Abstract
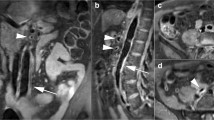
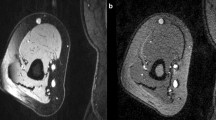
The purpose of this study is to primarily evaluate the lumen area and secondarily evaluate wall area measurements of in vivo lower extremity peripheral vein bypass grafts patients using high spatial resolution, limited field of view, cardiac gated, black blood inner volume three-dimensional fast spin echo MRI. Fifteen LE-PVBG patients prospectively underwent ultrasound followed by T1-weighted and T2-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. Lumen and vessel wall areas were measured by direct planimetry. For graft lumen areas, T1- and T2-weighted measurements were compared with ultrasound. For vessel wall areas, differences between T1- and T2-weighted measurements were evaluated. There was no significant difference between ultrasound and MR lumen measurements, reflecting minimal MR blood suppression artifact. Graft wall area measured from T1-weighted images was significantly larger than that measured from T2-weighted images (P < 0.001). The mean of the ratio of T1- versus T2-weighted vessel wall areas was 1.59 (95% CI: 1.48–1.69). The larger wall area measured on T1-weighted images was due to a significantly larger outer vessel wall boundary. Very high spatial resolution LE-PVBG vessel wall MR imaging can be performed in vivo, enabling accurate measurements of lumen and vessel wall areas and discerning differences in those measures between different tissue contrast weightings. Vessel wall area differences suggest that LE-PVBG vessel wall tissues produce distinct signal characteristics under T1 and T2 MR contrast weightings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies MG, Hagen PO (1995) Pathophysiology of vein graft failure: a review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 9:7–18
Mills JL Sr (2001) Infrainguinal vein graft surveillance: how and when. Semin Vasc Surg 14:169–176
Balu N, Chu B, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C, Yarnykh VL (2008) Comparison between 2D and 3D high-resolution black-blood techniques for carotid artery wall imaging in clinically significant atherosclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:918–924
Crowe LA, Gatehouse P, Yang GZ, Mohiaddin RH, Varghese A, Charrier C, Keegan J, Firmin DN (2003) Volume-selective 3D turbo spin echo imaging for vascular wall imaging and distensibility measurement. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:572–580
Edelman RR, Chien D, Kim D (1991) Fast selective black blood MR imaging. Radiology 181:655–660
Koktzoglou I, Chung YC, Carroll TJ, Simonetti OP, Morasch MD, Li D (2007) Three-dimensional black-blood MR imaging of carotid arteries with segmented steady-state free precession: initial experience. Radiology 243:220–228
Kuribayashi H, Tessier JJ, Checkley DR, Wang YX, Hultin L, Waterton JC (2004) Effective blood signal suppression using double inversion-recovery and slice reordering for multislice fast spin-echo MRI and its application in simultaneous proton density and T2 weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:881–888
Luk-Pat GT, Gold GE, Olcott EW, Hu BS, Nishimura DG (1999) High-resolution three-dimensional in vivo imaging of atherosclerotic plaque. Magn Reson Med 42:762–771
Mani V, Itskovich VV, Szimtenings M, Aguinaldo JG, Samber DD, Mizsei G, Fayad ZA (2004) Rapid extended coverage simultaneous multisection black-blood vessel wall MR imaging. Radiology 232:281–288
Mitsouras D, Mulkern RV, Owens CD, Conte MS, Ersoy H, Luu TM, Whitmore AG, Creager MA, Rybicki FJ (2008) High-resolution peripheral vein bypass graft wall studies using high sampling efficiency inner volume 3D FSE. Magn Reson Med 59:650–654
Morrisett J, Vick W, Sharma R, Lawrie G, Reardon M, Ezell E, Schwartz J, Hunter G, Gorenstein D (2003) Discrimination of components in atherosclerotic plaques from human carotid endarterectomy specimens by magnetic resonance imaging ex vivo. Magn Reson Imaging 21:465–474
Parker DL, Goodrich KC, Masiker M, Tsuruda JS, Katzman GL (2002) Improved efficiency in double-inversion fast spin-echo imaging. Magn Reson Med 47:1017–1021
Sharma R (2002) MR imaging in carotid artery atherosclerosis plaque characterization. Magn Reson Med Sci 1:217–232
Simonetti OP, Finn JP, White RD, Laub G, Henry DA (1996) “Black blood” T2-weighted inversion-recovery MR imaging of the heart. Radiology 199:49–57
Toussaint JF, LaMuraglia GM, Southern JF, Fuster V, Kantor HL (1996) Magnetic resonance images lipid, fibrous, calcified, hemorrhagic, and thrombotic components of human atherosclerosis in vivo. Circulation 94:932–938
Yarnykh VL, Yuan C (2003) Multislice double inversion-recovery black-blood imaging with simultaneous slice reinversion. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:478–483
Yarnykh VL, Yuan C (2006) Simultaneous outer volume and blood suppression by quadruple inversion-recovery. Magn Reson Med 55:1083–1092
Yuan C, Kerwin WS, Yarnykh VL, Cai J, Saam T, Chu B, Takaya N, Ferguson MS, Underhill H, Xu D, Liu F, Hatsukami TS (2006) MRI of atherosclerosis in clinical trials. NMR Biomed 19:636–654
Clarke SE, Hammond RR, Mitchell JR, Rutt BK (2003) Quantitative assessment of carotid plaque composition using multicontrast MRI and registered histology. Magn Reson Med 50:1199–1208
Crowe LA, Varghese A, Mohiaddin RH, Yang GZ, Firmin DN (2006) Elimination of residual blood flow-related signal in 3D volume-selective TSE arterial wall imaging using velocity-sensitive phase reconstruction. J Magn Reson Imaging 23:416–421
Varghese A, Merrifield RD, Crowe LA, Collins SA, Keenan NG, Firmin DN, Yang GZ, Pennell DJ (2006) Evaluation of carotid artery wall volume measurement using novel semiautomated analysis software. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:1401–1408
Fayad ZA (2001) The assessment of the vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque using MR imaging: a brief review. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 17:165–177
Worthley SG, Helft G, Fayad ZA, Fuster V, Rodriguez OJ, Zaman AG, Badimon JJ (2001) Cardiac gated breath-hold black blood MRI of the coronary artery wall: an in vivo and ex vivo comparison. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 17:195–201
Zimmermann GG, Erhart P, Schneider J, von Schulthess GK, Schmidt M, Debatin JF (1997) Intravascular MR imaging of atherosclerotic plaque: ex vivo analysis of human femoral arteries with histologic correlation. Radiology 204:769–774
Fayad ZA, Fuster V, Fallon JT, Jayasundera T, Worthley SG, Helft G, Aguinaldo JG, Badimon JJ, Sharma SK (2000) Noninvasive in vivo human coronary artery lumen and wall imaging using black-blood magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 102:506–510
Terry CM, Kim SE, Li L, Goodrich KC, Hadley JR, Blumenthal DK, Parker DL, Cheung AK (2009) Longitudinal assessment of hyperplasia using magnetic resonance imaging without contrast in a porcine arteriovenous graft model. Acad Radiol 16:96–107
Qiao Y, Ronen I, Viereck J, Ruberg FL, Hamilton JA (2007) Identification of atherosclerotic lipid deposits by diffusion-weighted imaging. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1440–1446
Koktzoglou I, Kirpalani A, Carroll TJ, Li D, Carr JC (2007) Dark-blood MRI of the thoracic aorta with 3D diffusion-prepared steady-state free precession: initial clinical evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:966–972
Larose E, Yeghiazarians Y, Libby P, Yucel EK, Aikawa M, Kacher DF, Aikawa E, Kinlay S, Schoen FJ, Selwyn AP, Ganz P (2005) Characterization of human atherosclerotic plaques by intravascular magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 112:2324–2331
Rogers WJ, Prichard JW, Hu YL, Olson PR, Benckart DH, Kramer CM, Vido DA, Reichek N (2000) Characterization of signal properties in atherosclerotic plaque components by intravascular MRI. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1824–1830
Wang J, Yarnykh VL, Hatsukami T, Chu B, Balu N, Yuan C (2007) Improved suppression of plaque-mimicking artifacts in black-blood carotid atherosclerosis imaging using a multislice motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium (MSDE) turbo spin-echo (TSE) sequence. Magn Reson Med 58:973–981
Crowe LA, Ariff B, Keegan J, Mohiaddin RH, Yang GZ, Hughes AD, Mc GTSA, Firmin DN (2005) Comparison between three-dimensional volume-selective turbo spin-echo imaging and two-dimensional ultrasound for assessing carotid artery structure and function. J Magn Reson Imaging 21:282–289
Mugler JP III, Bao S, Mulkern RV, Guttmann CR, Robertson RL, Jolesz FA, Brookeman JR (2000) Optimized single-slab three-dimensional spin-echo MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 216:891–899
Feinberg DA, Hoenninger JC, Crooks LE, Kaufman L, Watts JC, Arakawa M (1985) Inner volume MR imaging: technical concepts and their application. Radiology 156:743–747
Rybicki FJ, Mitsouras D, Owens CD, Whitmore AG, Ersoy H, Mulkern RV, Creager MA, Conte MS (2008) Lower extremity peripheral vein bypass graft wall thickness changes demonstrated at 1 and 6 months after surgery with ultra-high spatial resolution black blood inner volume three-dimensional fast spin echo magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 24:529–533
Mitsouras D, Mulkern RV, Rybicki FJ (2006) Strategies for inner volume 3D fast spin echo magnetic resonance imaging using nonselective refocusing radio frequency pulses. Med Phys 33:173–186
Mitsouras D, Owens CD, Conte MS, Ersoy H, Creager MA, Rybicki FJ, Mulkern RV (2009) In vivo differentiation of two vessel wall layers in lower extremity peripheral vein bypass grafts: application of high-resolution inner-volume black blood 3D FSE. Magn Reson Med 62:607–615
Owens CD, Ridker PM, Belkin M, Hamdan AD, Pomposelli F, Logerfo F, Creager MA, Conte MS (2007) Elevated C-reactive protein levels are associated with postoperative events in patients undergoing lower extremity vein bypass surgery. J Vasc Surg 45:2–9 Discussion 9
Owens CD, Wake N, Jacot JG, Gerhard-Herman M, Gaccione P, Belkin M, Creager MA, Conte MS (2006) Early biomechanical changes in lower extremity vein grafts–distinct temporal phases of remodeling and wall stiffness. J Vasc Surg 44:740–746
Rybicki FJ, Nallamshetty L, Yucel EK, Holtzman SR, Baum RA, Foley WD, Ho VB, Mammen L, Narra VR, Stein B, Moneta GL (2008) ACR appropriateness criteria on recurrent symptoms following lower-extremity angioplasty. J Am Coll Radiol 5:1176–1180
Cox JL, Chiasson DA, Gotlieb AI (1991) Stranger in a strange land: the pathogenesis of saphenous vein graft stenosis with emphasis on structural and functional differences between veins and arteries. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 34:45–68
Zwolak RM, Adams MC, Clowes AW (1987) Kinetics of vein graft hyperplasia: association with tangential stress. J Vasc Surg 5:126–136
Lau GT, Lowe HC, Kritharides L (2004) Cardiac saphenous vein bypass graft disease. Semin Vasc Med 4:153–159
Nishioka T, Luo H, Berglund H, Eigler NL, Kim CJ, Tabak SW, Siegel RJ (1996) Absence of focal compensatory enlargement or constriction in diseased human coronary saphenous vein bypass grafts. An intravascular ultrasound study. Circulation 93:683–690
Dobrin PB, Littooy FN, Golan J, Blakeman B, Fareed J (1988) Mechanical and histologic changes in canine vein grafts. J Surg Res 44:259–265
Kalra M, Miller VM (2000) Early remodeling of saphenous vein grafts: proliferation, migration and apoptosis of adventitial and medial cells occur simultaneously with changes in graft diameter and blood flow. J Vasc Res 37:576–584
Leotta DF, Primozich JF, Beach KW, Bergelin RO, Zierler RE, Strandness DE Jr (2003) Remodeling in peripheral vein graft revisions: serial study with three-dimensional ultrasound imaging. J Vasc Surg 37:798–807
Fillinger MF, Cronenwett JL, Besso S, Walsh DB, Zwolak RM (1994) Vein adaptation to the hemodynamic environment of infrainguinal grafts. J Vasc Surg 19:970–978 Discussion 978–979
Lau GT, Ridley LJ, Bannon PG, Wong LA, Trieu J, Brieger DB, Lowe HC, Freedman BS, Kritharides L (2006) Lumen loss in the first year in saphenous vein grafts is predominantly a result of negative remodeling of the whole vessel rather than a result of changes in wall thickness. Circulation 114:I435–I440
Park J, Mugler JP 3rd, Horger W, Kiefer B (2007) Optimized T1-weighted contrast for single-slab 3D turbo spin-echo imaging with long echo trains: application to whole-brain imaging. Magn Reson Med 58:982–992
Acknowlegments
Funding sources: This research was supported in part by NIH K23-EB00882 and NIH R01-HL075771.
Disclosures
The authors report no conflicts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rybicki, F.J., Mitsouras, D., Owens, C.D. et al. Multi-contrast high spatial resolution black blood inner volume three-dimensional fast spin echo MR imaging in peripheral vein bypass grafts. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 26, 683–691 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-010-9621-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-010-9621-4