Abstract
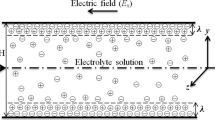
Electrowetting phenomenon in parallel plate microchannel is investigated numerically. The current study advances accuracy of numerical modeling of electrowetting by considering dynamic behavior of the tri-phase contact line using molecular-kinetic theory. This theory in conjunction with volume of fluid method, which has been proved to be a powerful approach for free surface modeling, is used to simulate the phenomenon. By comparing the results against experimental data from literature, the simulation demonstrates significant improvement in results. It is concluded that ignoring dynamic features of wetting leads to overestimation of the effect of electrowetting actuation on various parameters including contact angle, aspect ratio and velocity of the droplet.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamiak K (2006) Capillary and electrostatic limitations to the contact angle in electrowetting-on-dielectric. J Microfluid Nanofluid 2:471–480
Adamson AW (1990) Physical chemistry of surfaces, 5th edn. Wiley, New York
Antropov L (2001) Theoretical electrochemistry. University Press of the Pacific, Honolulu
Arzpeyma A, Bhaseen S, Dolatabadi A, Wood-Adams P (2008) A coupled electro-hydrodynamic numerical modeling of droplet actuation by electrowetting. J Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 323:28–35
Blake TD (1993) Dynamic contact angles and wetting kinetics. In: Berg JC (ed) Wettability. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 251–309
Blake TD (2006) The physics of moving wetting lines. J Colloid Interface Sci 299:1–13
Blake TD, Haynes JM (1969) Kinetics of liquid/liquid displacement. J Colloid Interface Sci 30:421–423
Blake TD, Clarke A, Stattersfield EH (2000) An investigation of electrostatic assist dynamic contact wetting. Langmuir 16:2928–2935
Brackbill JU, Kothe DB, Zemach C (1992) A continuum method for modeling surface tension. J Comput Phys 100:335–354
Bussmann M, Mostaghimi J, Chandra S (1999) On a three-dimensional volume tracking model of droplet impact. J Phys Fluids 11:1406–1417
Chen JH, Hsieh WH (2006) Electrowetting-induced capillary flow in a parallel-plate channel. J Colloid Interface Sci 296:276–283
Decamps C, De Coninck J (2000) Dynamics of spontaneous spreading under electrowetting conditions. Langmuir 16:10150–10153
Dussan VEB (1979) On the spreading of liquids in solid surfaces: static and dynamic contact lines. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 11:371–400
Erickson D (2005) Towards numerical prototyping of labs-on-chip: modeling for integrated microfluidic devices. J Microfluid Nanofluid 4:159–165
Fouillet Y, Jary D, Chabrol C, Claustre P, Peponnet C (2008) Digital microfluidic design and optimization of classic and new fluidic functions for lab on a chip systems. J Microfluid Nanofluid 4:159–165
Fukai J, Zhao Z, Poulikakos D, Megaridis CM, Miyatake O (1993) Modeling of deformation of a liquid droplet impinging upon a flat surface. J Phys Fluids A 5:2588–2599
Fukai J, Shiiba Y, Yamamoto T, Miyatake O, Poulikakos D, Megardis CM, Zhao Z (1995) Wetting effects on the spreading of a liquid droplet colliding with a flat surface experiment and modeling. J Phys Fluids 7:236–247
Glasstone S, Laidler KJ, Eyring HJ (1941) The theory of rate processes. McGraw-Hill, New York
Hirt CW, Nichols BD (1981) Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamic of free boundaries. J Comput Phys 39:201–225
Karl A, Rieber M, Shelkle M, Andres K, Frohn A (1996) Comparison of new numerical results for droplet wall interactions with experimental results. Proc ASME Fluid Eng Div Summer Meet 1:202–206
Mugele F, Baret J (2005) Electrowetting from basics to applications. Top Rev J Phys 17:705–774
Pollack M (2001) Electrowetting-based microactuation of droplets for digital microfluidics. PhD thesis, Duke University, Durham
Pollack MG, Fair RB (2000) Electrowetting-based actuation of liquid droplets for microfluidic applications. J Appl Phys Lett 77:1725–1726
Pollack MG, Shenderov AD, Fair RB (2002) Electrowetting-based actuation of droplets for integrated microfluidic. J Lab Chip 2:96–101
Ren H, Fair RB, Pollack MG, Shaughnessy EJ (2002) Dynamics of electro-wetting droplet transport. J Sens Actuators B 87:201–206
Shikhmurzaev YD (1993) The moving contact line on a smooth solid surface. Int J Multi-Phase Flow 19:589–610
Van Mourik S, Veldman AEP, Dreyer ME (2005) Simulation of capillary flow with a dynamic contact angle. J Microgravity Sci Technol 17:87–93
Wang KL, Jones TB (2005) Electrowetting dynamics of microfluidic actuation. Langmuir 21:4211–4217
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge SIMULENT Inc., Toronto, Ontario for making SIMULENT code accessible for this study. We thank four anonymous reviewers and Nima Maftoon for their many helpful comments. A. D. would like to thank the support of MDEIE and FQRNT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keshavarz-Motamed, Z., Kadem, L. & Dolatabadi, A. Effects of dynamic contact angle on numerical modeling of electrowetting in parallel plate microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 8, 47–56 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0460-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0460-3