Abstract
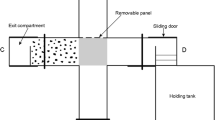
Much research has investigated spatial cognition in mammals and birds. Evidence suggests that the hippocampus plays a critical role in this; however, reptiles do not possess a hippocampus. It has been proposed that the reptilian medial cortex plays a similar role, yet little behavioral research has directly investigated this. Consequently, this study examined the role of extramaze cues in spatial navigation by the red-footed tortoise (Geochelone carbonaria) using an eight-arm radial maze. In Experiment 1 the maze was surrounded by a black curtain on which geometrical shapes were attached. After the tortoise reached above-chance performance we introduced test sessions in which the cues were removed. Performance was unaffected by cue removal. The tortoise appeared to have developed a “turn-by-one-arm” strategy. In a second experiment the curtain was removed and the tortoise was allowed access to a rich-cue environment. The use of the turn-by-one-arm strategy was significantly reduced and the tortoise appeared to be using the extramaze cues to navigate around the apparatus. This type of response-based strategy, and the specific contexts in which it was used, has not been observed in mammals and birds, suggesting that the mechanisms served by the reptilian medial cortex do not parallel exactly those of the hippocampus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balda R, Kamil A (2006) The ecology and life history of seed caching corvids. In: Brown MF, Cook RG (eds) Animal spatial cognition: comparative, neural, and computational approaches. Available on-line at: www.pigeon.psy.tufts.edu/asc/balda/
Broglio C, Gomez A, Duran E, Ocana F, Jimenez-Moya Rodriguez F, Salas C (2005) Hallmarks of a common forebrain vertebrate plan: specialized pallial areas for spatial, temporal and emotional memory in actinopterygian fish. Brain Res Bull 66:277–281
Burghardt GM (1977) Learning processes in reptiles. In: Gans C, Tinkle DW (eds) Biology of the Reptilia. Academic, London, pp 555–681
Cheng K (1986) A purely geometric module in the rat’s spatial representation. Cognition 23:149–178
Cheng K (2008) Whither geometry? Troubles of the geometric module. Trends Cogn Sci 12:355–361
Clarke DA (1980) Age- and sex-dependent foraging strategies of a small mammalian omnivore. J Anim Ecol 49:549–563
Day LB, Crews D, Wilczynski W (1999) Spatial and reversal learning in congeneric lizards with different foraging strategies. Anim Behav 57:393–407
Day LB, Crews D, Wilczynski W (2001) Effects of medial and dorsal cortex lessons on spatial memory in lizards. Behav Brain Res 118:27–42
Einon D (1980) Spatial memory and response strategies in rats: age, sex and rearing differences in performance. Q J Exp Psychol 32:473–489
Hart DR (1983) Dietary and habitat shift with size of red-eared turtle (Pseudemys scripta). Herpetologica 39:285–290
Holtzman DA, Harris TW, Aranguren G, Bostocks E (1999) Spatial learning of an escape task by young corn snakes (Elaphe guttata guttata). Anim Behav 57:51–60
Hughes RN, Blight CM (1999) Algorithmic behaviour and spatial memory are used by intertidal fish species to solve the radial maze. Anim Behav 58:601–613
Kamil AC, Balda RP, Olson DJ (1994) Performance of four seed caching corvid species in the radial-arm maze analog. J Comp Psychol 108:385–393
López JC, Rodríguez F, Gómez Y, Vargas JP, Broglio C, Salas C (2000) Place and cue learning in turtles. Anim Learn Behav 28:360–372
López JC, Gómez Y, Rodríguez F, Broglio C, Vargas JP, Salas C (2001) Spatial learning in turtles. Anim Cogn 4:49–59
López JC, Vargas JP, Gómez Y, Salas C (2003) Spatial and non-spatial learning in turtles: the role of the medial cortex. Behav Brain Res 143:109–120
MacPhail EM (1982) Brain and intelligence in vertebrates. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Mazmanian DS, Roberts WA (1983) Spatial memory in rats under restricted viewing conditions. Learn Motiv 14:123–139
O’Keefe J, Nadel L (1978) The hippocampus as a cognitive map. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Olton DS (1978) Characteristics of spatial memory. In: Hulse SH, Fowler H, Honig WK (eds) Cognitive processes in animal behavior. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, pp 341–373
Olton DS, Samuelson RJ (1976) Remembrance of places passed: spatial memory in rats. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 2:97–116
Quaranta JV (1952) An experimental study of color vision of the giant tortoise. Zoologica 37:295–314
Roberts WA, Dale RH (1981) Remembrance of places lasts. Proactive inhibition and patterns of choice in rat spatial memory. Learn Motiv 12:261–281
Roitblat HL, Tham W, Golub L (1982) Performance of Betta splendens in a radial arm maze. Anim Learn Behav 10:108–114
Strong JN (2005) Seed dispersal and the ecological implications of hunting Geochelone carbonaria and G. denticulate in Northwestern Brazil. Masters thesis, College of Environmental Science and Forestry, State University of New York, New York
Strong JN, Fragoso JMV (2006) Seed dispersal by Geochelone carbonaria and Geochelone denticulate in Northwestern Brazil. Biotropica 38:683–686
Tinklepaugh OL (1932) Maze learning of a turtle. J Comp Psychol 13:201–206
Wilkinson A, Chan H, Hall G (2007) Spatial learning and memory in the tortoise (Geochelone carbonaria). J Comp Psychol 121:412–418
Yoerg SI, Kamil AC (1982) Response strategies in the radial arm maze: running around in circles. Anim Learn Behav 10:530–534
Zoladek L, Roberts WA (1978) The sensory basis of spatial memory in the rat. Anim Learn Behav 6:77–81
Acknowledgment
The participation of Sacha Coward was made possible by a bursary from the UK Experimental Psychology Society. The authors would like to thank Paul McLaughlin and Simon Fletcher for making the maze. We are also indebted to the Behavioural Neuroscience Research Group at the University of York and the Biology of Cognition Research Group at the University of Vienna for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkinson, A., Coward, S. & Hall, G. Visual and response-based navigation in the tortoise (Geochelone carbonaria). Anim Cogn 12, 779–787 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-009-0237-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-009-0237-9