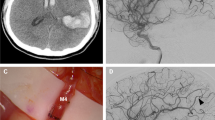
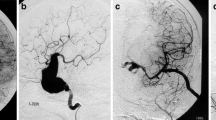
Abstract
Re-anastomosis end-to-end bypass is a straightforward subtype of intracranial-intracranial reconstruction technique that has been utilized to treat complex aneurysms and skull base tumors. This simple technique involves connecting the cut ends of an afferent and efferent artery under added tension after excising the lesion. The current study aims to provide a detailed description of the technical pitfalls, ideal anatomical sites and indications, and clinical outcomes for intracranial complex disorders. A literature search was performed using the terms “intracranial-intracranial bypass,” “re-anastomosis bypass,” “reconstructive bypass,” “end-to-end bypass,” and “end-to-end anastomosis” to identify pertinent articles. Articles involving end-to-end re-anastomosis combined with other bypass methods were excluded. Computer-tablet-drawn illustrations of this technique are provided to enhance comprehension. Eighty-six patients who met our search and inclusion criteria were identified between 1978 and the present. However, comprehensive descriptions of medical records and neuroimaging were available in only 41 cases (40 complex aneurysms and a skull base tumor). Of 40 reported cases of complex cerebral aneurysms treated by this technique, the overall rate of full recovery without complication is 87.5% (35/40). Meanwhile, all aneurysms were completely eliminated from the circulation, with 92.5% of bypasses being patent. End-to-end re-anastomosis remains a simple modality in the microsurgical bypass armamentarium. Safe and effective surgical outcomes can be achieved in select cases that rarely involve perforators or branches.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abla AA, Lawton MT (2014) Anterior cerebral artery bypass for complex aneurysms: an experience with intracranial-intracranial reconstruction and review of bypass options. J Neurosurg 120:1364–1377. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.3.jns132219
Abla AA, McDougall CM, Breshears JD, Lawton MT (2016) Intracranial-to-intracranial bypass for posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms: options, technical challenges, and results in 35 patients. J Neurosurg 124:1275–1286. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.5.jns15368
Al-Khayat H, Kopitnik TA (2004) Primary end-to-end anastomosis of anterior cerebral artery dissecting aneurysm: technical case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 55:E449–E454. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000130039.76769.60
Anson JA, Lawton MT, Spetzler RF (1996) Characteristics and surgical treatment of dolichoectatic and fusiform aneurysms. J Neurosurg 84:185–193. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1996.84.2.0185
Benes L, Kappus C, Sure U, Bertalanffy H (2006) Treatment of a partially thrombosed giant aneurysm of the vertebral artery by aneurysm trapping and direct vertebral artery-posterior inferior cerebellar artery end-to-end anastomosis: technical case report. Oper Neurosurg 59:ONSE166–ONSE167. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000220034.08995.37
Bonda DJ, Labib M, Katz JM, Ortiz RA, Chalif D, Setton A, Langer DJ, Dehdashti AR (2017) Intracranial bypass of posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms: indications, technical aspects, and clinical outcomes. Oper Neurosurg 13:586–595. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opx064
Ceylan S, Karakuş A, Duru S, Baykal S, İlbay K (1998) Reconstruction of the middle cerebral artery after excision of a giant fusiform aneurysm. Neurosurg Rev 21:189–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02389331
Chang HS, Fukushima T, Miyazaki S, Tamagawa T (1986) Fusiform posterior cerebral artery aneurysm treated with excision and end-to-end anastomosis. J Neurosurg 64:501–504. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1986.64.3.0501
Chang HS, Fukushima T, Takakura K, Shimizu T (1986) Aneurysms of the posterior cerebral artery: report of ten cases. Neurosurgery 19:1006–1011. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198612000-00017
Davies JM, Lawton MT (2014) Advances in open microsurgery for cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 74:S7–S16. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000193
Dolenc V (1978) Treatment of fusiform aneurysms of the peripheral cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg 49:272–277. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1978.49.2.0272
Dolenc V (1982) End-to-end suture of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery after the excision of a large aneurysm: case report. Neurosurgery 11:690–693. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198211000-00014
Evans JJ, Sekhar LN, Rak R, Stimac D (2004) Bypass grafting and revascularization in the management of posterior circulation aneurysms. Neurosurgery 55:1036–1049. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000140822.64362.c6
Hage ZA, Charbel FT (2015) Clipping of a ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysm with right A1–A2 sectioning and reanastomosis. Neurosurg Focus 39:V10. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.7.focusvid.14602
Hamada J-I, Nagahiro S, Mimata C, Kaku T, Ushio Y (1996) Reconstruction of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery in the treatment of giant aneurysms. J Neurosurg 85:496–499. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1996.85.3.0496
Hoh BL, Putman CM, Budzik RF, Carter BS, Ogilvy CS (2001) Combined surgical and endovascular techniques of flow alteration to treat fusiform and complex wide-necked intracranial aneurysms that are unsuitable for clipping or coil embolization. J Neurosurg 95:24–35. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.95.1.0024
Ikeda A, Yamaguchi T, Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto I, Sato O (1991) Excision and end-to-end anastomosis of a fusiform aneurysm of the distal posterior inferior cerebellar artery associated with ischemia. Neurol Med Chir 31:351–355. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.31.351
Kalani MYS, Ramey W, Albuquerque FC, McDougall CG, Nakaji P, Zabramski JM, Spetzler RF (2014) Revascularization and aneurysm surgery. Neurosurgery 74:482–497. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000312
Kawashima M, Rhoton AL, Tanriover N, Ulm AJ, Yasuda A, Fujii K (2005) Microsurgical anatomy of cerebral revascularization. Part II: posterior circulation. J Neurosurg 102:132–147. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.1.0132
Laborde G, Gilsbach J, Harders A (1988) The microvascular Doppler—an intraoperative tool for the treatment of large and giant aneurysms. In: Proceedings of the 8th European congress of neurosurgery, Barcelona. Springer, Vienna, pp 75–80
Lawton MT (2018) Seven bypasses: tenets and techniques for revascularization. Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, Germany
Lawton MT, Spetzler RF (1999) Surgical strategies for giant intracranial aneurysms. In: Langmoen IA, Lundar T, Aaslid R, Reulen HJ (eds) Neurosurgical management of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Springer, Vienna, pp 141–156
Lim SM, Choi IS, Hum BA, David CA (2010) Dissecting aneurysms of the distal segment of the posterior inferior cerebellar arteries: clinical presentation and management. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1118–1122. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.a2014
Madsen JR, Heros RC (1988) Giant peripheral aneurysm of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery treated with excision and end-to-end anastomosis. Surg Neurol 30:140–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-3019(88)90100-0
Mascitelli JR, Ben-Haim S, Paramasivam S, Zarzour HK, Rothrock RJ, Bederson JB (2015) Association of a distal intradural-extracranial posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm with chiari type I malformation. Neurosurgery 77:E660–E665. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000870
Matsushima K, Kawashima M, Suzuyama K, Takase Y, Takao T, Matsushima T (2011) Thrombosed giant aneurysm of the distal anterior cerebral artery treated with aneurysm resection and proximal pericallosal artery-callosomarginal artery end-to-end anastomosis: case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol Int 2:135. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.85608
Meybodi AT, Deng H, Benet A, Lawton MT (2018) Intracranial-intracranial bypass. Contemp Neurosurg 40:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.cne.0000530871.39106.b4
Meybodi AT, Huang W, Benet A, Kola O, Lawton MT (2017) Bypass surgery for complex middle cerebral artery aneurysms: an algorithmic approach to revascularization. J Neurosurg 127:463–479. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.7.jns16772
Miyagi J, Shigemori M, Sugita Y, Nishio N, Harada K, Kuramoto S (1991) Giant aneurysm of the middle cerebral artery presenting with complex partial seizure. Neurol Med Chir 31:953–956. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.31.953
Nakajima H, Kamiyama H, Nakamura T, Takizawa K, Ohata K (2013) Direct surgical treatment of giant intracranial aneurysms on the anterior communicating artery or anterior cerebral artery. Neurol Med Chir 53:153–156. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.53.153
Newell DW, Schuster JM, Avellino AM (2002) Intracranial-to-intracranial vascular anastomosis created using a microanastomotic device for the treatment of distal middle cerebral artery aneurysms. J Neurosurg 97:486–491. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.97.2.0486
Nossek E, Langer DJ (2018) Internal maxillary artery to middle cerebral artery cranial bypass: the new “work horse” for cerebral flow replacement. World Neurosurg 115:44–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.03.214
Nussbaum ES, Mendez A, Camarata P, Sebring L (2003) Surgical management of fusiform aneurysms of the peripheral posteroinferior cerebellar artery. Neurosurgery 53:831–835. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000084162.29616.43
Ogasawara K, Kubo Y, Tomitsuka N, Sasoh M, Otawara Y, Arai H, Ogawa A (2006) Treatment of vertebral artery aneurysms with transposition of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery to the vertebral artery combined with parent artery occlusion. J Neurosurg 105:781–784. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.105.5.781
Päsler D, Baldauf J, Runge U, Schroeder HWS (2011) Intrameatal thrombosed anterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm mimicking a vestibular schwannoma. J Neurosurg 114:1057–1060. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.9.jns10491
Pavesi G, Dimitriadis S, Baroni S, Vallone S, Valzania F, Costella GB, Feletti A (2015) Intraoperative functional and perfusion monitoring during surgery for giant serpentine middle cerebral artery aneurysms. World Neurosurg 84:592.e515–592.e521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.03.014
Quiñones-Hinojosa A, Lawton MT (2005) In situ bypass in the management of complex intracranial aneurysms: technique application in 13 patients. Oper Neurosurg 57:140–145. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000163599.78896.f4
Rahme R, Alimi M, Sudhakar TD, Langer DJ (2018) Management of complex intracranial aneurysms: principles of microsurgical deconstruction and cerebrovascular bypass. Intracranial Aneurysms. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811740-8.00015-0
Rodríguez-Hernández A, Lawton MT (2014) End-to-end reanastomosis technique for fusiform aneurysms. Oper Neurosurg 10:157; discussion 157–158–158. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000124
Rodríguez-Hernández A, Zador Z, Rodríguez-Mena R, Lawton MT (2013) Distal aneurysms of intracranial arteries: application of numerical nomenclature, predilection for cerebellar arteries, and results of surgical management. World Neurosurg 80:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2012.09.010
Samii M, Turel KE (1985) Possibility of the excision of aneurysms in the vertebrobasilar system followed by end-to-end anastomosis for the maintenance of circulation. Neurol Res 7:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.1985.11739699
Sanai N, Zador Z, Lawton MT (2009) Bypass surgery for complex brain aneurysms. Neurosurgery 65:670–683; discussion 683. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000348557.11968.f1
Schönmayr R, Zierski J (1983) Middle cerebral artery revascularisation. Neurosurg Rev 6:25–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01742982
Sekhar LN, Kalavakonda C (2002) Cerebral revascularization for aneurysms and tumors. Neurosurgery 50:321–331. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-200202000-00014
Seo B-R, Kim T-S, Joo S-P, Lee J-M, Jang J-W, Lee JK, Kim JH, Kim SH (2009) Surgical strategies using cerebral revascularization in complex middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 111:670–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2009.06.002
Silva MA, See AP, Aziz-Sultan MA, Patel NJ (2017) Surgical treatment of a double origin posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm and insights from embryology: case report and literature review. Oper Neurosurg 13:E8–E12. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opx002
Singh H, da Silva HB, Straus DC, Zeinalizadeh M, Sekhar LN (2017) Microsurgical management of large, fusiform, partially thrombosed middle cerebral artery (M2) aneurysm with end-to-end M2 anastomosis: 3-dimensional operative video. Oper Neurosurg 13:535. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opx008
Smith RR, Parent AD (1982) End-to-end anastomosis of the anterior cerebral artery after excision of a giant aneurysm. J Neurosurg 56:577–580. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1982.56.4.0577
Touho H (1999) End-to-end anastomosis of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery before excision of a meningioma involving the lower clivus and the foramen magnum. Surg Neurol 52:185–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-3019(99)00067-1
Wang L, Cai L, Lu S, Qian H, Lawton MT, Shi X (2018) The history and evolution of internal maxillary artery bypass. World Neurosurg 113:320–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.02.158
Wang L, Cai L, Qian H, Lawton MT, Shi X (2018) The in situ side-to-side bypass technique: a comprehensive review of the technical characteristics, current anastomosis approaches, and surgical experience. World Neurosurg 115:357–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.173
Wang L, Lu S, Qian H, Shi X (2017) Internal maxillary artery bypass with radial artery graft treatment of giant intracranial aneurysms. World Neurosurg 105:568–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.06.014
Wang L, Lu S, Qian H, Shi X (2017) Internal maxillary bypass for complex pediatric aneurysms. World Neurosurg 103:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.04.055
Wang L, Shi X, Liu F, Qian H (2016) Bypass surgery to treat symptomatic fusiform dilation of the internal carotid artery following craniopharyngioma resection: report of 2 cases. Neurosurg Focus 41:E17. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.focus16252
Wang L, Shi X, Qian H (2017) Flow reversal bypass surgery: a treatment option for giant serpentine and dolichoectatic aneurysms—internal maxillary artery bypass with an interposed radial artery graft followed by parent artery occlusion. Neurosurg Rev 40:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0778-8
Xu F, Xu B, Huang L, Xiong J, Gu Y, Lawton MT (2018) Surgical treatment of large or giant fusiform middle cerebral artery aneurysms: a case series. World Neurosurg 115:e252–e262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.031
Yokoh A, Ausman JI, Dujovny M, Diaz FG, Berman SK, Sanders J, Mirchandani HG (1986) Anterior cerebral artery reconstruction. Neurosurgery 19:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-198607000-00004
Funding
We received financial support from the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 7161005 to X.S.) and the Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Beijing (Grant No. Z161100000516019 to X.S.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Cai, L., Qian, H. et al. The re-anastomosis end-to-end bypass technique: a comprehensive review of the technical characteristics and surgical experience. Neurosurg Rev 42, 619–629 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-1036-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-1036-z