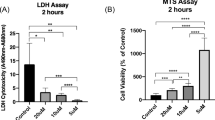
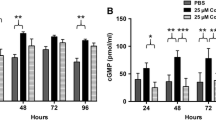
Abstract
High oxidative stress can occur during ischemic reperfusion and chronic inflammation. It has been hypothesized that such oxidative challenges could contribute to clinical risks such as deep tissue pressure ulcers. Skeletal muscles can be challenged by inflammation-induced or reperfusion-induced oxidative stress. Oxidative stress reportedly can lower the compressive damage threshold of skeletal muscles cells, causing actin filament depolymerization, and reduce membrane sealing ability. Skeletal muscles thus become easier to be damaged by mechanical loading under prolonged oxidative exposure. In this study, we investigated the preventive effect of poloxamer 188 (P188) on skeletal muscle cells against extrinsic oxidative challenges (H2O2). It was found that with 1 mM P188 pre-treatment for 1 h, skeletal muscle cells could maintain their compressive damage threshold. The actin polymerization dynamics largely remained stable in term of the expression of cofilin, thymosin beta 4 and profilin. Laser photoporation demonstrated that membrane sealing ability was preserved even as the cells were challenged by H2O2. These findings suggest that P188 pre-treatment can help skeletal muscle cells retain their normal mechanical integrity in oxidative environments, adding a potential clinical use of P188 against the combined challenge of mechanical-oxidative stresses. Such effect may help to prevent deep tissue ulcer development.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aragno, M., J. C. Cutrin, R. Mastrocola, M. G. Perrelli, F. Restivo, G. Poli, O. Danni, and G. Boccuzzi. Oxidative stress and kidney dysfunction due to ischemia/reperfusion in rat: attenuation by dehydroepiandrosterone. Kidney Int. 64(3):836–843, 2003.
Bouten, C. V., M. M. Knight, D. A. Lee, and D. L. Bade. Compressive deformation and damage of muscle cell subpopulations in a model system. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 29(2):153–163, 2001.
Carmo-Araujo, E. M., M. Dal-Pai-Silva, V. Dal-Pai, R. Cecchini, and A. L. A. Ferreira. Ischemia and reperfusion effects on skeletal muscle tissue: morphological and histochemical studies. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 88(3):147–154, 2007.
Collins, J. M., F. Despa, and R. C. Lee. Structural and functional recovery of electropermeabilized skeletal muscle in vivo after treatment with surfactant poloxamer 188. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1768(5):1238–1246, 2007.
Dastgheyb R. M., M. C. Cochran, and K. A. Barbee. Interactions of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled poloxamer P188 with cultured cells. Bioengineering Conference (NEBEC), 2012. doi:10.1109/NEBC.2012.62070989.
Dedova, I. V., O. P. Nikolaeva, D. Safer, E. M. De La Cruz, and C. G. dos Remedios. Thymosin beta 4 induces a conformational change in actin monomers. Biophys. J. 90(2):985–992, 2006.
Duan, X., K. T. Chan, K. K. H. Lee, and A. F. T. Mak. Oxidative stress and plasma membrane repair in single myoblasts after femtosecond laser photoporation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43(11):2735–2744, 2015.
Emanuele, M., and B. Balasubramaniam. differential effects of commercial-grade and purified poloxamer 188 on renal function. Drugs R & D 14:73–83, 2014.
Greenebaum, B., K. Blossfield, J. Hannig, C. S. Carrillo, M. A. Beckett, R. R. Weichselbaum, and R. C. Lee. Poloxamer 188 prevents acute necrosis of adult skeletal muscle cells following high-dose irradiation. Burns 30(6):539–547, 2004.
Gu, J., J. Ge, M. Li, H. Xu, F. Wu, and Z. Qin. Poloxamer 188 protects neurons against ischemia/reperfusion injury through preserving integrity of cell membranes and blood brain barrier. PLoS One 8(4):e61641, 2013.
Hunter, R. L., A. Z. Luo, R. Zhang, R. A. Kozar, and F. A. Moore. Poloxamer 188 inhibition of ischemia/reperfusion injury: evidence for a novel anti-adhesive mechanism. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. Spring 40(2):115–125, 2010.
Korolenko, T. A., T. P. Johnston, N. I. Dubrovina, Y. A. Kisarova, S. Y. Zhanaeva, M. S. Cherkanova, E. E. Filijushina, T. V. Alexeenko, E. Machova, and N. A. Zhukova. Effect of poloxamer 407 administration on the serum lipids profile, anxiety level and protease activity in the heart and liver of mice. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 6(1):18–25, 2013.
Kozakowska, M., K. P. Gremplewicz, A. Jozkowicz, and J. Dulak. The role of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle injury and regeneration: focus on antioxidant enzymes. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 26:377–393, 2015.
Ma, Z., Y. S. Wu, and A. F. T. Mak. Rheological behavior of actin stress fibers in myoblasts after nanodissection: effect of oxidative stress. Biorheology 52(3):225–234, 2015.
Marks, J. D., C. Pan, T. Bushell, W. Cromie, and R. C. Lee. Amphiphilic, tri-block copolymers provide potent, membrane-targeted neuroprotection. FASEB J. 15(6):1107–1109, 2001.
Maskarinec, S. A., J. Hannig, R. C. Lee, and K. Y. C. Lee. Direct observation of poloxamer 188 insertion into lipid monolayers. Biophys. J . 82(3):1453–1459, 2002.
McGinley, C., A. Shafat, and A. E. Donnelly. Does antioxidant vitamin supplementation protect against muscle damage? Sports Med. 39(12):1011–1032, 2009.
Merchant, F. A., W. H. Holmes, M. Capelli-Schellpfeffer, R. C. Lee, and M. Toner. Poloxamer 188 enhances functional recovery of lethally heat-shocked fibroblasts. J. Surg. Res. 74(2):131–140, 1998.
Mina, E. W., C. Lasagna-Reeves, C. G. Glabe, and R. Kayed. Poloxamer 188 copolymer membrane sealant rescues toxicity of amyloid oilgomers in vitro. J. Mol. Biol. 390:577–585, 2009.
Moloughney, J. G., and N. Weisleder. Poloxamer 188 (P188) as a membrane resealing reagent in biomedical applications. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 6(3):200–211, 2012.
Murphy, A. D., M. C. McCormack, D. A. Bichara, J. T. Nguyen, M. A. Randolph, M. T. Watkins, R. C. Lee, and W. G. Austen. poloxamer 188 protects against ischemia–reperfusion injury in a murine hind-limb model. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 125(6):1651–1660, 2010.
Ng, R., J. M. Metzger, D. R. Claflin, and J. A. Faulkner. Poloxamer 188 reduces the contraction-induced force decline in lumbrical muscles from mdx mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 295(1):C146–C150, 2008.
Peirce, S. M., T. C. Skalak, and G. T. Rodeheaver. Ischemia–reperfusion injury in chronic pressure ulcer formation: a skin model in rat. Wound Repair Regen. 8(1):68–76, 2000.
Plataki, M., Y. D. Lee, D. L. Rasmussen, and R. D. Hubmayr. Poloxamer 188 facilitates the repair of alveolus resident cells in ventilator-injured lungs. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Med. 184(8):939–947, 2011.
Powers, S. K., and M. J. Jackson. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol. Rev. 88(4):1243–1276, 2008.
Powers, S. K., A. J. Smuder, and A. R. Judge. Oxidative stress and disuse muscle atrophy: cause or consequence? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 15(3):240–245, 2012.
Quinlan, J. G., B. L. Wong, R. T. Niemeier, A. S. McCullough, L. Levin, and M. Manuele. Poloxamer 188 failed to prevent exercise-induced membrane breakdown in mdx skeletal muscle fibers. Neuromuscul. Disord. 16(12):855–864, 2006.
Sasaki, M., and T. Joh. Oxidative stress and ischemia–reperfusion injury in gastrointestinal tract and antioxidant, protective agents. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 40(1):1–12, 2007.
Spurney, C. F., A. D. Guerron, Q. Yu, A. Sali, J. H. van der Meulen, E. P. Hoffman, and K. Nagaraju. Membrane sealant poloxamer P188 protects against isoproterenol induced cardiomyopathy in dystrophin deficient mice. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 16:11–20, 2011.
Terry, R. L., H. M. Kaneb, and D. J. Wells. Poloxamer 188 has a deleterious effect on dystrophic skeletal muscle function. PLoS One 10(3):e0119252, 2014.
Tidball, J. G. Inflammatory process in muscle injury and repair. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 288(2):R345–R353, 2005.
Tsuji, S., S. Ichioka, N. Sekiya, and T. Nakatsuka. Analysis of ischemia–reperfusion injury in a microcirculatory model of pressure ulcer. Wound Repair Regen. 13(2):209–215, 2005.
Walters, T. J., V. J. Mase, J. L. Roe, M. A. Dubick, and R. J. Christy. Poloxamer-188 reduces muscular edema after tourniquet-induced ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. J. Trauma 70(5):1192–1197, 2011.
Wong, S. W., S. Sun, M. Cho, K. K. H. Lee, and A. F. T. Mak. H2O2 exposure affects myotube stiffness and actin filament polymerization. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43(5):1178–1188, 2015.
Wu, G., J. Majewski, C. Ege, K. Kjaer, M. J. Weygand, and K. Y. C. Lee. Interaction between lipid monolayers and poloxamer 188: an X-ray reflectivity and diffraction study. Biophys. J. 89(5):3159–3173, 2005.
Yao, Y., Z. Xiao, S. W. Wong, Y. Hsu, T. Cheng, C. Chang, L. Bian, and A. F. T. Mak. The effect of oxidative stress on the compressive damage thresholds of C2C12 mouse myoblasts—implications for deep tissue injury. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43(2):287–296, 2015.
Yasuda, S., D. Townsend, D. E. Michele, E. G. Favre, S. M. Day, and J. M. Metzger. Dystrophic heart failure blocked by membrane sealant poloxamer. Nature 436(7053):1025–1029, 2005.
Zweier, J. L., and M. A. Talukder. The role of oxidant and free radicals in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 70(2):181–190, 2006.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by General Research Fund from the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC Ref. No.: CUHK415413).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Sean S. Kohles oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, S.W., Yao, Y., Hong, Y. et al. Preventive Effects of Poloxamer 188 on Muscle Cell Damage Mechanics Under Oxidative Stress. Ann Biomed Eng 45, 1083–1092 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-016-1733-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-016-1733-0