Abstract
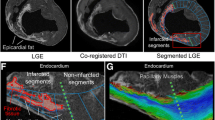
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is used to quantify myocardial fiber orientation based on helical angles (HA). Accurate HA measurements require multiple excitations (NEX) and/or several diffusion encoding directions (DED). However, increasing NEX and/or DED increases acquisition time (TA). Therefore, in this study, we propose to reduce TA by implementing a 3D adaptive anisotropic Gaussian filter (AAGF) on the DTI data acquired from ex-vivo healthy and infarcted porcine hearts. DTI was performed on ex-vivo hearts [9-healthy, 3-myocardial infarction (MI)] with several combinations of DED and NEX. AAGF, mean (AVF) and median filters (MF) were applied on the primary eigenvectors of the diffusion tensor prior to HA estimation. The performance of AAGF was compared against AVF and MF. Root mean square error (RMSE), concordance correlation-coefficients and Bland–Altman’s technique was used to determine optimal combination of DED and NEX that generated the best HA maps in the least possible TA. Lastly, the effect of implementing AAGF on the infarcted porcine hearts was also investigated. RMSE in HA estimation for AAGF was lower compared to AVF or MF. Post-filtering (AAGF) fewer DED and NEX were required to achieve HA maps with similar integrity as those obtained from higher NEX and/or DED. Pathological alterations caused in HA orientation in the MI model were preserved post-filtering (AAGF). Our results demonstrate that AAGF reduces TA without affecting the integrity of the myocardial microstructure.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunter PJ, Pullan AJ, Smaill BH (2003) Modeling total heart function. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 5:147–177
Kanai A, Salama G (1995) Optical mapping reveals that repolarization spreads anisotropically and is guided by fiber orientation in guinea pig hearts. Circ Res 77(4):784–802
Taccardi B, Lux RL, Ershler PR et al (1997) Anatomical architecture and electrical activity of the heart. Acta Cardiol 52(2):91–105
LeGrice IJ, Takayama Y, Covell JW (1995) Transverse shear along myocardial cleavage planes provides a mechanism for normal systolic wall thickening. Circ Res 77(1):182–193
Waldman LK, Nosan D, Villarreal F, Covell JW (1988) Relation between transmural deformation and local myofiber direction in canine left ventricle. Circ Res 63(3):550–562
Cutler MJ, Jeyaraj D, Rosenbaum DS (2011) Cardiac electrical remodeling in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 32(3):174–180
Weisman HF, Bush DE, Mannisi JA, Bulkley BH (1985) Global cardiac remodeling after acute myocardial infarction: a study in the rat model. J Am Coll Cardiol 5(6):1355–1362
Tezuka F (1975) Muscle-fiber orientation in normal and hypertrophied hearts. Tohoku J Exp Med 117(3):289–297
Scollan DF, Holmes A, Winslow R, Forder J (1998) Histological validation of myocardial microstructure obtained from diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Physiol 275(6 Pt 2):H2308–H2318
Streeter DD Jr, Spotnitz HM, Patel DP, Ross J Jr, Sonnenblick EH (1969) Fiber orientation in the canine left ventricle during diastole and systole. Circ Res 24(3):339–347
Wu MT, Tseng WY, Su MY et al (2006) Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging mapping the fiber architecture remodeling in human myocardium after infarction: correlation with viability and wall motion. Circulation 114(10):1036–1045
Tseng WY, Dou J, Reese TG, Wedeen VJ (2006) Imaging myocardial fiber disarray and intramural strain hypokinesis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 23(1):1–8
Qin X, Wang S, Shen M et al (2015) Simulating cardiac ultrasound image based on MR diffusion tensor imaging. Med Phys 42(9):5144–5156
Wu Y, Zou C, Liu W et al (2013) Effect of B-value in revealing postinfarct myocardial microstructural remodeling using MR diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 31(6):847–856
Wu Y, Zhang LJ, Zou C, Tse HF, Wu EX (2011) Transmural heterogeneity of left ventricular myocardium remodeling in postinfarct porcine model revealed by MR diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 34(1):43–49
Mekkaoui C, Huang S, Chen HH et al (2012) Fiber architecture in remodeled myocardium revealed with a quantitative diffusion CMR tractography framework and histological validation. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 14:70
Martin-Fernandez M, Munoz-Moreno E, Cammoun L et al (2009) Sequential anisotropic multichannel Wiener filtering with Rician bias correction applied to 3D regularization of DWI data. Med Image Anal 13(1):19–35
Hamarneh G, Hradsky J (2006) Bilateral filtering of diffusion tensor MR images. In: 2006 IEEE international symposium on signal processing and information technology, Vols 1 and 2, pp. 507–512
Basu S, Fletcher T, Whitaker R (2006) Rician noise removal in diffusion tensor MRI. Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—Miccai 2006, Pt 1, 2006. 4190 pp. 117–125
Pizurica A, Philips W, Lemahieu I, Acheroy M (2003) A versatile wavelet domain noise filtration technique for medical imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22(3):323–331
Parker GJ, Schnabel JA, Symms MR, Werring DJ, Barker GJ (2000) Nonlinear smoothing for reduction of systematic and random errors in diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 11(6):702–710
Chen B, Hsu EW (2005) Noise removal in magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 54(2):393–401
Castano-Moraga CA, Lenglet C, Deriche R, Ruiz-Alzola J (2007) A Riemannian approach to anisotropic filtering of tensor fields. Signal Process 87(2):263–276
McGraw T, Vemuri BC, Chen Y, Rao M, Mareci T (2004) DT-MRI denoising and neuronal fiber tracking. Med Image Anal 8(2):95–111
Bai H, Gao Y, Wang S, Luo L (2008) A robust diffusion tensor estimation method for DTI. J Comput Res Dev 45:1232–1238
Liu M, Vemuri BC, Deriche R (2013) A robust variational approach for simultaneous smoothing and estimation of DTI. Neuroimage 67:33–41
Pennec X, Fillard P, Ayache N (2006) A Riemannian framework for tensor computing. Int J Comput Vision 66(1):41–66
Fillard P, Pennec X, Arsigny V, Ayache N (2007) Clinical DT-MRI estimation, smoothing, and fiber tracking with log-Euclidean metrics. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26(11):1472–1482
Kim W, Jeong MH, Sim DS et al (2011) A porcine model of ischemic heart failure produced by intracoronary injection of ethyl alcohol. Heart Vessels 26(3):342–348
Holmes JW, Borg TK, Covell JW (2005) Structure and mechanics of healing myocardial infarcts. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7:223–253
Lin LI (1989) A concordance correlation-coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 45(1):255–268
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Kocica MJ, Corno AF, Carreras-Costa F et al (2006) The helical ventricular myocardial band: global, three-dimensional, functional architecture of the ventricular myocardium. Eur J Cardio Thorac 29:S21–S40
Ross DN (2006) Torrent-Guasp’s anatomical legacy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 29(Suppl 1):S18–S20
Jones DK (2004) The effect of gradient sampling schemes on measures derived from diffusion tensor MRI: a Monte Carlo study. Magn Reson Med 51(4):807–815
Nielles-Vallespin S, Mekkaoui C, Gatehouse P et al (2013) In vivo diffusion tensor MRI of the human heart: reproducibility of breath-hold and navigator-based approaches. Magn Reson Med 70(2):454–465
Lau AZ, Tunnicliffe EM, Frost R et al (2015) Accelerated human cardiac diffusion tensor imaging using simultaneous multislice imaging. Magn Reson Med 73(3):995–1004
Gamper U, Boesiger P, Kozerke S (2007) Diffusion imaging of the in vivo heart using spin echoes–considerations on bulk motion sensitivity. Magn Reson Med 57(2):331–337
Nguyen C, Fan Z, Sharif B et al (2014) In vivo three-dimensional high resolution cardiac diffusion-weighted MRI: a motion compensated diffusion-prepared balanced steady-state free precession approach. Magn Reson Med 72(5):1257–1267
Wu EX, Wu Y, Nicholls JM et al (2007) MR diffusion tensor imaging study of postinfarct myocardium structural remodeling in a porcine model. Magn Reson Med 58(4):687–695
Smerup M, Agger P, Nielsen EA et al (2013) Regional and epi- to endocardial differences in transmural angles of left ventricular cardiomyocytes measured in ex vivo pig hearts: functional implications. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 296(11):1724–1734
Crawford GN, Barer R (1951) The action of formaldehyde on living cells as studied by phase-contrast microscopy. J Microscopical Sci 92(4):403–452
Acknowledgments
The authors thank DHLRI Interventional Cardiology Catheterization Core Lab and Joseph Matthew for their help in preparing the animal models. We also thank Siemens Healthcare for supporting this project by providing us with the required pulse sequence.
Funding
This manuscript has been supported by Grant sponsor: American Heart Association; Grant Number: 13SDG14690027; Grant Sponsor: Center for Clinical and Translational Sciences; Grant Number: UL1TR000090; Grant Sponsor: NIH–NHLBI; Grant Number: NIH-R01HL24096.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the university’s institutional animal care and use committee guidelines.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazumder, R., Clymer, B.D., Mo, X. et al. Adaptive anisotropic gaussian filtering to reduce acquisition time in cardiac diffusion tensor imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 32, 921–934 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-016-0848-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-016-0848-6