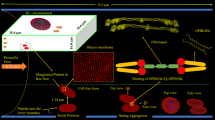
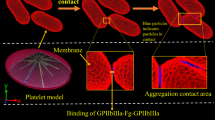
Abstract
Our hemostatic system, when called to action, depends on the complex arrangement of a tightly regulated and extensive network of molecules with versatile functionality. Experimental methods have demonstrated marked improvement through enhanced condition-control and monitoring. However, this approach continues to provide limited explanations of the role of individual elements or of a specific component within the entire system. To fill this void, multiscale simulations based on high throughput computing and comprehensive mathematical models are showing their strength in not only revealing hidden physiological mechanisms but also predicting pharmacological/phenotypical outcome in hemostasis reactions based on quantitative analysis. In this review article, we present up-to-date computational methods that simulate the process of platelet adhesion and thrombus growth, compare and summarize their advantages and drawbacks, verify their predictive power, and project their future directions. We provide an in-depth summary of one such computational method—Platelet Adhesive Dynamics (PAD)—and discuss its application in simulating platelet aggregation and thrombus development.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. D. Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Basics with Applications. McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering. New York: McGraw-Hill, p. xxiv, 547 pp., 1995.
Arya, M., B. Anvari, G. M. Romo, M. A. Cruz, J. F. Dong, L. V. McIntire, J. L. Moake, and J. A. Lopez. Ultralarge multimers of von Willebrand factor form spontaneous high-strength bonds with the platelet glycoprotein Ib–IX complex: studies using optical tweezers. Blood 99(11):3971–3977, 2002.
Ataullakhanov, F. I., and M. A. Panteleev. Mathematical modeling and computer simulation in blood coagulation. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 34(2–3):60–70, 2005.
Auton, M., C. Zhu, and M. A. Cruz. The mechanism of VWF-mediated platelet GPIb alpha binding. Biophys. J. 99(4):1192–1201, 2010.
Bell, G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science 200(4342):618–627, 1978.
Bennett, J. S. Structure and function of the platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3. J. Clin. Investig. 115(12):3363–3369, 2005.
Brady, J. F., and G. Bossis. Stokesian dynamics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 20:111–157, 1988.
Chatterjee, M. S., W. S. Denney, H. Y. Jing, and S. L. Diamond. Systems biology of coagulation initiation: kinetics of thrombin generation in resting and activated human blood. PLoS Comput. Biol. 6(9):e1000950, 2010.
Chu, S. G., R. C. Becker, P. B. Berger, D. L. Bhatt, J. W. Eikelboom, B. Konkle, E. R. Mohler, M. P. Reilly, and J. S. Berger. Mean platelet volume as a predictor of cardiovascular risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 8(1):148–156, 2010.
Coburn, L. A., V. S. Damaraju, S. Dozic, S. G. Eskin, M. A. Cruz, and L. V. McIntire. GPIb alpha-vWF rolling under shear stress shows differences between type 2B and 2M von Willebrand disease. Biophys. J. 100(2):304–312, 2011.
Colman, R. W. Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice, 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, p. xxiv, 1827 pp., 2006.
Davi, G., and C. Patrono. Platelet activation and atherothrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 357(24):2482–2494, 2007.
Diamond, S. L. Systems biology to predict blood function. J. Thromb. Haemost. 7:177–180, 2009.
Doggett, T. A., G. Girdhar, A. Lawshe, D. W. Schmidtke, I. J. Laurenzi, S. L. Diamond, and T. G. Diacovo. Selectin-like kinetics and biomechanics promote rapid platelet adhesion in flow: the GPIb(alpha)-vWF tether bond. Biophys. J. 83(1):194–205, 2002.
Einav, S., and D. Bluestein. Dynamics of blood flow and platelet transport in pathological vessels. Cardiac engineering: from genes and cells to structure and function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1015:351–366, 2004.
Filipovic, N., M. Kojic, and A. Tsuda. Modelling thrombosis using dissipative particle dynamics method. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 366(1879):3265–3279, 2008.
Fogelson, A. L. Continuum models of platelet-aggregation—formulation and mechanical-properties. Siam J. Appl. Math. 52(4):1089–1110, 1992.
Fogelson, A. L., and R. D. Guy. Platelet-wall interactions in continuum models of platelet thrombosis: formulation and numerical solution. IMA Math. Med. Biol. J. 21(4):293–334, 2004.
Fogelson, A. L., Y. H. Hussain, and K. Leiderman. Blood clot formation under flow: the importance of factor XI depends strongly on platelet count. Biophys. J. 102(1):10–18, 2012.
Fogelson, A. L., and J. P. Keener. Toward an understanding of fibrin branching structure. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 81(5 Pt 1):051922, 2010.
Fogelson, A. L., and N. Tania. Coagulation under flow: the influence of flow-mediated transport on the initiation and inhibition of coagulation. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 34(2–3):91–108, 2005.
Gailani, D., and T. Renne. Intrinsic pathway of coagulation and arterial thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27(12):2507–2513, 2007.
Gawaz, M., H. Langer, and A. E. May. Platelets in inflammation and atherogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 115(12):3378–3384, 2005.
Gay, L. J., and B. Felding-Habermann. Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 11(2):123–134, 2011.
Hammer, D. A., and S. M. Apte. Simulation of cell rolling and adhesion on surfaces in shear flow: general results and analysis of selectin-mediated neutrophil adhesion. Biophys. J. 63(1):35–57, 1992.
Honn, K. V., D. G. Tang, and J. D. Crissman. Platelets and cancer metastasis—a causal relationship. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 11(3–4):325–351, 1992.
http://www.imagwiki.nibib.nih.gov/mediawiki/index.php?title=Multiscale_Systems_Biology_Working_Group
Hyakutake, T., T. Matsumoto, and S. Yanase. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of blood cell behavior at microvascular bifurcations. Math. Comput. Simul. 72(2–6):134–140, 2006.
Jen, C. J., and L. V. Mcintire. The structural-properties and contractile—force of a clot. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2(5):445–455, 1982.
Jones, K. C., and K. G. Mann. A model for the tissue factor pathway to thrombin. 2. A mathematical simulation. J. Biol. Chem. 269(37):23367–23373, 1994.
Jung, S. M., and M. Moroi. Activation of the platelet collagen receptor integrin alpha(2)beta(1): its mechanism and participation in the physiological functions of platelets. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 10(7):285–292, 2000.
Kim, S., and S. J. Karrila. Microhydrodynamics: Principles and Selected Applications. Butterworth-Heinemann Series in Chemical Engineering. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann, p. xxiii, 507 pp., 1991.
Kim, J., C. Z. Zhang, X. H. Zhang, and T. A. Springer. A mechanically stabilized receptor–ligand flex-bond important in the vasculature. Nature 466(7309):992–995, 2010.
King, M. R., and D. A. Hammer. Multiparticle adhesive dynamics: hydrodynamic recruitment of rolling leukocytes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98(26):14919–14924, 2001.
King, M. R., and D. A. Hammer. Multiparticle adhesive dynamics. Interactions between stably rolling cells. Biophys. J. 81(2):799–813, 2001.
Kroll, M. H., T. S. Harris, J. L. Moake, R. I. Handin, and A. I. Schafer. von Willebrand factor binding to platelet GpIb initiates signals for platelet activation. J. Clin. Investig. 88(5):1568–1573, 1991.
Kuharsky, A. L., and A. L. Fogelson. Surface-mediated control of blood coagulation: the role of binding site densities and platelet deposition. Biophys. J. 80(3):1050–1074, 2001.
Lam, W. A., O. Chaudhuri, A. Crow, K. D. Webster, T. D. Li, A. Kita, J. Huang, and D. A. Fletcher. Mechanics and contraction dynamics of single platelets and implications for clot stiffening. Nat. Mater. 10(1):61–66, 2011.
Laurens, N., P. Koolwijk, and M. P. de Maat. Fibrin structure and wound healing. J. Thromb. Haemost. 4(5):932–939, 2006.
Leiderman, K., and A. L. Fogelson. Grow with the flow: a spatial-temporal model of platelet deposition and blood coagulation under flow. IMA Math. Med. Biol. J. 28(1):47–84, 2011.
Lippi, G., E. J. Favaloro, M. Franchini, and G. C. Guidi. Milestones and perspectives in coagulation and hemostasis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 35(1):9–22, 2009.
Lo, K., W. S. Denney, and S. L. Diamond. Stochastic modeling of blood coagulation initiation. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 34(2–3):80–90, 2005.
Luan, D., F. Szlam, K. A. Tanaka, P. S. Barie, and J. D. Varner. Ensembles of uncertain mathematical models can identify network response to therapeutic interventions. Mol. BioSyst. 6(11):2272–2286, 2010.
Luan, D., M. Zai, and J. D. Varner. Computationally derived points of fragility of a human cascade are consistent with current therapeutic strategies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 3(7):e142, 2007.
Mackman, N., R. E. Tilley, and N. S. Key. Role of the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation in hemostasis and thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27(8):1687–1693, 2007.
MacMeccan, R. M., J. R. Clausen, G. P. Neitzel, and C. K. Aidun. Simulating deformable particle suspensions using a coupled lattice-Boltzmann and finite-element method. J. Fluid Mech. 618:13–39, 2009.
Merrill, E. W. Rheology of blood. Physiol. Rev. 49(4):863–868, 1969.
Mody, N. A., and M. R. King. Three-dimensional simulations of a platelet-shaped spheroid near a wall in shear flow. Phys. Fluids 17(11):113302, 2005.
Mody, N. A., and M. R. King. Influence of Brownian motion on blood platelet flow behavior and adhesive dynamics near a planar wall. Langmuir 23(11):6321–6328, 2007.
Mody, N. A., and M. R. King. Platelet adhesive dynamics. Part II: high shear-induced transient aggregation via GPIbalpha–Vwf–GPIbalpha bridging. Biophys. J. 95(5):2556–2574, 2008.
Mody, N. A., and M. R. King. Platelet adhesive dynamics. Part I: characterization of platelet hydrodynamic collisions and wall effects. Biophys. J. 95(5):2539–2555, 2008.
Mody, N. A., O. Lomakin, T. A. Doggett, T. G. Diacovo, and M. R. King. Mechanics of transient platelet adhesion to von Willebrand factor under flow. Biophys. J. 88(2):1432–1443, 2005.
Mori, D., K. Yano, K. Tsubota, T. Ishikawa, S. Wada, and T. Yamaguchi. Simulation of platelet adhesion and aggregation regulated by fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor. Thromb. Haemost. 99(1):108–115, 2008.
Mori, D., K. Yano, K. Tsubota, T. Ishikawa, S. Wada, and T. Yamaguchi. Computational study on effect of red blood cells on primary thrombus formation. Thromb. Res. 123(1):114–121, 2008.
Munn, L. L., and M. M. Dupin. Blood cell interactions and segregation in flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 36(4):534–544, 2008.
Munnix, I. C. A., J. M. E. M. Cosemans, J. M. Auger, and J. W. M. Heemskerk. Platelet response heterogeneity in thrombus formation. Thromb. Haemost. 102(6):1149–1156, 2009.
Murata, T. Theory of non-newtonian viscosity of red-blood-cell suspension—effect of red-cell deformation. Biorheology 20(5):471–483, 1983.
Phan-Thien, N., D. Tullock, and S. Kim. Completed double-layer in half-space: a boundary element method. Comput. Mech. 9:121–135, 1992.
Pivkin, I. V., P. D. Richardson, and G. Karniadakis. Blood flow velocity effects and role of activation delay time on growth and form of platelet thrombi. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103(46):17164–17169, 2006.
Pivkin, I. V., P. D. Richardson, and G. E. Karniadakis. Effect of red blood cells on platelet aggregation. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 28(2):32–37, 2009.
Pozrikidis, C. Numerical simulation of the flow-induced deformation of red blood cells. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31(10):1194–1205, 2003.
Pozrikidis, C. Axisymmetric motion of a file of red blood cells through capillaries. Phys. Fluids 17(3):031503, 2005.
Purvis, J. E., M. S. Chatterjee, L. F. Brass, and S. L. Diamond. A molecular signaling model of platelet phosphoinositide and calcium regulation during homeostasis and P2Y1 activation. Blood 112(10):4069–4079, 2008.
Purvis, J. E., R. Radhakrishnan, and S. L. Diamond. Steady-state kinetic modeling constrains cellular resting states and dynamic behavior. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5(3):e1000298, 2009.
Rayz, V. L., L. Boussel, L. Ge, J. R. Leach, A. J. Martin, M. T. Lawton, C. McCulloch, and D. Saloner. Flow residence time and regions of intraluminal thrombus deposition in intracranial aneurysms. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38(10):3058–3069, 2010.
Sakariassen, K. S., P. A. Bolhuis, and J. J. Sixma. Human blood platelet adhesion to artery subendothelium is mediated by factor VIII-Von Willebrand factor bound to the subendothelium. Nature 279(5714):636–638, 1979.
Savage, B., E. Saldivar, and Z. M. Ruggeri. Initiation of platelet adhesion by arrest onto fibrinogen or translocation on von Willebrand factor. Cell 84(2):289–297, 1996.
Singh, I., E. Themistou, L. Porcar, and S. Neelamegham. Fluid shear induces conformation change in human blood protein von Willebrand factor in solution. Biophys. J. 96(6):2313–2320, 2009.
Sorensen, E. N., G. W. Burgreen, W. R. Wagner, and J. F. Antaki. Computational simulation of platelet deposition and activation: I. Model development and properties. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 27(4):436–448, 1999.
Sorensen, E. N., G. W. Burgreen, W. R. Wagner, and J. F. Antaki. Computational simulation of platelet deposition and activation: II. Results for Poiseuille flow over collagen. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 27(4):449–458, 1999.
Steinman, D. A. Image-based computational fluid dynamics modeling in realistic arterial geometries. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 30(4):483–497, 2002.
Tokarev, A. A., A. A. Butylin, E. A. Ermakova, E. E. Shnol, G. P. Panasenko, and F. I. Ataullakhanov. Finite platelet size could be responsible for platelet margination effect. Biophys. J. 101(8):1835–1843, 2011.
Undas, A., and R. A. S. Ariens. Fibrin clot structure and function a role in the pathophysiology of arterial and venous thromboembolic diseases. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31(12):E88–E99, 2011.
Wang, N. T., and A. L. Fogelson. Computational methods for continuum models of platelet aggregation. J. Comput. Phys. 151(2):649–675, 1999.
Weisel, J. W. Structure of fibrin: impact on clot stability. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5(Suppl 1):116–124, 2007.
Wiggs, B. R., D. English, W. M. Quinlan, N. A. Doyle, J. C. Hogg, and C. M. Doerschuk. Contributions of capillary pathway size and neutrophil deformability to neutrophil transit through rabbit lungs. J. Appl. Physiol. 77(1):463–470, 1994.
Wu, J. S., and C. K. Aidun. Simulating 3D deformable particle suspensions using lattice Boltzmann method with discrete external boundary force. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 62(7):765–783, 2010.
Xu, Z., N. Chen, M. M. Kamocka, E. D. Rosen, and M. Alber. A multiscale model of thrombus development. J. R. Soc. Interface 5(24):705–722, 2008.
Xu, Z., M. Kamocka, M. Alber, and E. D. Rosen. Computational approaches to studying thrombus development. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31(3):500–505, 2011.
Xu, Z. L., J. H. Lioi, J. A. Mu, M. M. Kamocka, X. M. Liu, D. Z. Chen, E. D. Rosen, and M. Alber. A multiscale model of venous thrombus formation with surface-mediated control of blood coagulation cascade (vol 98, pg 1723, 2010). Biophys. J. 99(7):2384–2385, 2010.
Yago, T., J. Lou, T. Wu, J. Yang, J. J. Miner, L. Coburn, J. A. Lopez, M. A. Cruz, J. F. Dong, L. V. McIntire, R. P. McEver, and C. Zhu. Platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha forms catch bonds with human WT vWF but not with type 2B von Willebrand disease vWF. J. Clin. Investig. 118(9):3195–3207, 2008.
Yamaguchi, T., T. Ishikawa, Y. Imai, N. Matsuki, M. Xenos, Y. F. Deng, and D. Bluestein. Particle-based methods for multiscale modeling of blood flow in the circulation and in devices: challenges and future directions. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38(3):1225–1235, 2010.
Zhao, H., A. H. G. Isfahani, L. N. Olson, and J. B. Freund. A spectral boundary integral method for flowing blood cells. J. Comput. Phys. 229(10):3726–3744, 2010.
Zhao, R., M. V. Kameneva, and J. F. Antaki. Investigation of platelet margination phenomena at elevated shear stress. Biorheology 44(3):161–177, 2007.
Zhao, H., E. S. G. Shaqfehhear, and V. Narsimhan. Shear-induced particle migration and margination in a cellular suspension. Phys. Fluids 24:011902, 2012.
Zucker, M. B., and V. T. Nachmias. Platelet activation. Arteriosclerosis 5(1):2–18, 1985.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank John P. Lindsey for discussions and review of the manuscript. The work is funded by NIH Grant No. HL097971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Scott L. Diamond oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., King, M.R. Multiscale Modeling of Platelet Adhesion and Thrombus Growth. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 2345–2354 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0558-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0558-8