Abstract
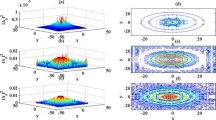
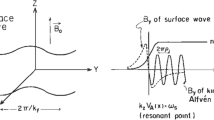
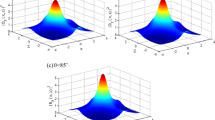
Spacecraft observations indicate the signatures of highly oblique kinetic Alfvén waves (KAWs) and whistler waves in the solar wind plasma. In the present work, we explore the possible role of KAWs and whistler waves in the observed solar wind magnetic turbulent spectrum. The nonlinear spatial evolution of KAW is studied including the effects of the ponderomotive force which results in intense localized structures due to the background density modification. Weak quasi-transverse whistler wave propagating through these localized structures also gets localized in the form of small-scale localized structures. We present numerically calculated magnetic power spectra for both KAW as well as for whistler wave. Our obtained results demonstrate the important role that KAWs and whistler waves play in the energy cascading from larger to smaller scales. The relevance of these results to recent spacecraft observations is also pointed out.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrova, O., Saur, J., Lacombe, C., Mangeney, A., Mitchell, J., Schwartz, S.J., Robert, P.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 165003 (2009)
Alexandrova, O., Chen, C.H.K., Sorriso-Valvo, L., Horbury, T.S., Bale, S.D.: Space Sci. Rev. 178, 101–139 (2013)
Bale, S.D., Kellogg, P.J., Mozer, F.S., Horbury, T.S., Reme, H.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 215002 (2005)
Beinroth, H.J., Neubauer, F.M.: J. Geophys. Res. 86, 7755 (1981)
Belcher, J.W., Davis, L. Jr.: J. Geophys. Res. 76, 3534 (1971)
Breneman, A., Cattell, C., Schreiner, S., Kersten, K., Wilson, L.B. III, Kellogg, P., Goetz, K., Jian, L.K.: J. Geophys. Res. 115, A08104 (2010)
Chang, O., Gary, S.P., Wang, J.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L22102 (2011)
Chang, O., Gary, S.P., Wang, J.: J. Geophys. Res. 118, 2824 (2013)
Chang, O., Gary, S.P., Wang, J.: Phys. Plasmas. 21, 052305 (2014)
Chang, O., Gary, S.P., Wang, J.: Astrophys. J. 800, 87 (2015)
Chmyrev, V.M., Bilichenko, S.V., Pokhotelov, .A., Marchenko, V.A., Lazarev, V.I., Streltsov, A.V., Stenflo, L.: Physica Scr.. 38, 841 (1988)
Galtier, S.: J. Plasma Phys. 72, 721 (2006)
Gary, S.P., Smith, C.W.: J. Geophys. Res. 114, A12105 (2009)
Gary, S.P., Saito, S., Li, H.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L02104 (2008)
Gary, S.P., Hughes, R.S., Wang, J., Chang, O.: J. Geophys. Res. 119, 1429 (2014)
Goldstein, M.L., Roberts, D.A., Fitch, C.A.: J. Geophys. Res. 99, 11519 (1994)
Goldstein, M.L., Roberts, D.A., Matthaeus, W.H.: Astrophys. J. 33, 283 (1995)
Hasegawa, A.: J. Geophys. Res. 81, 5083 (1976)
He, J., Marsch, E., Tu, C., Yao, S., Tian, H.: Astrophys. J. 731, 85 (2011)
Howes, G.G.: Trans. R. Soc. A 373, 20140145 (2015)
Howes, G.G., Quattaert, E.: Astrophys. J. 709, L49 (2010)
Krishan, V., Mahajan, S.M.: J. Geophys. Res. 109, A11105 (2004)
Lacombe, C., Alexandrova, O., Matteini, L., Santolik, O., Cornilleau-Wehrlin, N., Mangeney, A., De Conchy, Y., Maksimovic, M.: Astrophys. J. 796, 5 (2014)
Leamon, R.J., Smith, C.W., Ness, N.F., Matthaeus, W.H., Wong, H.K.: J. Geophys. Res. 103, 4775 (1998)
Leamon, R.J., Matthaeus, W.H., Smith, C.W., Zank, G.P., Mullan, D.J., Oughton, S.: Astrophys. J. 537, 1054 (2000)
Mathioudakis, M., Jess, D.B., Erdélyi, R.: Space Sci. Rev. 175, 1–27 (2013)
Matthaeus, W.H., Brown, M.: Phys. Fluids 31, 3634 (1988)
Matthaeus, W.H., Servidio, S., Dmitru, P.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 149501 (2008)
Nandal, P., Yadav, N., Sharma, R.P.: Phys. Plasmas 23, 042310 (2016)
Narita, Y., Gary, S.P.: Ann. Geophys. 28, 597–601 (2010)
Neubauer, F.M., Beinroth, H.J., Bamstorf, H., Dehmel, V.: J. Geophys. Res. 42, 599 (1977)
Podesta, J.J., Borovsky, J.E., Garry, S.P.: Astrophys. J. 712, 685 (2010)
Pokhotelov, O.A., Onishchenko, O.G., Sagdeev, R.Z., Treumann, R.A.: J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1291 (2003)
Sahraoui, F., Goldstein, M.L., Robert, P., Khotyaintsev, Y.V.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 231102 (2009)
Saito, S., Nariyuki, Y.: Phys. Plasmas 21, 042303 (2014)
Salem, C.S., Howes, G.G., Sundkvist, D., Bale, S.D., Chaston, C.C., Chen, C.H.K., Mozer, F.S.: Astrophys. J. 745, L9 (2012)
Schekochihin, A.A., Cowley, S.C., Dorland, W., Hammett, G.W., Howes, G.G., Quataert, E., Tatsuno, T.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 182, 310 (2009)
Shaikh, D.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 405, 2521 (2010)
Shukla, P.K., Stenflo, L.: Phys. Plasmas 7, 2738 (2000)
Stefant, R.J.: Phys. Fluids 13, 440–450 (1970)
Yadav, N., Sharma, R.P.: Sol. Phys. 289, 1803 (2014)
Zhao, J.: Phys. Plasmas 22, 042115 (2015)
Zhao, J.S., Wu, D.J., Lu, J.Y.: J. Geophys. Res. 115, A12227 (2010)
Zhao, J.S., Wu, D.J., Lu, J.Y., Yang, L., Yu, M.Y.: New J. Phys. 13, 063043 (2011)
Zhao, J.S., Wu, D.J., Yu, M.Y., Lu, J.Y.: Phys. Plasmas 19, 062901 (2012)
Zhao, J.S., Voitenko, Y., Yu, M.Y., Lu, J.Y., Wu, D.J.: Astrophys. J. 793, 107 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) under RESPOND program and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandal, P., Yadav, N., Sharma, R.P. et al. Potential role of kinetic Alfvén waves and whistler waves in solar wind plasmas. Astrophys Space Sci 361, 239 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2824-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2824-y