Abstract
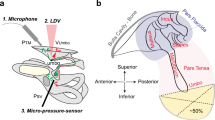
The conductive hearing loss caused by acute otitis media (AOM) is commonly related to a reduction of the tympanic membrane (TM) mobility in response to sound stimuli. However, spatial alterations of the TM surface motion associated with AOM have rarely been addressed. In this study, the TM surface motion was determined using scanning laser Doppler vibrometry (SLDV) in a chinchilla model of AOM. The AOM was established by transbullar injection of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. The TM surface vibration was measured in control (uninfected) animals and two AOM groups of animals: 4 days (4D) and 8 days (8D) post inoculation. To quantify the effect of middle ear pressure in those infected ears, the SLDV measurement was first conducted in unopened AOM ears and then in middle ear pressure released ears. Results showed that middle ear infection generally reduced the TM displacement across the entire surface, but the reduction in the umbo displacement over the time course, from 4 to 8 days post inoculation, was less than the reduction in the displacement at the center of each quadrant. The presence of middle ear fluid shifted the occurrence of traveling-wave-like motion on the TM surface to lower frequencies. The observation of the spatial variations of TM surface motion from this study will help refine our understanding of the middle ear sound transmission characteristics in relation to AOM.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarnisalo AA, Cheng JT, Ravicz ME, Hulli N, Harrington EJ, Hernandez-Montes MS, Furlong C, Merchant SN, Rosowski JJ (2009) Middle ear mechanics of cartilage tympanoplasty evaluated by laser holography and vibrometry. Otol Neurotol 30(8):1209–1214
Burkhardt A, Kirsten L, Bornitz M, Zahnert T, Koch E (2014) Investigation of the human tympanic membrane oscillation ex vivo by Doppler optical coherence tomography. J Biophotinics 7(6):434–441
Cheng JT, Aarnisalo AA, Harrington E, Hernadez-Montes MS, Furlong C, Merchant SN, Rosowski JJ (2010) Motion of the surface of the human tympanic membrane measured with stroboscopic holography. Hear Res 263(1–2):66–77
Cheng JT, Hamade M, Harring E, Furlong C, Merchant SN, Rosowski JJ (2013) Wave motion on the surface of the human tympanic membrane: holographic measurement and modeling analysis. J Acoust Soc Am 133(2):918–937
Dai C, Gan RZ (2008) Change of middle ear transfer function in otitis media with effusion model of guinea pig. Hear Res 243(1–2):78–86
Gan RZ, Dai C, Wood MW (2006) Laser interferometry measurements of middle ear fluid and pressure effects on sound transmission. J Acoust Soc Am 120(6):3799–3810
Guan X (2014) Middle ear biomechanics in chinchilla model of acute otitis media. Ph. D dissertation, University of Oklahoma
Guan X, Gan RZ (2011) Effect of middle ear fluid on sound transmission and auditory brainstem response in guinea pigs. Hear Res 277(1–2):96–106
Guan X, Gan RZ (2013) Mechanisms of tympanic membrane and incus mobility loss in acute otitis media model of guinea pig. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 14(3):295–307
Guan X, Chen Y, Gan RZ (2014) Factors affecting loss of tympanic membrane mobility in acute otitis media model of chinchilla. Hear Res 309:136–146
Guinan JJ Jr, Peake WT (1967) Middle-ear characteristics of anesthetized cats. J Acoust Soc Am 41(5):1237–1261
Huber AM, Schwab C, Linder T, Stoeckli SJ, Ferrazzini M, Dillier N, Fisch U (2001) Evaluation of eardrum laser Doppler interferometry as a diagnostic tool. Laryngoscope 111(3):501–507
Jakob A, Bornitz M, Kuhlisch E, Zahnert T (2009) New aspects in the clinical diagnosis of otosclerosis using laser Doppler vibrometry. Otol Neurotol 30(8):1049–1057
Keefe DH, Simmons JL (2003) Energy transmittance predicts conductive hearing loss in older children and adults. J Acoust Soc Am 114(6):3217–3238
Khanna SM, Tonndorf J (1972) Tympanic membrane vibrations in cats studied by time-averaged holography. J Acoust Soc Am 51(6):1904–1920
Lee CY, Rosowski JJ (2001) Effects of middle ear static pressure on par tensa and pars flaccida of gerbil ears. Hear Res 153(1–2):146–163
Liu Y, Sanford CA, Ellison JC, Fitzpatrick DF, Gorga MP, Keefe DH (2008) Wideband absorbance tympanometry using pressure sweeps: system development and results on adults with normal hearing. J Acoust Soc Am 124(6):3708–3719
Minovi A, Dazert S (2014) Diseases of the middle ear in childhood. GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13(11):1–29
Morton DJ, Hempel RJ, Seale TW, Whitby PW, Stull TL (2012) A functional tonB gene is required for both virulence and competitive fitness in a chinchilla model of Haemophilus influenzae otitis media. BMC Res Notes 5:327
Nakajima HH, Pisano DV, Roosli C, Hamade MA, Merchant GR, Mahfoud L, Halpin CF, Rosowski JJ, Merchant SN (2012) Comparison of ear-canal reflectance and umbo velocity in patients with conductive hearing loss: a preliminary study. Ear Hear 33(1):35–43
Ravicz ME, Rosowski JJ (2013) Middle-ear velocity transfer function, cochlear input impedance and middle-ear efficiency in chinchilla. J Acoust Soc Am 134(4):2852–2865
Ravicz ME, Rosowski JJ, Merchant SN (2004) Mechanisms of hearing loss resulting from middle-ear fluid. Hear Res 195(1–2):103–130
Rosowski JJ, Cheng JT, Ravicz ME, Hulli M, Hernandez-Montes MS, Harrington EJ, Furlong C (2009) Computer-assisted time-averaged holograms of the motion of the surface of the mammalian tympanic membrane with sound stimuli of 0.4–25 kHz. Hear Res 253(1–2):83–96
Rosowski JJ, Cheng JT, Merchant SN, Harrington E, Furlong C (2011) New data on the motion of the normal and reconstructed tympanic membrane. Otol Neurotol 32(9):1559–1567
Rosowski JJ, Dobrev I, Khaleghi M, LU W, Cheng JT, Harrington E, Furlong C (2013) Measurements of three-dimensional shape and sound-induced motion of the chinchilla tympanic membrane. Hear Res 301:44–52
Rovers MM, Schilder AG, Zielhuis GA, Rosenfeld RM (2004) Otitis media. Lancet 363:465–473
Ruggero MA, Rich NC, Robles L, Shivapuja BG (1990) Middle-ear response in the chinchilla and its relationship to mechanics at the base of the cochlea. J Acoust Soc Am 87(4):1612–1629
Stasche N, Foth HJ, Hörmann K, Baker A, Huthoff C (1994) Middle ear transmission disorders-tympanic membrane vibration analysis by laser-Doppler vibrometey. Acta Otolaryngol 114(1):59–63
Thornton JL, Chevallier KM, Koka K, Gabbard SA, Tollin D (2013) Conductive hearing loss induced by experimental middle-ear effusion in a chinchilla model reveals impaired tympanic membrane-coupled ossicular chain movement. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 14:451–464
Tonndorf J, Khanna SM (1972) Tympanic-membrane vibrations in human cadaver ears studied by time-averaged holography. J Acoust Soc Am 52(4):1221–1233
Ulku CH, Cheng JT, Guignard J, Rosowski JJ (2014) Comparisons of the mechanics of partial and total ossicular replacement prostheses with cartilage in a cadaveric temporal bone preparation. Acta Otolaryngol 134(8):776–784
Vrettakos PA, Dear SP, Saunders JC (1988) Middle ear structure in the chinchilla: a quantitative study. Am J Otolaryngol 9(2):58–67
Wada H, Ando M, Takeuchi M, Sugawara H, Koike T, Kobayashi T, Hozawa K, Gemma T, Nara M (2002) Vibration measurement of the tympanic membrane of guinea pig temporal bones using time-averaged speckle pattern interferometry. J Acoust Soc Am 111(5):2189–2199
Wang X, Gan RZ (2016) 3D finite element model of the chinchilla ear for characterizing middle ear functions. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 15(5):1263–1277
Wang X, Nakmali D, Gan RZ (2015) Complex modulus of round window membrane over auditory frequencies in normal and otitis media chinchilla ears. Int J Exp Comput Biomech 3(1):27–44
Wang X, Guan X, Pineda M, Gan RZ (2016) Motion of tympanic membrane in guinea pig otitis media model measured by scanning laser Doppler vibrometry. Hear Res 339:184–194
Wever EG, Lawrence M (1954) Physiological acoustics. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Yokell Z, Wang X, Gan RZ (2015) Dynamic properties of tympanic membrane in a chinchilla otitis media model measured with acoustic loading. ASME. J Biomech Eng 137:0810061–0810069
Zhang X, Guan X, Nakmali D, Palan V, Pineda M, Gan RZ (2014) Experimental and modeling study of human tympanic membrane motion in the presence of middle ear liquid. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 15(6):867–881
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Xiangming Zhang and Dr. Xiying Guan, former graduate students in the Biomedical Engineering Lab at the University of Oklahoma, and Mario Pineda, at Polytec Inc., for participating in SLDV measurement. This work was supported by NIH R01DC011585.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Gan, R.Z. Surface Motion of Tympanic Membrane in a Chinchilla Model of Acute Otitis Media. JARO 19, 619–635 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-018-00683-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-018-00683-2