Abstract
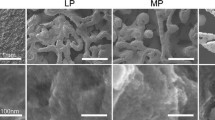
The objective of this study was to examine the ability of 3D implants with trabecular-bone-inspired porosity and micro-/nano-rough surfaces to enhance vertical bone ingrowth. Porous Ti–6Al–4V constructs were fabricated via laser-sintering and processed to obtain micro-/nano-rough surfaces. Male and female human osteoblasts were seeded on constructs to analyze cell morphology and response. Implants were then placed on rat calvaria for 10 weeks to assess vertical bone ingrowth, mechanical stability and osseointegration. All osteoblasts showed higher levels of osteocalcin, osteoprotegerin, vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein 2 on porous constructs compared to solid laser-sintered controls. Porous implants placed in vivo resulted in an average of 3.1 ± 0.6 mm3 vertical bone growth and osseointegration within implant pores and had significantly higher pull-out strength values than solid implants. New bone formation and pull-out strength was not improved with the addition of demineralized bone matrix putty. Scanning electron images and histological results corroborated vertical bone growth. This study indicates that Ti–6Al–4V implants fabricated by additive manufacturing to have porosity based on trabecular bone and post-build processing to have micro-/nano-surface roughness can support vertical bone growth in vivo, and suggests that these implants may be used clinically to increase osseointegration in challenging patient cases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghaloo, T. L., and P. K. Moy. Which hard tissue augmentation techniques are the most successful in furnishing bony support for implant placement? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 22(Suppl):49–70, 2007.
Brauner, E., G. Guarino, S. Jamshir, P. Papi, V. Valentini, V. Pompa, and G. Pompa. Evaluation of highly porous dental implants in postablative oral and maxillofacial cancer patients: a prospective pilot clinical case series report. Implant Dent. 24(5):631–637, 2015.
Chavassieux, P. M., C. Chenu, A. Valentin-Opran, B. Merle, P. D. Delmas, P. J. Meunier, D. J. Hartmann, and S. Saez. Influence of experimental conditions on osteoblast activity in human primary bone cell cultures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 5(4):337–343, 1990.
Cheng, A., D. J. Cohen, B. D. Boyan, and Z. Schwartz. Laser sintered constructs with bio-inspired porosity and surface micro/nano roughness enhance mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and matrix mineralization in vitro. Calcif. Tissue Int. 99:625–637, 2016.
Cheng, A., A. Humayun, B. D. Boyan, and Z. Schwartz. Enhanced osteoblast response to porosity and resolution of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V constructs with trabeculae-inspired porosity. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 3(1):10–21, 2016.
Cheng, A., A. Humayun, D. J. Cohen, B. D. Boyan, and Z. Schwartz. Additively manufactured 3D porous Ti-6Al-4V constructs mimic trabecular bone structure and regulate osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and local factor production in a porosity and surface roughness dependent manner. Biofabrication 6(4):045007, 2014.
Cohen, D. J., A. Cheng, A. Kahn, M. Aviram, A. J. Whitehead, S. L. Hyzy, R. M. Clohessy, B. D. Boyan, and Z. Schwartz. Novel osteogenic Ti-6Al-4V device for restoration of dental function In patients with large bone deficiencies: design, development and implementation. Sci. Rep. 6:20493, 2016.
Elias, C. N., D. J. Fernandes, C. R. S. Resende, and J. Roestel. Mechanical properties, surface morphology and stability of a modified commercially pure high strength titanium alloy for dental implants. Dent. Mater. 31(2):e1–e13, 2015.
Esposito, M., M. G. Grusovin, P. Felice, G. Karatzopoulos, H. V. Worthington, and P. Coulthard. The efficacy of horizontal and vertical bone augmentation procedures for dental implants—a Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol 2(3):167–184, 2009.
Gealh, W. C., V. Mazzo, F. Barbi, and E. T. Camarini. Osseointegrated implant fracture: causes and treatment. J Oral Implantol 37(4):499–503, 2011.
Geetha, M., A. K. Singh, R. Asokamani, and A. K. Gogia. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 54(3):397–425, 2009.
Gittens, R. A., L. Scheideler, F. Rupp, S. L. Hyzy, J. Geis-Gerstorfer, Z. Schwartz, and B. D. Boyan. A review on the wettability of dental implant surfaces II: biological and clinical aspects. Acta Biomater. 10(7):2907–2918, 2014.
Hyzy, S. L., A. Cheng, D. J. Cohen, G. Yatzkaier, A. J. Whitehead, R. M. Clohessy, R. A. Gittens, B. D. Boyan, and Z. Schwartz. Novel hydrophilic nanostructured microtexture on direct metal laser sintered Ti-6Al-4V surfaces enhances osteoblast response in vitro and osseointegration in a rabbit model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 104(8):2086–2098, 2016.
Jonitz-Heincke, A., J. Wieding, C. Schulze, D. Hansmann, and R. Bader. Comparative analysis of the oxygen supply and viability of human osteoblasts in three-dimensional titanium scaffolds produced by laser-beam or electron-beam melting. Materials 6(11):5398–5409, 2013.
Kim, D. G., S. S. Huja, B. C. Tee, P. E. Larsen, K. S. Kennedy, H. H. Chien, J. W. Lee, and H. B. Wen. Bone ingrowth and initial stability of titanium and porous tantalum dental implants: a pilot canine study. Implant Dent. 22(4):399–405, 2013.
Maniatopoulos, C., A. Rodriguez, D. A. Deporter, and A. H. Melcher. An improved method for preparing histological sections of metallic implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1(1):31–37, 1986.
Moy, P. K., D. Medina, V. Shetty, and T. L. Aghaloo. Dental implant failure rates and associated risk factors. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 20(4):569–577, 2005.
Olivares-Navarrete, R., S. L. Hyzy, B. D. Boyan, Z. Schwartz. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by acid-etched and/or grit-blasted titanium substrate topography Is enhanced by 1,25(OH)2D3 in a sex-dependent manner. BioMed Res. Intl. 2015, 2015. Article ID 365014.
Olivares-Navarrete, R., A. L. Raines, S. L. Hyzy, J. H. Park, D. L. Hutton, D. L. Cochran, B. D. Boyan, and Z. Schwartz. Osteoblast maturation and new bone formation in response to titanium implant surface features are reduced with age. J. Bone Miner. Res. 27(8):1773–1783, 2012.
Peterson, B., P. G. Whang, R. Iglesias, J. C. Wang, and J. R. Lieberman. Osteoinductivity of commercially available demineralized bone matrix. Preparations in a spine fusion model. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 86(10):2243–2250, 2004.
Scarano, A., V. Perrotti, L. Artese, M. Degidi, D. Degidi, A. Piattelli, and G. Iezzi. Blood vessels are concentrated within the implant surface concavities: a histologic study in rabbit tibia. Odontology 102(2):259–266, 2013.
Simion, M., P. Trisi, and A. Piattelli. Vertical ridge augmentation using a membrane technique associated with osseointegrated implants. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 14(6):496–511, 1994.
Tosi, L. L., B. D. Boyan, and A. L. Boskey. Does sex matter in musculoskeletal health? A workshop report. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 37(4):523–529, 2006.
Trisi, P., R. Lazzara, W. Rao, and A. Rebaudi. Bone-implant contact and bone quality: evaluation of expected and actual bone contact on machined and osseotite implant surfaces. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 22(6):535–545, 2002.
Acknowledgments
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number AR052102. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. The authors would like to thank AB Dental for generously donating materials for this study. AC was supported by a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship. BDB is a paid consultant for Titan Spine LLC and an unpaid consultant for Institut Straumann AG. ZS is a paid consultant for AB Dental.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Sean S. Kohles oversaw the review of this article.
Alice Cheng and David J. Cohen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, A., Cohen, D.J., Kahn, A. et al. Laser Sintered Porous Ti–6Al–4V Implants Stimulate Vertical Bone Growth. Ann Biomed Eng 45, 2025–2035 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1831-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1831-7