Abstract
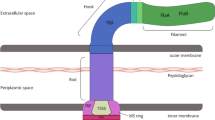
For nearly 20 years, it was believed that Legionella pneumophila does not produce siderophores. Yet, we have now determined that L. pneumophila secretes a siderophore (legiobactin) that is detectable by the CAS assay. We have optimized conditions for legiobactin expression, shown its biological activity, and found genes (lbtAB) involved in its production and secretion. LbtA is homologous with siderophore synthetases from E. coli (aerobactin), Sinorhizobium (rhizobactin), and Bordetella (alcaligin), while LbtB is a member of the major facilitator superfamily of multidrug efflux pumps. Mutants lacking lbtAB produce 40’70% less CAS reactivity. The lbtA mutant is also defective for growth in deferrated media containing citrate, indicating that legiobactin is required in conditions of severe iron limitation. lbtAB mutants grow normally in macrophages and amoebae host cells as well as within the lungs of mice. L. pneumophila does express lbtA in macrophages, suggesting that legiobactin has a dispensable role in infection. Legiobactin is iron repressed and does not react in the Csáky and Arnow assays. Anion-exchange HPLC has been used to purify legiobactin, and thus far, structural analysis suggests that the molecule is similar but not identical to rhizobactin, rhizoferrin, and alcaligin. The residual CAS reactivity present in supernatants of the lbtAB mutants suggests that L. pneumophila might produce a second siderophore. Besides siderophores, we have determined that ferrous iron transport, encoded by feoB, is critical for L. pneumophila growth in low-iron conditions, in host cells, and in the mammalian lung. Some of our other studies have discovered a critical, yet undefined, role for the L. pneumophila cytochrome c maturation locus in low-iron growth, intracellular infection, and virulence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard KA, Viswanathan VK, Cianciotto NP (2006) lbtA and lbtB are required for production of the Legionella pneumophila siderophore legiobactin. J Bacteriol 188:1351–1363
Brickman TJ, Armstrong SK (2005) Bordetella AlcS transporter functions in alcaligin siderophore export and is central to inducer sensing in positive regulation of alcaligin system gene expression. J Bacteriol 187:3650–3661
Byrd TF, Horwitz MA (2000) Aberrantly low transferrin receptor expression on human monocytes is associated with nonpermissiveness for Legionella pneumophila growth. J Infect Dis 181:1394–1400
Challis GL (2005) A widely distributed bacterial pathway for siderophore biosynthesis independent of nonribosomal peptide synthetases. Chembiochem 6:601–611
Cianciotto NP, Cornelis P, Baysse C (2005) Impact of the bacterial type I cytochrome c maturation system on different biological processes. Mol Microbiol 56:1408–1415
Daltrop O, Stevens JM, Higham CW, Ferguson SJ (2002) The CcmE protein of the c-type cytochrome biogenesis system: unusual in vitro heme incorporation into apo-CcmE and transfer from holo-CcmE to apocytochrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9703–9708
Deng K, Blick RJ, Liu W, Hansen EJ (2006) Identification of Francisella tularensis genes affected by iron limitation. Infect Immun 74:4224–4236
Fields BS, Benson RF, Besser RE (2002) Legionella and Legionnaires’ disease: 25 years of investigation. Clin Microbiol Rev 15:506–526
Franza T, Mahe B, Expert D (2005) Erwinia chrysanthemi requires a second iron transport route dependent of the siderophore achromobactin for extracellular growth and plant infection. Mol Microbiol 55:261–275
Furrer JL, Sanders DN, Hook-Barnard IG, McIntosh MA (2002) Export of the siderophore enterobactin in Escherichia coli: involvement of a 43 kDa membrane exporter. Mol Microbiol 44:1225–1234
Gebran SJ, Newton C, Yamamoto Y, Widen R, Klein TW, Friedman H (1994) Macrophage permissiveness for Legionella pneumophila growth modulated by iron. Infect Immun 62:564–568
Goldoni P, Visca P, Pastoris MC, Valenti P, Orsi N (1991) Growth of Legionella spp. under conditions of iron restriction. J Med Microbiol 34:113–118
Hickey EK, Cianciotto NP (1994) Cloning and sequencing of the Legionella pneumophila fur gene. Gene 143:117–121
Hickey EK, Cianciotto NP (1997) An iron- and fur-repressed Legionella pneumophila gene that promotes intracellular infection and encodes a protein with similarity to the Escherichia coli aerobactin synthetases. Infect Immun 65:133–143
James BW, Mauchline WS, Dennis PJ, Keevil CW (1997) A study of iron acquisition mechanisms of Legionella pneumophila grown in chemostat culture. Curr Microbiol 34:238–243
James BW, Mauchline WS, Fitzgeorge RB, Dennis PJ, Keevil CW (1995) Influence of iron-limited continuous culture on physiology and virulence of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun 63:4224–4230
Johnson W, Varner L, Poch M (1991) Acquisition of iron by Legionella pneumophila: role of iron reductase. Infect Immun 59:2376–2381
Koebnik R (2005) TonB-dependent trans-envelope signalling: the exception or the rule? Trends Microbiol 13:343–347
Liles MR, Cianciotto NP (1996) Absence of siderophore-like activity in Legionella pneumophila supernatants. Infect Immun 64:1873–1875
Liles MR, Aber Scheel T, Cianciotto NP (2000) Discovery of a nonclassical siderophore, legiobactin, produced by strains of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol 182:749–757
Mengaud JM, Horwitz MA (1993) The major iron-containing protein of Legionella pneumophila is an aconitase homologous with the human iron-responsive element-binding protein. J Bacteriol 175:5666–5676
Naylor J, Cianciotto NP (2004) Cytochrome c maturation proteins are critical for in vivo growth of Legionella pneumophila. FEMS Microbiol Lett 241:249–256
Neilands JB (1981) Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem 50:715–731
O’Brien-Ladner AR, Nelson SR, Murphy WJ, Blumer BM, Wesselius LJ (2000) Iron is a regulatory component of human IL-1beta production: Support for regional variability in the lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23:112–119
O’Connell WA, Hickey EK, Cianciotto NP (1996) A Legionella pneumophila gene that promotes hemin binding. Infect Immun 64:842–848
Poch MT, Johnson W (1993) Ferric reductases of Legionella pneumophila. Biometals 6:107–114
Pope CD, O’Connell W, Cianciotto NP (1996) Legionella pneumophila mutants that are defective for iron acquisition and assimilation and intracellular infection. Infect Immun 64:629–636
Ratledge C, Dover LG (2000) Iron metabolism in pathogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:881–941
Reeves MW, Pine L, Neilands JB, Balows A (1983) Absence of siderophore activity in Legionella species grown in iron-deficient media. J Bacteriol 154:324–329
Reeves MW, Pine L, Hutner SH, George JR, Harrell WK (1981) Metal requirements of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol 13:688–695
Robey M, Cianciotto NP (2002) Legionella pneumophila feoAB promotes ferrous iron uptake and intracellular infection. Infect Immun 70:5659–5669
Seeliger S, Cord-Ruwisch R, Schink B (1998) A periplasmic and extracellular c-type cytochrome of Geobacter sulfurreducens acts as a ferric iron reductase and as an electron carrier to other acceptors or to partner bacteria. J Bacteriol 180:3686–3691
Starkenburg SR, Casey JM, Cianciotto NP (2004) Siderophore activity among members of the Legionella genus. Curr Microbiol 49:203–207
Stevens JM, Gordon EH, Ferguson SJ (2004) Overproduction of CcmABCDEFGH restores cytochrome c maturation in a DsbD deletion strain of E. coli: another route for reductant? FEBS Lett 576:81–85
Sullivan JT, Jeffery EF, Shannon JD, Ramakrishnan G (2006) Characterization of the siderophore of Francisella tularensis and role of fslA in siderophore production. J Bacteriol 188:3785–8795
Vikram HR, Bia FJ (2002) Severe Legionella pneumophila pneumonia in a patient with iron overload. Scand J Infect Dis 34:772–774
Viswanathan VK, Edelstein PH, Pope CD, Cianciotto NP (2000) The Legionella pneumophila iraAB locus is required for iron assimilation, intracellular infection, and virulence. Infect Immun 68:1069–1079
Viswanathan VK, Kurtz S, Pedersen LL, Abu-Kwaik Y, Krcmarik K, Mody S, Cianciotto NP (2002) The cytochrome c maturation locus of Legionella pneumophila promotes iron assimilation and intracellular infection and contains a strain-specific insertion sequence element. Infect Immun 70:1842–1852
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the many contributions of both past and present lab members. Kim Allard, in particular, is acknowledged for her genetic and biochemical work on legiobactin. Dom Castignetti, Prakash Sanjeevaiah, and David Crumrine at Loyola University, Chicago are thanked for their assistance with purifying legiobactin and characterizing its structure. This work is supported by NIH grant AI34937.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cianciotto, N.P. Iron Acquisition by Legionella pneumophila . Biometals 20, 323–331 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-006-9057-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-006-9057-4