Abstract
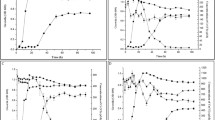
Substrates and nutrients are often added to contaminated soil or groundwater to enhance bioremediation. Nevertheless, this practice may be counterproductive in some cases where nutrient addition might relieve selective pressure for pollutant biodegradation. Batch experiments with a homoacetogenic pure culture of Acetobacterium paludosum showed that anaerobic RDX degradation is the fastest when auxiliary growth substrates (yeast extract plus fructose) and nitrogen sources (ammonium) are not added. This bacterium degraded RDX faster under autotrophic (H2-fed) than under heterotrophic conditions, even though heterotrophic growth was faster. The inhibitory effect of ammonium is postulated to be due to the repression of enzymes that initiate RDX degradation by reducing its nitro groups, based on the known fact that ammonia represses nitrate and nitrite reductases. This observation suggests that the absence of easily assimilated nitrogen sources, such as ammonium, enhances RDX degradation. Although specific end products of RDX degradation were not determined, the production of nitrous oxide (N2O) suggests that A. paludosum cleaved the triazine ring.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RDX:
-
hexahydro-l,3,5-trinitro-l,3,5-triazine
References
NR Adrian CM Arnett (2004) ArticleTitleAnaerobic biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5- triazine (RDX) by Acetobacterium malicum strain haap-1 isolated from a methanogenic mixed culture Curr. Microbiol. 48 332–340 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXisl2msbc%3D
NR Adrian CM Arnett RF Hickey (2003) ArticleTitleStimulating the anaerobic biodegradation of explosives by the addition of hydrogen or electron donors that produce hydrogen Water Res. 37 3499–3507 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXkvFemtLw%3D
NR Adrian T Chow (2001) ArticleTitleIdentification of hydroxylamino-dinitroso-1,3,5-triazine as a transient intermediate formed during the anaerobic biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20 1874–1877 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmt12ltr4%3D
NR Adrian A Lowder (1999) Biodegradation of RDX and HMX by a Methanogenic Enrichment Culture Bioremediation of Nitroaromatic and Haloaromatic Compounds B. C. Ohio Battelle Press Alleman Columbus 1–6
W Balch S Schoberth R Tanner R Wolfe (1977) ArticleTitleAcetobacterium, a new genus of hydrogen-oxidizing, carbon dioxide-reducing, anaerobic bacteria Int. J. Systemat. Bacteriol. 27 355–361 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXjsVehtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1099/00207713-27-4-355
HR Beller (2002) ArticleTitleAnaerobic biotransformation of RDX (hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro- 1,3,5-triazine) by aquifer bacteria using hydrogen as the sole electron donor Water Res. 36 2533–2540 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XktFaqt78%3D
B Bhushan A Halasz J Spain S Thiboutot G Ampleman J Hawari (2002) ArticleTitleBiotransformation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-tiazine catalyzed by a nad(p)h: nitrate oxidoreductase from Aspergillus niger Environ. Sci. Technol. 36 3104–3108 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xktl2nurk%3D
PR Binks S Nicklin NC Bruce (1995) ArticleTitleDegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (rdx) by stenotrophomonas-maltophilia pb1 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61 1318–1322 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXksl2lsrk%3D
NV Coleman DR Duxbury T Nelson (1998) ArticleTitleAerobic biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) as a nitrogen source by a rhodococcus sp., strain dn22 Soil Biol. Biochem 30 1159–1167
ES Fiala (1977) ArticleTitleInvestigations into the metabolism and mode of action of the colon carcinogens 1,2-dimethylhydrazine and azoxymethane Cancer 40 22436–23445
G Greenhouse (1976) ArticleTitleEvaluation of the teratogenic effects of hydrazine, methylhydrazine, and dimethylhydrazine on embryos of xenopus laevis, the south african clawed toad Teratology 13 167–177 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28XktFCruro%3D
J Hawari A Halasz S Beaudet L Paquet G Ampleman S Thiboutot (2001) ArticleTitleBiotransformation routes of octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro- 1,3,5,7-tetrazocine by municipal anaerobic sludge Environ. Sci. Technol. 35 70–75 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnvVKnsbc%3D
J Hawari A Halasz T Sheremata S Beaudet C Groom L Paquet C Rhofir G Ampleman S Thiboutot (2000) ArticleTitleCharacterization of metabolites during biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) with municipal anaerobic sludge Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66 2652–2657 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjvFWnsbs%3D
T Held G Draude FRJ Schmidt A Brokamp KH Reis (1997) ArticleTitleEnhanced humification as an in-situ bioremediation technique for 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) contaminated soils Environ. Technol. 18 479–487 Occurrence Handle10.1080/09593331808616563 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjvVWmtL8%3D
LS Hundal J Singh EL Bier PJ Shea SD Comfort WL Powers (1997) ArticleTitleRemoval of TNT and RDX from water and soil using iron metal Environ. Pollut. 97 55–64 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXntVKhsLg%3D
OR Kotsyurbenko MV Simankova AN Nozhevnikova TN Zhilina NP Bolotina AM Lysenko GA Osipov (1995) ArticleTitleNew species of psychrophilic acetogens–Acetobacterium bakii sp nov, a Paludosum sp nov, a. Fimetarium sp nov. Arch. Microbiol. 163 29–34 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXkvVOhsL4%3D
N Lovanh PJJ Alvarez (2004) ArticleTitleEffect of ethanol, acetate, and phenol on toluene degradation activity and tod-lux expression in Pseudomonas putida tod102: Evaluation of the metabolic flux dilution model Biotechnol. Bioeng. 86 801–808 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXkslCgt7c%3D
MT Madigan JM Martinko J Parker (2000) Brock Biology of Microorganisms Upper Saddle River New Jersey Inc Prentice-Hall
NG McCormick JH Cornell AM Kaplan (1981) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 42 817–823 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XhtlOhtLc%3D
McLellan W, Hartley WR & Brower M (1992) Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) drinking water health advisory: munitions. In: Roberts WC & Hartley WR (Eds) (pp 132–180) Boca Raton, FL Lewis Publishers.
P Morgan RJ Watkinson (1992) ArticleTitleFactors limiting the supply and efficiency of nutrient and oxygen supplements for the in situ biotreatment of contaminated soil and groundwater Water Res. 26 73–78 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XptV2iug%3D%3D
BT Oh PJJ Alvarez (2002) ArticleTitleHexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) degradation in biologically-active iron columns Water Air Soil Pollut. 141 325–335 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xpt1altLY%3D
BT Oh CL Just PJJ Alvarez (2001) ArticleTitleHexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine mineralization by zerovalent iron and mixed anaerobic cultures Environ. Sci. Technol. 35 4341–4346 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXntVCgtr0%3D
DC Schmelling KA Gray PV Kamat (1997) ArticleTitleThe influence of solution matrix on the photocatalytic degradation of TNT in tio2 slurries Water Res. 31 1439–1447 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjt12rs74%3D
Sherburne LA (2003) Biological removal of RDX using selected pure cultures of homoacetogens, Master’s Thesis, The University of Iowa
TW Sheremata J Hawari (2000) ArticleTitleMineralization of RDX by the white rot fungus phanerochaete chrysosporium to carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide Environ. Sci. Technol. 34 3384–3388 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXksFejsb8%3D
Skopek TR, Liber HL, Krolewski JJ & Thilly WG (1978) Quantitative forward mutation assay in Salmonella typhimurium using 8-azaguanine resistance as a genetic marker. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA.
F Testud JM Glanclaude J Descotes (1996) ArticleTitleAcute hexogen poisoning after occupational exposure J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxicol. 34 109–111 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK283itlyqsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.3109/15563659609020244
MJ Wildman PJJ Alvarez (2001) ArticleTitleRDX degradation using an integrated Fe(0)-microbial treatment approach Water Sci. Technol. 43 25–33 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtFWgtro%3D
JS Zhao L Paquet A Halasz J Hawari (2003a) ArticleTitleMetabolism of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine through initial reduction to hexahydro-1-nitroso-3,5-dinitro-1,3,5-triazine followed by denitration in Clostridium bifermentans HAW-1 Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 63 187–193 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpsVOjsb0%3D
JS Zhao J Spain M Hawari (2003b) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic and metabolic diversity of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX)-transforming bacteria in strictly anaerobic mixed cultures enriched on RDX as nitrogen source FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 46 189–196 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXosFSltL8%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherburne, L.A., Shrout, J.D. & Alvarez, P.J. Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) degradation by Acetobacterium paludosum . Biodegradation 16, 539–547 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-004-6945-6
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-004-6945-6