Abstract
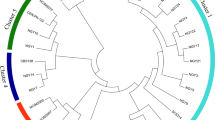
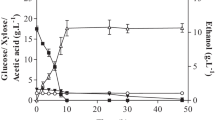
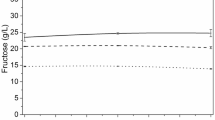
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is commonly employed in industrial ethanol production, regardless of the capability of Kluyveromyces marxianus strains to produce ethanol at similar or higher levels and on inhibitory conditions. Therefore, in this work strains of S. cerevisiae (ethanol RED and AR5) and K. marxianus (SLP1 and OFF1) were compared for ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse (SCB) and wheat straw (WS) hydrolysates. As it is known, during the lignocellulosic hydrolysis not only free sugars were obtained (SCB, g L−1: glucose 7.64, xylose 8.38, arabinose 2.43; and WS, g L−1: glucose 6.07, xylose 6.36, arabinose 2.09) but also growth inhibitors of yeast such as hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural that could modify the fermentation capability. The volumetric ethanol productivity (Q p) was evaluated, and it was observed that the K. marxianus SLP1 was the most efficient for ethanol production reaching a Q p of 0.292 and 0.250 g L−1 h−1 on SCB and WS hydrolysates, respectively. In contrast, S. cerevisiae AR5 and ethanol RED exhibited a reduced Q p on SCB, but similar values of Q p to K. marxianus OFF1 on WS. The results obtained show that it is possible to select K. marxianus yeast strains for ethanol production using SCB and WS hydrolysates obtaining higher Q p than S. cerevisiae yeast strains. Considering the efficiency of ethanol production and the tolerance to inhibitors, K. marxianus strain SLP1 possesses a great potential as an industrial yeast for lignocellulosic ethanol production.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinosho H, Rydzak T, Borole A, Ragauskas A, Close D (2015) Toxicological challenges to microbial bioethanol production and strategies for improved tolerance. Ecotoxicology 24(10):2156–2174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1543-4
Alcázar M, Kind T, Gschaedler A, Silveria M, Arrizon J, Oliver F, Vallejo A, Higuera I, Lugo E (2017) Effect of steroidal saponins from Agave on the polysaccharide cell wall composition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kluyveromyces marxianus. Food Sci Technol 77:430–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.11.048
Amaya-Delgado L, Herrera-López EJ, Arrizon J, Arellano-Plaza M, Gschaedler A (2013) Performance evaluation of Pichia kluyveri, Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae at industrial tequila fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:875–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1242-8
Arellano-Plaza M, Gschaedler-Mathis A, Noriega-Cisneros R, Clemente-Guerrero M, Manzo-Ávalos S, González-Hernández JC, Saavedra-Molina A (2013) Respiratory capacity of the Kluyveromyces marxianus yeast isolated from the mezcal process during oxidative stress. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(7):1279–1287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1291-7
Arrizon J, Fiore C, Acosta G, Romano P, Gschaedler A (2006) Fermentation behaviour and volatile compound production by agave and grape must yeasts in high sugar Agave tequilana and grape must fermentations. Anton Leeuw Int J G 89:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-005-9022-1
Awad OI, Mamat R, Ibrahim TK, Hagos FY, Noor MM, Yusri IM, Leman AM (2017) Calorific value enhancement of fusel oil by moisture removal and its effect on the performance and combustion of a spark ignition engine. Energy Convers Manag 137:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.01.009
Barchyn D, Cenkowski S (2014) Process analysis of superheated steam pre-treatment of wheat straw and its relative effect on ethanol selling price. J Biofuel Res 4:123–128. https://doi.org/10.18331/BRJ2015.1.4.4
Batalha L, Han Q, Jameel H, Chang H, Colodette JL, Borges Gomes FJ (2015) Production of fermentable sugars from sugarcane bagasse by enzymatic hydrolysis after autohydrolysis and mechanical refining. Bioresour Technol 180:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.12.060
Bondesson PM, Galbe M (2016) Process design of SSCF for ethanol production from steam-pretreated, acetic acid impregnated wheat straw. Biotechnol Biofuel 9:222. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0635-6
Chen H, Fu X (2016) Industrial technologies for bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 57:468–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.069
Flores JA, Gschaedler A, Amaya-Delgado L, Herrera-López EJ, Arellano M, Arrizon J (2013) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of Agave tequilana fructans by Kluyveromyces marxianus yeasts for bioethanol and tequila production. Bioresour Technol 146:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.078
Fonseca GG, Heinzle E, Wittmann C, Gombert AK (2008) The yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus and its biotechnological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:339–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1458-6
Foster CE, Martin TM, Pauly M (2010a) Comprehensive compositional analysis of plant cell walls (Lignocellulosic biomass) Part I: lignin protocol. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/1745
Foster CE, Martin TM, Pauly M (2010b) Comprehensive compositional analysis of plant cell walls (Lignocellulosic biomass) Part II: carbohydrates. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/1837
Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2012) Development of yeast cell factories for consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulose to bioethanol through cell surface engineering. Biotechnol Adv 30(6):1207–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.10.011
Heer D, Sauer U (2008) Identification of furfural as a key toxin in lignocellulosic hydrolysates and evolution of a tolerant yeast strain. Microbiol Biotechnol 1(6):497–506. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7915.2008.00050.x
Jönsson LJ, Alriksson B, Nilvebrant N (2013) Bioconversion of lignocellulose: inhibitors and detoxification. Biotechnol Biofuels. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-6-16
Karagöz P, Özkan M (2014) Ethanol production from wheat straw by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Scheffersomyces stipitis co-culture in batch and continuous system. Bioresour Technol 158:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.022
Karp SG, Woiciechowski AL, Soccol VT, Soccol CR (2013) Pretreatment strategies for delignification of sugarcane bagasse: a review. Braz Arch Biol Technol 56(4):679–689. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132013000400019
Kim J, Block DE, Mills DA (2010) Simultaneous consumption of pentose and hexose sugars: an optimal microbial phenotype for efficient fermentation of lignocellulosic biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:1077–1085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2839-1
Klinke HB, Thomsen AB, Ahring BK (2004) Inhibition of ethanol-producing yeast and bacteria by degradation products produced during pre-treatment of biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:10–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1642-2
Lopez A, Sánchez A, De León A (2017) Simultaneous production of bioethanol and biohydrogen by Escherichia coli WDHL using wheat straw hydrolysate as substrate. Fuel 188:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.022
López-Alvarez A, Díaz-Perez AL, Sosa-Aguirre C, Macías-Rodríguez L, Campos-García J (2012) Ethanol yield and volatile compound content in fermentation of agave must by Kluyveromyces marxianus UMPe-1 comparing with Saccharomyces cerevisiae baker’s yeast used in tequila production. J Biosci Bioeng 113(5):614–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.12.015
Monschein M, Nidetzky B (2016) Effect of pretreatment severity in continuous steam explosion on enzymatic conversion of wheat straw: evidence from kinetic analysis of hydrolysis time courses. Bioresour Technol 200:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.020
Morrissey J, Etschmann M, Schrader J, Billerbeck G (2015) Cell factory applications of the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus for the biotechnological production of natural flavour and fragrance molecules. Yeast 32:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3054
Mussatto SI, Roberto IC (2004) Alternatives for detoxification of diluted-acid lignocellulosic hydrolyzates for use in fermentative processes: a review. Biores Technol 93(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2003.10.005
Nguyen TT, Iwaki A, Izawa S (2014) Vanillin causes the activation of Yap1 and mitochondrial fragmentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng 117(1):33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.06.008
Nielsen F, Zacchi G, Galbe M, Wallberg O (2016) Prefermentation improves ethanol yield in separate hydrolysis and cofermentation of steam-pretreated wheat straw. Sustein Chem Processes. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40508-016-0054-9
Oshoma CE, Greetham D, Louis EJ, Smart KA, Phister G, Powell C, Du C (2015) Screening of non-Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains for tolerance to formic acid in bioethanol fermentation. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135626
Pereira L, Comelli A, Paula A, Marcele L, Henrique M, Silveira L (2015) Enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-exploded sugarcane bagasse using high total solids and low enzyme loadings. Bioresour Technol 175:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.087
Rajan K, Carrier DJ (2014) Effect of dilute acid pretreatment conditions and washing on the production of inhibitors and on recovery of sugars during wheat straw enzymatic hydrolysis. Biomass Bioenergy 62:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.01.013
Ramadoss G, Muthukumar K (2016) Mechanistic study on ultrasound assisted pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse using metal salt with hydrogen peroxide for bioethanol production. Ultrason Sonochem 28:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2015.07.006
Rocha GJM, Martin C, Soares IB, Souto-Maior AM, Baudel HM, Moraes CA (2011) Dilute mixed-acid pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse for the ethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 35:663–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/jbiombioe.2010.10.018
Scott F, Quintero J, Morales M, Conejeros R, Cardona C, Aroca G (2013) Process design and sustainability in the production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials. Electron J Biotechnol 16(3):13
Toquero C, Bolado S (2014) Effect of four pretreatments on enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation of wheat straw. Influence of inhibitors and washing. Bioresour Technol 157:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.090
Valdez I, Acevedo J, Hernández C (2010) Distribution and potential of bioenergy resources from agricultural activities in Mexico. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:2147–2153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2010.03.034
Vallejos ME, Felissia FE, Kruyeniski J, Area MC (2015) Kinetic study of the extraction of hemicellulosic carbohydrates from sugarcane bagasse by hot water treatment. Ind Crop Prod 67:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.12.058
Velmurugan R, Muthukumar K (2011) Utilization of sugarcane bagasse for bioethanol production: Sono-assisted acid hydrolysis approach. Bioresour Technol 102(14):7119–7123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.045
Verdugo-Valdez A, Segura-García L, Kirchmayr M, Ramírez-Rodríguez P, González-Esquinca A, Gschaedler Mathis A (2001) Yeast communities associated with artisanal mezcal fermentations from Agave salmiana. Anton Leeuw Int J G 100(4):497–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9605-y
Wilkinson S, Greetham D, Tucker GA (2016) Evaluation of different lignocellulosic biomass pretreatments by phenotypic microarray-based metabolic analysis of fermenting yeast. Biofuel Res J 3(1):357–365. https://doi.org/10.18331/BRJ2016.3.1.5
Zhang Y, Wang C, Wang L, Yang R, Hou P (2017) Direct bioethanol production from wheat straw using xylose/glucose co-fermentation by co-culture of two recombinant yeasts. Jo Ind Microbiol Biot 44(3):453–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1893-9
Acknowledgements
The author deeply appreciated the CONACYT-SENER for the financial support (Fondo de Sustentabilidad Energética Project 248090) in this study. Sandoval-Nuñez Dania received a grant from CONACYT, México. The authors gratefully thank to Brian Walsh (Biotechnology Commercialization Specialist CIATEJ/Peace Corps) for the english revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandoval-Nuñez, D., Arellano-Plaza, M., Gschaedler, A. et al. A comparative study of lignocellulosic ethanol productivities by Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Clean Techn Environ Policy 20, 1491–1499 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1470-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1470-6