Abstract
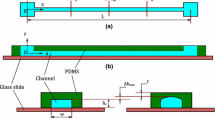
We present a detailed numerical study of the flow of a Newtonian fluid through microrheometric devices featuring a sudden contraction–expansion. This flow configuration is typically used to generate extensional deformations and high strain rates. The excess pressure drop resulting from the converging and diverging flow is an important dynamic measure to quantify if the device is intended to be used as a microfluidic extensional rheometer. To explore this idea, we examine the effect of the contraction length, aspect ratio and Reynolds number on the flow kinematics and resulting pressure field. Analysis of the computed velocity and pressure fields show that, for typical experimental conditions used in microfluidic devices, the steady flow is highly three-dimensional with open spiraling vortical structures in the stagnant corner regions. The numerical simulations of the local kinematics and global pressure drop are in good agreement with experimental results. The device aspect ratio is shown to have a strong impact on the flow and consequently on the excess pressure drop, which is quantified in terms of the dimensionless Couette and Bagley correction factors. We suggest an approach for calculating the Bagley correction which may be especially appropriate for planar microchannels.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves MA, Pinho FT, Oliveira PJ (2000) Effect of a high-resolution differencing scheme on finite-volume predictions of viscoelastic flows. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 93:287–314
Alves MA, Oliveira PJ, Pinho FT (2003) A convergent and universally bounded interpolation scheme for the treatment of advection. Int J Num Meth Fluids 41:47–75
Alves MA, Oliveira PJ, Pinho FT (2004) On the effect of contraction ratio in viscoelastic flow through abrupt contractions. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 122:117–130
Alves MA, Pinho FT, Oliveira PJ (2005) Visualizations of Boger fluid flows in a 4:1 square–square contraction. AIChE J 51:2908–2922
Alves MA, Poole RJ (2007) Divergent flow in contractions. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 144:141–148
Bagley EB (1957) End corrections in the capillary flow of polyethylene. J Appl Phys 28:624–627
Barnes HA, Hutton JF, Walters K (1989) An introduction to rheology. Elsevier: Distributors for the U.S. and Canada, Elsevier Science Pub. Co., Amsterdam, New York
Barrat JL, Bocquet L (1999) Large slip effect at a nonwetting fluid-solid interface. Phys Rev Lett 82:4671–4674
Battaglia F, Tavener SJ, Kulkarni AK, Merkle CL (1997) Bifurcation of low Reynolds number flows in symmetric channels. AIAA J 35:99–105
Bayraktar T, Pidugu SB (2006) Characterization of liquid flows in microfluidic systems. Int J Heat Mass Transf 49:815–824
Binding DM (1988) An approximate analysis for contraction and converging flows. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 27:173–189
Binding DM, Couch MA, Walters K (1998) The pressure dependence of the shear and elongational properties of polymer melts. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 79:137–155
Boger DV (1982) Circular entry flows of inelastic and viscoelastic fluids. In: Mujumdar AS, Mashelkar RA (eds) Advances of transport processes, vol 2. Wiley Eastern, New Delhi, pp 43–98
Boger DV (1987) Viscoelastic flows through contractions. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 19:157–182
Boger DV, Binnington RJ (1990) Circular entry flows of fluid M1. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 35:339–360
Brown RA, McKinley GH (1994) Report on the VIIIth Int. workshop on numerical methods in viscoelastic flows. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 52:407–413
Cherdron W, Durst F, Whitelaw JH (1978) Asymmetric flows and instabilities in symmetric ducts with sudden expansions. J Fluid Mech 84:13–31
Chiang TP, Sheu TWH, Wang SK (2000) Side wall effects on the structure of laminar flow over a plane-symmetric sudden expansion. Comp Fluids 29:467–492
Cogswell FN (1972a) Converging flow of polymer melts in extrusion dies. Polymer Eng Sci 12:64–73
Cogswell FN (1972b) Measuring extensional rheology of polymer melts. Trans Soc Rheol 16:383–403
Drikakis D (1997) Bifurcation phenomena in incompressible sudden expansion flows. Phys Fluids 9:76–87
Durst F, Melling A, Whitelaw JH (1974) Low Reynolds-number flow over a plane symmetric sudden expansion. J Fluid Mech 64:111–128
Fearn RM, Mullin T, Cliffe KA (1990) Nonlinear flow phenomena in a symmetric sudden expansion. J Fluid Mech 211:595–608
Gad-el-Hak M (2002) The MEMS handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hassager O (1988) Working group on numerical techniques (Vth workshop on numerical methods in non-Newtonian flow). J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 29:2–5
Hawa T, Rusak Z (2001) The dynamics of a laminar flow in a symmetric channel with a sudden expansion. J Fluid Mech 436:283–320
James DF, Chandler GM, Armour SJ (1990) A converging channel rheometer for the measurement of extensional viscosity. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 35:421–443
Kang K, Lee LJ, Koelling KW (2005) High shear microfluidics and its application in rheological measurement. Exp Fluids 38: 222–232
Kang K, Koelling KW, Lee LJ (2006) Microdevice end pressure evaluations with Bagley correction. Microfluid Nanofluid 2:223–235
Karniadakis G, Beskok A, Aluru NR (2005) Microflows and nanoflows: fundamentals and simulation. Springer, New York
Kim S, Dealy JM (2001) Design of an orifice die to measure entrance pressure drop. J Rheol 45:1413–1419
Lauga E, Stroock AD, Stone HA (2004) Three-dimensional flows in slowly varying planar geometries. Phys Fluids 16:3051–3062
Lee WY, Wong M, Zohar Y (2002) Microchannels in series connected via a contraction/expansion section. J Fluid Mech 459:187–206
Leonard BP (1979) Stable and accurate convective modeling procedure based on quadratic upstream interpolation. Comp Meth Appl Mech Eng 19:59–98
McDonald JC, Duffy DC, Anderson JR, Chiu DT, Wu HK, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (2000) Fabrication of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Electrophoresis 21:27–40
Mishra S, Jayaraman K (2002) Asymmetric flows in planar symmetric channels with large expansion ratio. Int J Num Meth Fluids 38:945–962
Mitsoulis E, Hatzikiriakos SG, Christodoulou K, Vlassopoulos D (1998) Sensitivity analysis of the Bagley correction to shear and extensional rheology. Rheol Acta 37:438–448
Moffatt HK (1964) Viscous and resistive eddies near a sharp corner. J Fluid Mech 18:1–18
Neto C, Evans DR, Bonaccurso E, Butt HJ, Craig VSJ (2005) Boundary slip in Newtonian liquids: a review of experimental studies. Rep Prog Phys 68:2859–2897
Oliveira MSN, Alves MA, McKinley GH, Pinho FT (2007a) Viscous flow through microfabricated hyperbolic contractions. Exp Fluids 43:437–451
Oliveira MSN, Oliveira PJ, Pinho FT, Alves MA (2007b) Effect of contraction ratio upon viscoelastic flow in contractions: the axisymmetric case. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 147:92–108
Oliveira MSN, Yeh R, McKinley GH (2006) Iterated stretching, extensional rheology and formation of beads-on-a-string structures in polymer solutions. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 137:137–148
Oliveira PJ (2003) Asymmetric flows of viscoelastic fluids in symmetric planar expansion geometries. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 114:33–63
Oliveira PJ, Pinho FT (1999) Numerical procedure for the computation of fluid flow with arbitrary stress-strain relationships. Num Heat Transf B 35:295–315
Oliveira PJ, Pinho FT, Pinto GA (1998) Numerical simulation of non-linear elastic flows with a general collocated finite-volume method. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 79:1–43
Owens RG, Phillips NT (2002) Computational rheology. Imperial College Press, London
Pit R, Hervet H, Leger L (2000) Direct experimental evidence of slip in hexadecane: solid interfaces. Phys Rev Lett 85:980–983
Revuelta A (2005) On the two-dimensional flow in a sudden expansion with large expansion ratios. Phys Fluids 17:028102 1–4
Rodd LE, Scott TP, Boger DV, Cooper-White JJ, McKinley GH (2005) The inertio-elastic planar entry flow of low-viscosity elastic fluids in micro-fabricated geometries. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 129:1–22
Rothstein JP, McKinley GH (2001) The axisymmetric contraction–expansion: the role of extensional rheology on vortex growth dynamics and the enhanced pressure drop. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 98:33–63
Shapira M, Degani D, Weihs D (1990) Stability and existence of multiple solutions for viscous-flow in suddenly enlarged channels. Comp Fluids 18:239–258
Sobey IJ, Drazin PG (1986) Bifurcations of two-dimensional channel flows. J Fluid Mech 171:263–287
Townsend P, Walters K (1994) Expansion flows of non-Newtonian liquids. Chem Eng Sci 49:749–763
Tsai C-H, Chen H-T, Wang Y-N, Lin C-H, Fu L-M (2006) Capabilities and limitations of 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional numerical methods in modeling the fluid flow in sudden expansion microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:13–18
Tuladhar TR, Mackley MR (2008) Filament stretching rheometry and break-up behaviour of low viscosity polymer solutions and inkjet fluids. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 148:97–108. doi:10.1016/j.jnnfm.2007.04.015
Wereley ST, Meinhart CD (2004) Micron-resolution particle image velocimetry. In: Breuer KS (ed) Microscale diagnostic techniques. Springer, Berlin
White SA, Gotsis AD, Baird DG (1987) Review of the entry flow problem—experimental and numerical. J Non-Newt Fluid Mech 24:121–160
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373
Whitesides GM, Stroock AD (2001) Flexible methods for microfluidics. Phys Today 54:42–48
Wille R, Fernholz H (1965) Report on first European mechanics colloquium on Coanda effect. J Fluid Mech 23:801–819
Acknowledgement
M. S. N. Oliveira would like to thank Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal, for financial support (SFRH/BPD/15005/2004, SFRH/BPD/34141/2006). M. S. N. Oliveira and M. A. Alves acknowledge the financial support provided by FCT and FEDER under program POCI 2010 (projects PPTDC/EME/59338/2004 and POCI/EQU/59256/2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, M.S.N., Rodd, L.E., McKinley, G.H. et al. Simulations of extensional flow in microrheometric devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 5, 809–826 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0277-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0277-5