Abstract
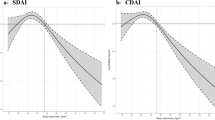
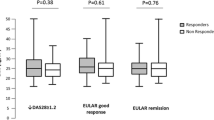
Some evidences suggest that obesity impairs the effectiveness of TNF inhibitors. We examined the impact of body mass index (BMI) on the clinical effectiveness of abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. This is a pooled analysis of 10 prospective cohorts of RA patients. All patients with available BMI were included in this study. The primary endpoint was drug retention of abatacept in the different BMI categories. Multivariable Cox regression was used to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) for drug discontinuation. A secondary endpoint was EULAR/LUNDEX response rates at 6/12 months. Of the 2015 RA patients initiating therapy with IV abatacept, 380 (18.9%) were classified as obese. Obese patients had more functional disability, and were less often RF positive. The median abatacept retention time was 1.91 years for obese RA patients compared to 2.12 years for non-obese patients (p = 0.15). The risk of abatacept discontinuation was not significantly different for overweight (HR 1.03 (95% CI 0.89–1.19)), or for obese (HR 1.08 (95% CI 0.89–1.30)) compared to normal-weight patients. Rheumatoid factor positivity reduced the risk of abatacept discontinuation (HR 0.83 (95% CI 0.72–0.95)), while previous biologic therapy was positively associated with drug interruption (HRs increasing from 1.68 to 2.16 with the line of treatments). Obese and non-obese patients attained similar rates of EULAR/LUNDEX clinical response at 6/12 months. Drug retention and clinical response rates to abatacept do not seem to be decreased by obesity in RA patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu B, Hiraki LT, Sparks JA, Malspeis S, Chen CY, Awosogba JA et al (2014) Being overweight or obese and risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis among women: a prospective cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1914–1922
Ajeganova S, Andersson ML, Hafström I, BARFOT Study Group (2013) Association of obesity with worse disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis as well as with comorbidities: a long-term followup from disease onset. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 65:78–87
Baker JF, Ostergaard M, George M, Shults J, Emery P, Baker DG, Conaghan PG (2014) Greater body mass independently predicts less radiographic progression on X-ray and MRI over 1-2 years. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1923–1928
van der Helm-van Mil AH, van der Kooij SM, Allaart CF, Toes RE, Huizinga TW (2008) A high body mass index has a protective effect on the amount of joint destruction in small joints in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:769–774
Westhoff G, Rau R, Zink A (2007) Radiographic joint damage in early rheumatoid arthritis is highly dependent on body mass index. Arthritis Rheum 56:3575–3582
Humphreys JH, Verstappen SM, Mirjafari H, Bunn D, Lunt M, Bruce IN, Symmons DP (2013) Association of morbid obesity with disability in early inflammatory polyarthritis: results from the Norfolk arthritis register. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 65:122–126
Finckh A, Turesson C (2014) The impact of obesity on the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1911–1913
Turesson C, Bergström U, Pikwer M, Nilsson JÅ, Jacobsson LT (2016) A high body mass index is associated with reduced risk of rheumatoid arthritis in men, but not in women. Rheumatology (Oxford) 55:307–314
Iannone F, Lapadula G (2010) Obesity and inflammation—targets for OA therapy. Curr Drug Targets 11:586–598
Iannone F, Lapadula G (2011) Chemerin/ChemR23 pathway: a system beyond chemokines. Arthritis Res Ther 13:104
Wang QP, Li XP, Wang M, Zhao LL, Li H, Xie H, Lu ZY (2014) Adiponectin exerts its negative effect on bone metabolism via OPG/RANKL pathway: an in vivo study. Endocrine 47:845–853
Ellerby N, Mattey DL, Packham J, Dawes P, Hider SL (2014) Obesity and comorbidity are independently associated with a failure to achieve remission in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:74
Gremese E, Carletto A, Padovan M, Atzeni F, Raffeiner B, Giardina AR et al (2013) Obesity and reduction of the response rate to anti-tumor necrosis factor α in rheumatoid arthritis: an approach to a personalized medicine. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 65:94–100
Heimans L, van den Broek M, le Cessie S, Siegerink B, Riyazi N, Han KH et al (2013) Association of high body mass index with decreased treatment response to combination therapy in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 65:1235–1242
Klaasen R, Wijbrandts CA, Gerlag DM, Tak PP (2011) Body mass index and clinical response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 63:359–364
Rodrigues AM, Reis JE, Santos C, Pereira MP, Loureiro C, Martins F et al (2014) A1.1 obesity is a risk factor for worse treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis patients—results from reuma.pt. Ann Rheum Dis 73(Suppl 1):A1
Sandberg ME, Bengtsson C, Källberg H, Wesley A, Klareskog L, Alfredsson L, Saevarsdottir S (2014) Overweight decreases the chance of achieving good response and low disease activity in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:2029–2033
Iannone F, Fanizzi R, Notarnicola A, Scioscia C, Anelli MG, Lapadula G (2015) Obesity reduces the drug survival of second line biological drugs following a first TNF-α inhibitor in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Joint Bone Spine
Nüßlein HG, Alten R, Galeazzi M, Lorenz HM, Boumpas D, Nurmohamed MT et al (2014) Real-world effectiveness of abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis treatment in European and Canadian populations: a 6-month interim analysis of the 2-year, observational, prospective ACTION study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15:14
Finckh, Neto, Iannone, Loza, Lie, van Riel et al. (2015) The impact of patient heterogeneity and socioeconomic factors on abatacept retention in rheumatoid arthritis across nine European countries. RMD Open 1. doi:10.1136/rmdopen
Kearsley-Fleet L, Závada J, Hetland ML, Nordström DC, Aaltonen KJ, Listing J et al (2015) The EULAR Study Group for Registers and Observational Drug Studies: comparability of the patient case mix in the European biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug registers. Rheumatology (Oxford) 54:1074–1079
Fransen J, van Riel PL (2009) The disease activity score and the EULAR response criteria. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 35:745–757 vii-viii
Kristensen LE, Saxne T, Geborek P (2006) The LUNDEX, a new index of drug efficacy in clinical practice: results of a five-year observational study of treatment with infliximab and etanercept among rheumatoid arthritis patients in southern Sweden. Arthritis Rheum 54:600–606
Nüßlein H, Alten R, Galeazzi M, Lorenz HM, Nurmohame MT, Bensen WG, Burmester G (2014) Does body mass index impact long-term retention with abatacept in patients with RA who have received at least one prior biologic agent. 2-year results from a real-world, international, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum 66S:2492
Gottenberg JE, Courvoisier DS, Hernandez MV, Iannone F, Lie E, Canhão H et al. (2016) Rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated protein antibody positivity are associated with a better effectiveness of abatacept: results from the Pan-European registry analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol
De Keyser F, Hoffman I, Durez P, Kaiser MJ, Westhovens R, MIRA Study Group (2014) Longterm followup of rituximab therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Belgian MabThera in rheumatoid arthritis registry. J Rheumatol 41:1761–1765
Ottaviani S, Gardette A, Roy C, Tubach F, Gill G, Palazzo E et al (2015) Body mass index and response to rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 82:432–436
Pers YM, Godfrin-Valnet M, Lambert J, Fortunet C, Constant E, Mura T et al (2015) Response to tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis is not influenced by the body mass index of the patient. J Rheumatol 42:580–584
Gardette A, Ottaviani S, Sellam J, Berenbaum F, Lioté F, Meyer A et al. (2016) Body mass index and response to tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: a real life study. Clin Rheumatol
D'Agostino MA, Le Bars M, Taylor M, Chou B, Zhu J, Ranganath VK (2015) In patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate, does body mass index influence the efficacy of abatacept on inflammation when measured by power doppler ultrasonography? Results from the APPRAISE study. Ann Rheum Dis 74S2:231
Gardette A, Ottaviani S, Sellam J, Berenbaum F, Lioté F, Fautrel B et al. (2016) Body mass index and response to abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Clin Invest
Corbo, Valencia, Raymond, Agrawal, Townsend, Zhou et al (2009) Subcutaneous administration of abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: pharmacokinetics, safety and immunogenicity. Ann Rheum Dis 68(S3):574
Roy A, Mould DR, Wang XF, Tay L, Raymond R, Pfister M (2007) Modeling and simulation of abatacept exposure and interleukin-6 response in support of recommended doses for rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Pharmacol 47:1408–1420
Alten R, Nublein HG, Galeazzi M, Lorenz H-M, Mariette X, Cantagrel A et al (2015) Body mass index does not influence the efficacy of abatacept in patients with RA who are biologic Naïve: 6-month results from a real-world, international, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum 67S:553
Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M et al (2014) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis 73:492–509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Funding
The study was supported by an unrestricted research grant from Bristol–Myers Squibb (BMS). BMS had no role in the interpretation of the data nor in the decision to publish or not the results.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iannone, F., Courvoisier, D.S., Gottenberg, J.E. et al. Body mass does not impact the clinical response to intravenous abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Analysis from the “pan-European registry collaboration for abatacept (PANABA). Clin Rheumatol 36, 773–779 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3505-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3505-5