Abstract
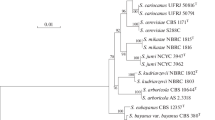
Zygosaccharomyces seidelii, a new species in the genus Zygosaccharomyces is described. The description of the species is based on a single strain that was isolated from flowers collected on the Maldives. On this occasion, the description of yeast species from single strains was revisited. Sequence analysis of the D1/D2 domain of the nuclear large subunit rRNA gene revealed that Z. seidelii is closely related to Z. gambellarensis. Both species differ by 2.6% (one indel of 7 bp and 9 substitutions) in the D1/D2 domain, 71 substitutions and 23 indels in the ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 (ITS) region and by several physiological tests. Two divergent copies of the ITS region were detected in Z. seidelii. Asexual and sexual reproduction as well as the physiological properties of Z. seidelii fit well in the genus Zygosaccharomyces. (Holotype strain: CBS 16021, Isotype strain: CLIB 3343; MycoBank no.: MB830900).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Ghosh S, Droby S, Korine C (2014) Seasonal and plant-dependent variations in diversity, abundance and stress tolerance of epiphytic yeasts in desert habitats. Environ Microbiol Rep 6:373–382
Barker B (1901) A conjugating “yeast”. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 194:467–485
Bovo B, Andrighetto C, Carlot M, Corich V, Lombardi A, Giacomini A (2009) Yeast population dynamics during pilot-scale storage of grape marcs for the production of Grappa, a traditional Italian alcoholic beverage. Int J Food Microbiol 129:221–228
Brezna B, Zenisova K, Chovanova K, Chebenova V, Krakova L, Kuchta T, Pangallo D (2010) Evaluation of fungal and yeast diversity in Slovakian wine-related microbial communities. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 98:519–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9469-6
Brysch-Herzberg M (2004) Ecology of yeasts in plant–bumblebee mutualism in Central Europe. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 50:87–100
Brysch-Herzberg M, Seidel M (2015) Yeast diversity on grapes in two German wine growing regions. Int J Food Microbiol 214:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.07.034
Brysch-Herzberg M et al (2019) Schizosaccharomyces osmophilus sp. nov., an osmophilic fission yeast occurring in bee bread of different solitary bee species FEMS yeast research. East West J Math Spec Vol Comput Math Model 19:143–146
Čadež N, Fülöp L, Dlauchy D, Péter G (2015) Zygosaccharomyces favi sp. nov., an obligate osmophilic yeast species from bee bread and honey. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 107:645–654
Carvalho C, Meirinho S, Estevinho M, Choupina A (2010) Yeast species associated with honey: different identification methods. Archivos de zootecnia 59:103–113
Christensen H, Bisgaard M, Frederiksen W, Mutters R, Kuhnert P, Olsen JE (2001) Is characterization of a single isolate sufficient for valid publication of a new genus or species? Proposal to modify recommendation 30b of the Bacteriological Code (1990 Revision). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2221–2225
Deak T (2008) Handbook of food spoilage yeasts. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Fabian F, Quinet R (1928) A study of the cause of honney fermentation. Tech Bull Agric Exp Stn Michigan St Coll 92:1–41
Fell J, Kurtzman C, Lachance M (2000) A debate on the description of new yeast species based on single strains. Yeast Newsletter 49:77–78
Golubev W (1977) Metschnikowia lunata sp. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 43:317–322
Guilliermond A (1912) Les Levures. Encyclopédie Scientifique. O, Doin et Fils
Helston RM, Box JA, Tang W, Baumann P (2010) Schizosaccharomyces cryophilus sp. nov., a new species of fission yeast. FEMS Yeast Res 10:779–786
Hyun S-H, Min J-H, Lee HB, Kim H-K, Lee J-S (2014) Isolation and diversity of yeasts from wild flowers in Ulleungdo and Yokjido, Korea. The Korean Journal of Mycology 42:28–33
James SA, Stratford M (2011) Zygosaccharomyces barker (1901). In: Kurtzman C, Fell JW, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts: a taxonomic study. Elsevier, London, pp 937–948
Janda JM, Abbott SL (2002) Bacterial identification for publication: when is enough enough? J Clin Microbiol 40:1887–1891
Jv Arx, Miranda Rd, Smith M, Yarrow D (1977) The genera of the yeasts and the yeast-like fungi. Stud Mycol 14:1–42
Kachalkin A, Abdullabekova D, Magomedova E, Magomedov G, Chernov IY (2015) Yeasts of the vineyards in Dagestan and other regions. Microbiology 84:425–432
Kurtzman CP (2010) Description of new yeast species–is one strain enough? Bull BISMiS 1:17–24
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (1998) Identification and phylogeny of ascomycetous yeasts from analysis of nuclear large subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA partial sequences. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73:331–371
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ, Basehoar-Powers E (2001) Zygosaccharomyces kombuchaensis, a new ascosporogenous yeast from ‘Kombucha tea’. FEMS Yeast Res 1:133–138
Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (2011) Methods for isolation, phenotypic characterization and maintenance of yeasts. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts: a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier, London, pp 21–30
Lachance M (2011a) Microbial species descriptions: the importance of multiple strains. In: JSCC and WFCC joint symposium on culture collections and microbial systematics, congress of the international union of microbiological Societies, Sapporo, Japan
Lachance MA (2011b) Metschnikowia Kamienski (1899). In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts: a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier, London, pp 575–621
Lopandic K et al (2008) Molecular profiling of yeasts isolated during spontaneous fermentations of Austrian wines. FEMS Yeast Res 8:1063–1075
Moubasher A, Abdel-Sater M, Zeinab S (2018) Diversity of floricolous yeasts and filamentous fungi of some ornamental and edible fruit plants in Assiut area, Egypt. Curr Res Environ Appl Mycol 8:135–161
Naganishi T (1917) Three new species of yeasts. Bot Mag Tokyo 31:107–115
Nguyen H-V, Boekhout T (2017) Characterization of Saccharomyces uvarum (Beijerinck, 1898) and related hybrids: assessment of molecular markers that predict the parent and hybrid genomes and a proposal to name yeast hybrids. FEMS yeast research 17. fox014
Pereira V, Ricardo J, Galinha R, Benoliel M, Crespo MB (2013) Occurrence and low pressure ultraviolet inactivation of yeasts in real water sources. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences 12:626–663
Peter G, Tornai-Lehoczki J, Suzuki M, Dlauchy D (2005) Metschnikowia viticola sp. nov., a new yeast species from grape. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 87:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-004-2842-6
Phaff H, Starmer W (1980) Specificity of natural habitats for yeasts and yeast-like organisms. In: Skinner FA, Passmore SM, Davenport R (eds) Biological and activities of yeasts. Academic Press, London, pp 79–101
Phaff H, Miller M, Mrak E (1978) The life of yeasts, vol 173, 2nd edn. Harvard University, Cambridge
Raggi P et al (2014) Debaryomyces hansenii and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa comprised the yeast core gut microbiota of wild and reared carnivorous salmonids, croaker and yellowtail. Environ Microbiol 16:2791–2803
Rhind N et al (2011) Comparative functional genomics of the fission yeasts. Science 332:930–936
Rosa CA, Lachance M-A (2005) Zygosaccharomyces machadoi sp. n., a yeast species isolated from a nest of the stingless bee Tetragonisca angustula. Lundiana 6:27–29
Saksinchai S, Suzuki M, Chantawannakul P, Ohkuma M, Lumyong S (2012) A novel ascosporogenous yeast species, Zygosaccharomyces siamensis, and the sugar tolerant yeasts associated with raw honey collected in Thailand. Fungal Divers 52:123–139
Santos ARO et al (2018) Starmerella camargoi fa, sp. nov., Starmerella ilheusensis fa, sp. nov., Starmerella litoralis fa, sp. nov., Starmerella opuntiae fa, sp. nov., Starmerella roubikii fa, sp. nov. and Starmerella vitae fa, sp. nov., isolated from flowers and bees, and transfer of related Candida species to the genus Starmerella as new combinations. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1333–1343
Skinner FA, Passmore SM, Davenport R (1980) Biology and activities of yeasts. Academic Press, London
Solieri L, Cassanelli S, Giudici P (2007) A new putative Zygosaccharomyces yeast species isolated from traditional balsamic vinegar. Yeast 24:403–417
Solieri L, Chand Dakal T, Croce MA, Giudici P (2013a) Unravelling genomic diversity of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii complex with a link to its life cycle. FEMS Yeast Res 13:245–258
Solieri L, Dakal TC, Giudici P (2013b) Zygosaccharomyces sapae sp. nov., isolated from Italian traditional balsamic vinegar. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:364–371
Spencer J, Gorin P, Hobbs G, Cooke D (1970) Yeasts isolated from bumblebee honey from Western Canada: identification with the aid of proton magnetic resonance spectra of their mannose-containing polysaccharides. Can J Microbiol 16:117–119
Steels H, James S, Roberts I, Stratford M (1999) Zygosaccharomyces lentus: a significant new osmophilic, preservative-resistant spoilage yeast, capable of growth at low temperature. J Appl Microbiol 87:520–527
Suh S-O, Gujjari P, Beres C, Beck B, Zhou J (2013) Proposal of Zygosaccharomyces parabailii sp. nov. and Zygosaccharomyces pseudobailii sp. nov., novel species closely related to Zygosaccharomyces bailii. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1922–1929
Sujaya IN et al (2003) Development of internal transcribed spacer regions amplification restriction fragment length polymorphism method and its application in monitoring the population of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii M2 in miso fermentation. J Biosci Bioeng 96:438–447
Tokuoka K, Ishitani T (1991) Minimum water activities for the growth of yeasts isolated from high-sugar foods. J Gen Appl Microbiol 37:111–119
Torriani S, Lorenzini M, Salvetti E, Felis GE (2011) Zygosaccharomyces gambellarensis sp. nov., an ascosporogenous yeast isolated from an Italian ‘passito’style wine. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:3084–3088
Vu D et al (2016) DNA barcoding analysis of more than 9000 yeast isolates contributes to quantitative thresholds for yeast species and genera delimitation. Stud Mycol 85:91–105
White TJ, Bruns TD, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, London, pp 315–322
Zhu T, Niu D-K (2013) Mechanisms of intron loss and gain in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces. PLoS ONE 8:e61683
Funding
This work was supported by The Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt DBU (German Federal Environmental Foundation) [34053/01-32].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brysch-Herzberg, M., Wohlmann, E. & Fischer, R. Zygosaccharomyces seidelii sp. nov. a new yeast species from the Maldives, and a revisit of the single-strain species debate. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 113, 427–436 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01352-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01352-x