (1998) Low-shear viscosity of isotropic dispersions of (Brownian) rods and fibres; a review of theory and experiments. Colloids Surf A 137:355–372
Wong S-C, Baji A, Leng S (2008) Effect of fiber diameter on tensile properties of electrospun poly (ɛ-caprolactone). Polymer 49:4713–4722
Yu JH, Fridrikh SV, Rutledge GC (2006) The role of elasticity in the formation of electrospun fibers. Polymer 47:4789–4797
Yu D-G, Li X-Y, Wang X, Chian W, Liao Y-Z, Li Y (2013) Zero-order drug release cellulose acetate nanofibers prepared using coaxial electrospinning. Cellulose 20:379–389
Zhou C, Wu Q (2012) Recent development in applications of cellulose nanocrystals for advanced polymer-based nanocomposites by novel fabrication strategies. In: Neralla S (ed) Nanocrystals–synthesis, characterization, and applications. InTech, pp 103-120
Zhou C, Chu R, Wu R, Wu Q (2011a) Electrospun polyethylene oxide/cellulose nanocrystal composite nanofibrous mats with homogeneous and heterogeneous microstructures. Biomacromolecules 12:2617–2625
Zhou W, He J, Cui S, Gao W (2011b) Studies of electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibrous membranes. Open Mater Sci J 5:51–55
Zoppe JO, Peresin MS, Habibi Y, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ (2009) Reinforcing poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers with cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:1996–2004
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge personnel and equipment funding provided by NSERC and Canadian Foundation for Innovation (CFI) for the completion of this research project. Additionally, the CNC used in this research was provided by Alberta Innovates Technology Futures (AITF) in Edmonton, AB, Canada; therefore, the authors would like to thank AITF for the material provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Boluk, Y. & Ayranci, C. Investigation of nanofiber nonwoven meshes produced by electrospinning of cellulose nanocrystal suspensions in cellulose acetate solutions. Cellulose 22, 2457–2470 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0665-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0665-4