Abstract
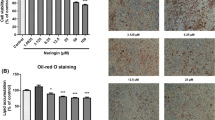
This study aims to investigate anti-adipogenic effects of long-chain bases from Cucumaria frondosa (Cf-LCBs) in vitro. Results showed that Cf-LCBs inhibited adipocyte differentiation and the expressions of CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins (C/EBPs) and peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor γ (PPARγ). Cf-LCBs increased β-catenin mRNA and nuclear translocation and increased its target genes, cyclin D1 and c-myc. Cf-LCBs enhanced fizzled and lipoprotein-receptor-related protein5/6 (LRP5/6) expressions, whereas wingless-type MMTV integration site10b (WNT10b) and glycogen syntheses kinase 3β (GSK3β) remained unchanged. Cf-LCBs also reduced adipogenesis and recovered WNT/β-catenin signaling in the cells suffering from 21H7, a β-catenin inhibitor. In addition, Cf-LCBs decreased triglyceride content and the expressions of lipogenesis genes. Cf-LCBs increased FFA levels and the expressions of lipidolytic factors. Cf-LCBs promoted the phosphorylation of adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase. These findings indicate that Cf-LCBs inhibit adipogenesis through activation of WNT/β-catenin signaling and regulate lipid metabolism via activation of AMPK pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 404: 635–643 (2000)
Kang SI, Shin HS, Kim SJ. Sinensetin enhances adipogenesis and lipolysis by increasing cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38: 552–558 (2015)
Kowalska K, Olejnik A, Rychlik J, Grajek W. Cranberries (Oxycoccus quadripetalus) inhibit adipogenesis and lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Food Chem. 148: 246–252 (2014)
Choi K, Ghaddar B, Moya C, Shi H, Sridharan GV, Lee K, Jayaraman A. Analysis of transcription factor network underlying 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. PLoS ONE 9: e100177 (2014)
Lim H, Yeo E, Song E, Chang YH, Han BK, Choi HJ, Hwang J. Bioconversion of Citrus unshiu pell extracts with cytolase suppresses adipogenic activity in 3T3-L1 cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 9: 599–605 (2015)
Vanella L, Sodhi K, Kim DH, Puri N, Maheshwari M, Hinds TD, Bellner L, Goldstein D, Peterson SJ, Shapiro JI, Abraham NG. Increased heme-oxygenase 1 expression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived adipocytes decreases differentiation and lipid accumulation via upregulation of the canonical Wnt signaling cascade. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 4, 28 (2013)
He H, Chen K, Wang F, Zhao L, Wan X, Wang L, Mo Z. miR-204-5p promotes the adipogenic differentiation of human adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells by modulating DVL3 expression and suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 35: 1587–1595 (2015)
Christodoulides C, Lagathu C, Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig A. Adipogenesis and WNT signaling. Trends Endocrin. Met. 20: 16–24 (2009)
Lee H, Bae S, Kim K, Kim W, Chung S, Yoon Y. Beta-Catenin mediates the antiadipogenic effect of baicalin. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 398: 741–746 (2010)
Kowalska K, Olejnik A, Rychlik J, Grajek W. Cranberries (Oxycoccus quadripetalus) inhibit lipid metabolism and modulate leptin and adiponectin secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Chem. 185: 383–388 (2015)
Kim SK, Kong CS. Anti-adipogenic effect of dioxinodehydroeckol via AMPK activation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 186: 24–29 (2010)
Samovski D, Sun J, Pietka T, Gross RW, Eckel RH, Su X, Stahi PD, Abumrad NA. Regulation of AMPK activation by CD36 links fatty acid uptake to β-oxidation. Diabetes 64: 353–359 (2015)
Shimajiri J, Shiota M, Hosokawa M, Miyashita K. Synergistic antioxidant activity of milk sphingomyeline and its sphingoid base with α-tocopherol on fish oil triacylglycerol. J. Agr. Food Chem. 61: 7969–7975 (2013)
Rozema E, Binder M, Bulusu M, Bochkov V, Krupitza G, Kopp B. Effects on inflammatory responses by the sphingoid base 4:8-sphingadienine. Int. J. Mol. Med. 30: 703–707 (2012)
Alden KP. Dhondt-Cordelier S, McDonald KL, Reape TJ, Ng CK, McCabe PF, Leaver CJ. Sphingolipid long chain base phosphates can regulate apoptoticlike programmed cell death in plants. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 410: 574–580 (2011)
Wei N, Pan J, Pop-Busui R, Othman A, Alecu I, Hornemann T, Eichler FS. Altered sphingoid base profiles in type 1 compared to type 2 diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 13, 161 (2014)
Sigruener A, Tarabin V, Paragh G, Liebisch G, Koehler T, Farwick M, Schmitz G. Effects of sphingoid bases on the sphingolipidome in early keratinocyte differentiation. Exp. Dermatol. 22: 677–679 (2013)
Bordbar S, Anwar F, Saari N. High-value components and bioactives from sea cucumbers for functional foods—A review. Mar. Drugs. 9: 1761–1805 (2011)
Hossain Z, Sugawara T, Hirata T. Sphingoid bases from sea cucumber induce apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells through p-AKT and DR5. Oncol. Rep. 29: 1201–1207 (2013)
Gao Z, Zhou X, Hu X, Xue C, Xu J, Wang Y. Effects of sea cucumber cerebroside and its long-chain base on lipid and glucose metabolism in obese mice. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 41: 60–64 (2012) (in Chinese)
Sugawara T, Zaima N, Yamamoto A, Sakai S, Noguchi R, Hirata T. Isolation of sphingoid bases of sea cucumber cerebrosides and their cytotoxicity against human colon cancer cells. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 70: 2906–2912 (2006)
Siersbaek R, Nielsen R, Mandrup S. PPARgamma in adipocyte differentiation and metabolism—novel insights from genome-wide studies. FEBS Lett. 584: 3242–3249 (2010)
Kim JH, Park KW, Lee EW, Jang WS, Seo J, Shin S, Hwang KA, Song J. Suppression of PPARγ through MKRN1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation prevents adipocyte differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 21: 594–603 (2014)
Yang J, Croniger CM, Lekstrom-Himes J, Zhang P, Fenyus M, Tenen DG, Darlington GJ, Hanson RW. Metabolic response of mice to a postnatal ablation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 38689–38699 (2005)
Yao Y, Zhu Y, Gao Y, Shi Z, Hu Y, Ren G. Suppressive effects of saponin-enriched extracts from quinoa on 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. Food Funct. 6: 3282–3290 (2015)
Madsen MS, Siersbaek R, Boergesen M, Nielsen R, Mandrup S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and C/EBPα synergistically activate key metabolic adipocyte genes by assisted loading. Mol. Cell. Biol. 34: 939–954 (2014)
Chen C, Peng Y, Peng Y, Peng J, Jiang S. m iR-135a-5p i nhibits 3 T3-L1 adipogenesis through activation of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 52: 311–320 (2014)
Lee H, Bae S, Yoon Y. Anti-adipogenic effects of 1:25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 are mediated by the maintenance of the wingless-type MMTV integration site/β-catenin pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 30: 1219–1224 (2012)
Park YK, Park B, Lee S, Choi K, Moon Y, Park H. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α-dependent hypoxic induction of Wnt10b expression in adipogenic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 288: 26311–26322 (2013)
Xu H, Wang F, Wang J, Xu J, Wang Y, Xue C. The WNT/â-catenin pathway is involved in the anti-adipogenic activity of cerebrosides from the sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa. Food Funct. 6: 2396–2404 (2015)
Cho YM, Kim DH, Kwak SN, Jeong SW, Kwon OJ. X-box binding protein 1 enhances adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells through the downregulation of Wnt10b expression. FEBS Lett. 587: 1644–1649 (2013)
Xu H, Wang J, Zhang X, Li Z, Wang Y, Xue C. Inhibitory effect of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioides on adipogenesis is dependent on Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 119: 85–91 (2015)
Ferrante MC, Amero P, Santoro A, Monnolo A, Simeoli R, Di Guida F, Mattace Raso G, Meli R. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB 101: PCB 153 and PCB 180) alter leptin signaling and lipid metabolism in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 279: 401–408 (2014)
Chang JJ, Hsu MJ, Huang HP, Chung DJ, Chang YC, Wang CJ. Mulberry anthocyanins inhibit oleic acid induced lipid accumulation by reduction of lipogenesis and promotion of hepatic lipid clearance. J. Agr. Food Chem. 61: 6069–6076 (2013)
Zheng G, Lin L, Zhong S, Zhang Q, Li D. Effects of puerarin on lipid accumulation and metabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice. PLoS ONE 10: e0122925 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Hu, S., Xu, H. et al. Long-chain bases from Cucumaria frondosa inhibit adipogenesis and regulate lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Sci Biotechnol 25, 1753–1760 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-016-0267-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-016-0267-4