Abstract
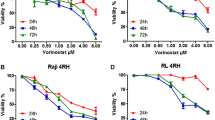
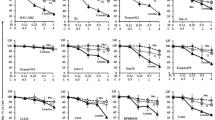
Enzastaurin is an investigational PKCβ inhibitor that has growth inhibitory and pro-apoptotic effects in both B and T-cell lymphomas. We investigated the cytotoxicity and mechanisms of cell death of the combination of enzastaurin and low concentrations of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in B-cell and T-cell lymphoma cell lines and primary lymphoma/leukemia cells. Combined enzastaurin/suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid treatment synergistically induced apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and T-cell lymphoma cell lines, and primary lymphoma/leukemia samples. Similarly, combined treatment of B-cell-like lymphoma cells with enzastaurin and two different HDAC inhibitors, valproic acid and (2E,4E)-6-(4-chlorophenylsulfanyl)-2,4-hexadienoic acid hydroxyamide synergistically induced apoptosis, suggesting the synergy is generalizable to other HDAC inhibitors. Our data indicate that enzastaurin/HDAC inhibitors therapy can synergistically inhibit growth and induce apoptosis in lymphoid malignancies and may be an effective therapeutic strategy. Potential mechanisms including enzastaurin mediated inhibition of HDAC inhibitor-induced compensatory survival pathways are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Podar K, Raab MS, Chauhan D, Anderson KC (2007) The therapeutic role of targeting protein kinase C in solid and hematologic malignancies. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 16:1693–1707
Spalding AC, Zeitlin BD, Wilder-Romans K, Davis ME, Nor JE, Lawrence TS, Ben-Josef E (2008) Enzastaurin, an inhibitor of PKCbeta, enhances antiangiogenic effects and cytotoxicity of radiation against endothelial cells. Transl Oncol 1:195–201
Brautigam K, Bauerschlag DO, Weigel MT, Biernath-Wupping J, Bauknecht T, Arnold N, Maass N, Meinhold-Heerlein I (2009) Combination of enzastaurin and pemetrexed inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis of chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells regulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation. Transl Oncol 2:164–173
Tekle C, Giovannetti E, Sigmond J, Graff JR, Smid K, Peters GJ (2008) Molecular pathways involved in the synergistic interaction of the PKC beta inhibitor enzastaurin with the antifolate pemetrexed in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Br J Cancer 99:750–759
Bali P, George P, Cohen P, Tao J, Guo F, Sigua C, Vishvanath A, Scuto A, Annavarapu S, Fiskus W, Moscinski L, Atadja P, Bhalla K (2004) Superior activity of the combination of histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 and the FLT-3 kinase inhibitor PKC412 against human acute myelogenous leukemia cells with mutant FLT-3. Clin Cancer Res 10:4991–4997
Vogl UM, Berger W, Micksche M, Pirker C, Lamm W, Pichelmeyer O, Zielinski CC, Schmidinger M (2009) Synergistic effect of Sorafenib and Sunitinib with Enzastaurin, a selective protein kinase C inhibitor in renal cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett 277:218–226
Morgillo F, Martinelli E, Troiani T, Laus G, Pepe S, Gridelli C, Ciardiello F (2008) Sequence-dependent, synergistic antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of the combination of cytotoxic drugs and enzastaurin, a protein kinase Cbeta inhibitor, in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1698–1707
Moreau AS, Jia X, Ngo HT, Leleu X, O’Sullivan G, Alsayed Y, Leontovich A, Podar K, Kutok J, Daley J, Lazo-Kallanian S, Hatjiharissi E, Raab MS, Xu L, Treon SP, Hideshima T, Anderson KC, Ghobrial IM (2007) Protein kinase C inhibitor enzastaurin induces in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood 109:4964–4972
Graff JR, McNulty AM, Hanna KR, Konicek BW, Lynch RL, Bailey SN, Banks C, Capen A, Goode R, Lewis JE, Sams L, Huss KL, Campbell RM, Iversen PW, Neubauer BL, Brown TJ, Musib L, Geeganage S, Thornton D (2005) The protein kinase Cbeta-selective inhibitor, Enzastaurin (LY317615.HCl), suppresses signaling through the AKT pathway, induces apoptosis, and suppresses growth of human colon cancer and glioblastoma xenografts. Cancer Res 65:7462–7469
Spalding AC, Watson R, Davis ME, Kim AC, Lawrence TS, Ben-Josef E (2007) Inhibition of protein kinase Cbeta by enzastaurin enhances radiation cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:6827–6833
Herman JG, Baylin SB (2003) Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med 349:2042–2054
Chen J, Fiskus W, Eaton K, Fernandez P, Wang Y, Rao R, Lee P, Joshi R, Yang Y, Kolhe R, Balusu R, Chappa P, Natarajan K, Jillella A, Atadja P, Bhalla KN (2009) Cotreatment with BCL-2 antagonist sensitizes cutaneous T-cell lymphoma to lethal action of HDAC7-Nur77-based mechanism. Blood 113:4038–4048
Glaser KB (2007) HDAC inhibitors: clinical update and mechanism-based potential. Biochem Pharmacol 74:659–671
Ocker M, Alajati A, Ganslmayer M, Zopf S, Luders M, Neureiter D, Hahn EG, Schuppan D, Herold C (2005) The histone-deacetylase inhibitor SAHA potentiates proapoptotic effects of 5-fluorouracil and irinotecan in hepatoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131:385–394
Bhalla S, Balasubramanian S, David K, Sirisawad M, Buggy J, Mauro L, Prachand S, Miller R, Gordon LI, Evens AM (2009) PCI-24781 induces caspase and reactive oxygen species-dependent apoptosis through NF-kappaB mechanisms and is synergistic with bortezomib in lymphoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 15:3354–3365
Drexler HC, Euler M (2005) Synergistic apoptosis induction by proteasome and histone deacetylase inhibitors is dependent on protein synthesis. Apoptosis 10:743–758
Lee CK, Wang S, Huang X, Ryder J, Liu B (2010) HDAC inhibition synergistically enhances alkylator-induced DNA damage responses and apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Lett 296:233–240
Rahmani M, Reese E, Dai Y, Bauer C, Payne SG, Dent P, Spiegel S, Grant S (2005) Coadministration of histone deacetylase inhibitors and perifosine synergistically induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells through Akt and ERK1/2 inactivation and the generation of ceramide and reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res 65:2422–2432
Goode N, Hughes K, Woodgett JR, Parker PJ (1992) Differential regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by protein kinase C isotypes. J Biol Chem 267:16878–16882
Bodo J, Durkin L, Hsi ED (2009) Quantitative in situ detection of phosphoproteins in fixed tissues using quantum dot technology. J Histochem Cytochem 57:701–708
Chou TC, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 22:27–55
Mellert HS, Stanek TJ, Sykes SM, Rauscher FJ III, Schultz DC, McMahon SB (2011) Deacetylation of the DNA-binding domain regulates p53-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 286:4264–4270
Aeder SE, Martin PM, Soh JW, Hussaini IM (2004) PKC-eta mediates glioblastoma cell proliferation through the Akt and mTOR signaling pathways. Oncogene 23:9062–9069
Balendran A, Hare GR, Kieloch A, Williams MR, Alessi DR (2000) Further evidence that 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) is required for the stability and phosphorylation of protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms. FEBS Lett 484:217–223
Kawakami Y, Nishimoto H, Kitaura J, Maeda-Yamamoto M, Kato RM, Littman DR, Leitges M, Rawlings DJ, Kawakami T (2004) Protein kinase C betaII regulates Akt phosphorylation on Ser-473 in a cell type- and stimulus-specific fashion. J Biol Chem 279:47720–47725
Partovian C, Simons M (2004) Regulation of protein kinase B/Akt activity and Ser473 phosphorylation by protein kinase Calpha in endothelial cells. Cell Signal 16:951–957
Fang X, Yu S, Tanyi JL, Lu Y, Woodgett JR, Mills GB (2002) Convergence of multiple signaling cascades at glycogen synthase kinase 3: Edg receptor-mediated phosphorylation and inactivation by lysophosphatidic acid through a protein kinase C-dependent intracellular pathway. Mol Cell Biol 22:2099–2110
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N, Clevers H, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (1997) Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta-catenin or APC. Science 275:1787–1790
Damalas A, Ben-Ze’Ev A, Simcha I, Shtutman M, Leal JF, Zhurinsky J, Geiger B, Oren M (1999) Excess beta-catenin promotes accumulation of transcriptionally active p53. EMBO J 18:3054–3063
Kim K, Pang KM, Evans M, Hay ED (2000) Overexpression of beta-catenin induces apoptosis independent of its transactivation function with LEF-1 or the involvement of major G1 cell cycle regulators. Mol Biol Cell 11:3509–3523
Raab MS, Breitkreutz I, Tonon G, Zhang J, Hayden PJ, Nguyen T, Fruehauf JH, Lin BK, Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Munshi NC, Anderson KC, Podar K (2009) Targeting PKC: a novel role for beta-catenin in ER stress and apoptotic signaling. Blood 113:1513–1521
Gwak J, Cho M, Gong SJ, Won J, Kim DE, Kim EY, Lee SS, Kim M, Kim TK, Shin JG, Oh S (2006) Protein-kinase-C-mediated beta-catenin phosphorylation negatively regulates the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J Cell Sci 119:4702–4709
Tetsu O, McCormick F (1999) Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature 398:422–426
Billin AN, Thirlwell H, Ayer DE (2000) Beta-catenin-histone deacetylase interactions regulate the transition of LEF1 from a transcriptional repressor to an activator. Mol Cell Biol 20:6882–6890
Kristeleit R, Stimson L, Workman P, Aherne W (2004) Histone modification enzymes: novel targets for cancer drugs. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 9:135–154
Blagosklonny MV, Robey R, Sackett DL, Du L, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z, Fojo T, Bates SE (2002) Histone deacetylase inhibitors all induce p21 but differentially cause tubulin acetylation, mitotic arrest, and cytotoxicity. Mol Cancer Ther 1:937–941
Yu X, Guo ZS, Marcu MG, Neckers L, Nguyen DM, Chen GA, Schrump DS (2002) Modulation of p53, ErbB1, ErbB2, and Raf-1 expression in lung cancer cells by depsipeptide FR901228. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:504–513
Saegusa M, Hashimura M, Kuwata T, Hamano M, Okayasu I (2004) Beta-catenin simultaneously induces activation of the p53–p21WAF1 pathway and overexpression of cyclin D1 during squamous differentiation of endometrial carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 164:1739–1749
Kelly WK, O’Connor OA, Krug LM, Chiao JH, Heaney M, Curley T, MacGregore-Cortelli B, Tong W, Secrist JP, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Chu E, Olgac S, Marks PA, Scher H, Richon VM (2005) Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:3923–3931
Carducci MA, Musib L, Kies MS, Pili R, Truong M, Brahmer JR, Cole P, Sullivan R, Riddle J, Schmidt J, Enas N, Sinha V, Thornton DE, Herbst RS (2006) Phase I dose escalation and pharmacokinetic study of enzastaurin, an oral protein kinase C beta inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:4092–4099
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Lisa Durkin for her technical expertise in cell culturing and immunostaining.
Conflict of Interest Statement
Juraj Bodo, Jan Sedlak, Jaroslaw P. Maciejewski, Alex Almasan have no financial or personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence this work. Eric Hsi receives research support from Eli Lilly and Company. Eli Lilly and Company had no role or input in the experimental design, data analysis, or manuscript writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bodo, J., Sedlak, J., Maciejewski, J.P. et al. HDAC inhibitors potentiate the apoptotic effect of enzastaurin in lymphoma cells. Apoptosis 16, 914–923 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0617-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0617-x