Abstract
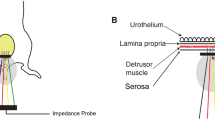
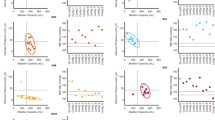
We have demonstrated that bladder wall tissue in spinal cord injury (SCI) rats at 10 days post-injury is more compliant and accompanied by changes in material class from orthotropic to isotropic as compared to normal tissue. The present study examined the long-term effects (3-, 6-, and 10-weeks) post-SCI on the mechanical properties of bladder wall tissues, along with quantitative changes in smooth muscle orientation and collagen and elastin content. Bladder wall compliance (defined as det(F) − 1 under an equi-biaxial stress state of 100 kPa, where F is the deformation gradient tensor) was found to be significantly greater at 3- and 6-weeks (0.873 ± 0.092 and 0.864 ± 0.112, respectively) when compared to the normal bladders (0.260 ± 0.028), but at 10 weeks the compliance reduced (0.389 ± 0.061) to near that of normal bladders. This trend in mechanical compliance closely paralleled the collagen/elastin ratio. Moreover, changes in material class, assessed using a graphical technique, correlated closely with quantitative changes in smooth muscle fiber orientation. The results of the present study provide the first evidence that, while similarities exist between acute and chronic responses of the urinary bladder wall tissue to SCI, the overall alterations are distinct, result in profound and complex time dependent changes in bladder wall structure, and will lay the basis for simulations of the bladder wall disease process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cortivo R., F. Pagano, G. Passerini, G. Abatangelo, I. Castellani (1981). Elastin and collagen in the normal and obstructed urinary bladder. Br. J. Urol. 53(2): 134–137
Criscione J. C., M. S. Sacks, W. C. Hunter (2003). Experimentally tractable, pseudo-elastic constitutive law for biomembranes: I. Theory. J. Biomech. Eng. 125(1): 94–99. doi:10.1115/1.1530770
de Groat W. C. (1997). A neurologic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology 50(6A Suppl): 36–52; discussion 53–56
de Groat, W. C., A. M. Booth, and N. Yoshimura. Neurophysiology of micturition and its modification in animal models of human disease. In: Nervous Control of the Urogenital System, Vol. 3, edited by C. A. Maggi. Chur: Harwood Academic Publishers, 1993, pp. 227–290
Deveaud C. M., E. J. Macarak, U. Kucich, D. H. Ewalt, W. R. Abrams, P. S. Howard (1998). Molecular analysis of collagens in bladder fibrosis. J. Urol. 160(4): 1518–1527. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)62606-5
Drake M. J., P. Hedlund, I. W. Mills, R. McCoy, G. McMurray, B. P. Gardner, K. E. Andersson, A. F. Brading (2000). Structural and functional denervation of human detrusor after spinal cord injury. Lab. Invest. 80(10): 1491–1499
Fung Y. C. (1993). Biomechanics: Mechanical Properties of Living Tissues. New York, Springer Verlag
Gloeckner, D. C. Tissue Biomechanics of the Urinary Bladder Wall. Pittsburgh: Department of Bioengineering, University of Pittsburgh, 258 p, 2003
Gloeckner D. C., M. S. Sacks, M. O. Fraser, G. T. Somogyi, W. C. de Groat, M. B. Chancellor (2002). Passive biaxial mechanical properties of the rat bladder wall after spinal cord injury. J. Urol. 167(5): 2247–2252. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)65137-3
Hackler R. H., M. K. Hall, T. A. Zampieri (1989). Bladder hypocompliance in the spinal cord injury population. J. Urol. 141(6): 1390–1393
Humphrey J. D. (2002). Cardiovascular Solid Mechanics: Cells, Tissues, and Organs. New York, Springer
Kim J. C., J. Y. Yoon, S. I. Seo, T. K. Hwang, Y. H. Park (2000). Effects of partial bladder outlet obstruction and its relief on types I and III collagen and detrusor contractility in the rat. Neurourol. Urodyn. 19(1): 29–42. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-6777(2000)19:1<29::AID-NAU5>3.0.CO;2-#
Kim K. M., B. A. Kogan, C. A. Massad, Y. C. Huang (1991). Collagen and elastin in the obstructed fetal bladder. J. Urol. 146(2 (Pt 2)): 528–531
Kondo A., J. G. Susset (1974). Viscoelastic properties of bladder. Investigat. Urol. 11(6):459–465
Kruse M. N., L. A. Bray, W. C. de Groat (1995). Influence of spinal cord injury on the morphology of bladder afferent and efferent neurons. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 54(3): 215–224. doi:10.1016/0165-1838(95)00011-L
Macarak E. J., D. Ewalt, L. Baskin, D. Coplen, H. Koo, R. Levin, J. W. Duckett, H. Snyder, J. Rosenbloom, P. S. Howard (1995). The collagens and their urologic implications. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 385: 173–177
Mimata H., F. Satoh, T. Tanigawa, Y. Nomura, J. Ogata (1993). Changes of rat urinary bladder during acute phase of spinal cord injury. Urol. Int. 51(2): 89–93
Nagatomi J., D. C. Gloeckner, M. B. Chancellor, W. C. DeGroat, M. S. Sacks (2004). Changes in the biaxial viscoelastic response of the urinary bladder following spinal cord injury. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 32(10): 1409–1419. doi:10.1114/B:ABME.0000042228.89106.48
Nagatomi, J., K. Toosi, M. Chancellor, and M. Sacks. Contribution of the extracellular matrix to the viscoelastic behavior: A new modeling approach for rat bladder wall tissue. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol., 2007. [Epub ahead of print]
Nagatomi J., K. K. Toosi, J. S. Grashow, M. B. Chancellor, M. S. Sacks (2005). Quantification of bladder smooth muscle orientation in normal and spinal cord injured rats. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33(8): 1078–1089. doi:10.1007/s10439-005-5776-x
Ogawa T. (1991). Bladder deformities in patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Urol. Int. 47(Suppl 1): 59–62
Sacks M. S. (2000). Biaxial mechanical evaluation of planar biological materials. J. Elast. 61: 199–246. doi:10.1023/A:1010917028671
Sandberg L. B., N. T. Soskel, J. G. Leslie (1981). Elastin structure, biosynthesis, and relation to disease states. N Engl J. Med. 304(10): 566–579
Shin J. C., C. I. Park, H. J. Kim, I. Y. Lee (2002). Significance of low compliance bladder in cauda equina injury. Spinal Cord 40(12): 650–655. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3101380
Sun W., M. S. Sacks, M. J. Scott (2005). Effects of boundary conditions on the estimation of the planar biaxial mechanical properties of soft tissues. J. Biomech. Eng. 127(4): 709–715. doi:10.1115/1.1933931
Sun W., M. S. Sacks, T. L. Sellaro, W. S. Slaughter, M. J. Scott (2003). Biaxial mechanical response of bioprosthetic heart valve biomaterials to high in-plane shear. J. Biomech. Eng. 125: 372–380. doi:10.1115/1.1572518
Uvelius B., A. Mattiasson (1984). Collagen content in the rat urinary bladder subjected to infravesical outflow obstruction. J. Urol. 132(3): 587–590
Vande Geest J. P., M. S. Sacks, D. A. Vorp (2006). The effects of aneurysm on the biaxial mechanical behavior of human abdominal aorta. J. Biomech. 39(7): 1324–1334. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.03.003
Watanabe T., D. A. Rivas, M. B. Chancellor (1996). Urodynamics of spinal cord injury. Urol. Clin. North Am. 23(3): 459–473. doi:10.1016/S0094-0143(05)70325-6
Weld K. J., M. J. Graney, R. R. Dmochowski (2000). Differences in bladder compliance with time and associations of bladder management with compliance in spinal cord injured patients. J. Urol. 163(4): 1228–1233. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67730-0
Yoshimura N., C. P. Smith, M. B. Chancellor, W. C. de Groat (2000). Pharmacologic and potential biologic interventions to restore bladder function after spinal cord injury. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 13(6): 677–681. doi:10.1097/00019052-200012000-00011
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge funding by NICDH P01-HD39768 and the Paralyzed Veterans of America Spinal Cord Research Foundation (#2289-01). KKT was supported by an NIH T32 training grant (DK7774). The authors wish to also thank Drs. Kazumasa Torimoto and Teruyuki Ogawa for providing the rat bladders used in this study, and Ms. Silvia Wognum for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toosi, K.K., Nagatomi, J., Chancellor, M.B. et al. The Effects of Long-Term Spinal Cord Injury on Mechanical Properties of the Rat Urinary Bladder. Ann Biomed Eng 36, 1470–1480 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-008-9525-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-008-9525-9