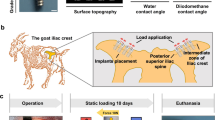
Abstract
Objectives
The objective of the current study was to examine whether the nanoindentation parameters can assess the alteration of bone quality resulting from different degrees of bone remodeling between bone tissue ages around the dental implant interface with different treatments and healing periods.
Materials and methods
Dental implants were placed in mandibles of six male dogs. Treatment groups included: resorbable blast media-treated titanium (Ti) implants, alumina-blasted zirconia implants (ATZ), alumina-blasted zirconia implants applied with demineralized bone matrix (ATZ-D), and alumina-blasted zirconia implants applied with rhBMP-2 (ATZ-B). Nanoindentation modulus (E), hardness (H), viscosity (η), and viscoelastic creep (Creep/P max) were measured for new and old bone tissues adjacent to the implants at 3 and 6 weeks of post-implantation. A total of 945 indentations were conducted for 32 implant systems.
Results
Significantly lower E, H, and η but higher Creep/P max were measured for new bone tissues than old bone tissues, independent of treatments at both healing periods (p < 0.001). All nanoindentation parameters were not significantly different between healing periods (p > 0.568). ATZ-D and ATZ-B implants had the stiffer slope of correlation between E and Creep/P max of the new bone tissue than Ti implant (p < 0.039).
Conclusions
Current results indicated that, in addition to elastic modulus and plastic hardness, measurement of viscoelastic properties of bone tissue surrounding the implant can provide more detailed information to understand mechanical behavior of an implant system.
Clinical relevance
Ability of energy absorption in the interfacial bone tissue can play a significant role in the long-term success of a dental implant system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isidor F (2006) Influence of forces on peri-implant bone. Clin Oral Implants Res 17(Supplement 2):8–18. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01360.x
Hoshaw SJ, Brunski JB, Cochran GV (1994) Mechanical loading of Brånemark implants affects interfacial bone modeling and remodeling. Int J Oral Max Impl 9(3):345–360
Lin D, Li Q, Li W, Duckmanton N, Swain M (2010) Mandibular bone remodeling induced by dental implant. J Biomech 43(2):287–293. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.08.024
Kim DG, Huja SS, Tee BC, Larsen PE, Kennedy KS, Chien HH, Lee JW, Wen HB (2013a) Bone ingrowth and initial stability of titanium and porous tantalum dental implants: a pilot canine study. Implant Dent 22(4):399–405. doi:10.1097/ID.0b013e31829b17b5
Brunski JB (1988) Biomaterials and biomechanics in dental implant design. The Int J Oral Max Impl 3(2):85–97
Baldassarri M, Bonfante E, Suzuki M, Marin C, Granato R, Tovar N, Coelho PG (2012) Mechanical properties of human bone surrounding plateau root form implants retrieved after 0.3–24 years of function. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 100(7):2015–2021. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.32786
Lee BC, Yeo IS, Kim DJ, Lee JB, Kim SH, Han JS (2013) Bone formation around zirconia implants combined with rhBMP-2 gel in the canine mandible. Clin Oral Implants Res 24(12):1332–1338. doi:10.1111/clr.12004
Piattelli A, Artese L, Penitente E, Iaculli F, Degidi M, Mangano C, Shibli JA, Coelho PG, Perrotti V, Iezzi G (2014) Osteocyte density in the peri-implant bone of implants retrieved after different time periods (4 weeks to 27 years). J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 102(2):239–243. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.33000
Garetto LP, Chen J, Parr JA, Roberts WE (1995) Remodeling dynamics of bone supporting rigidly fixed titanium implants: a histomorphometric comparison in four species including humans. Implant Dent 4(4):235–243
Maimoun L, Brennan TC, Badoud I, Dubois-Ferriere V, Rizzoli R, Ammann P (2010) Strontium ranelate improves implant osseointegration. Bone 46(5):1436–1441. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2010.01.379
Anchieta RB, Baldassarri M, Guastaldi F, Tovar N, Janal MN, Gottlow J, Dard M, Jimbo R, Coelho PG (2013) Mechanical property assessment of bone healing around a titanium-zirconium alloy dental implant. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. doi:10.1111/cid.12061
Jimbo R, Coelho PG, Bryington M, Baldassarri M, Tovar N, Currie F, Hayashi M, Janal MN, Andersson M, Ono D, Vandeweghe S, Wennerberg A (2012) Nano hydroxyapatite-coated implants improve bone nanomechanical properties. J Dent Res 91(12):1172–1177. doi:10.1177/0022034512463240
Morris MD, Mandair GS (2011) Raman assessment of bone quality. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(8):2160–2169. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1692-y
Gottlow J, Dard M, Kjellson F, Obrecht M, Sennerby L (2012) Evaluation of a new titanium-zirconium dental implant: a biomechanical and histological comparative study in the mini pig. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14(4):538–545. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8208.2010.00289.x
Shin D, Blanchard SB, Ito M, Chu TM (2011) Peripheral quantitative computer tomographic, histomorphometric, and removal torque analyses of two different non-coated implants in a rabbit model. Clin Oral Implants Res 22(3):242–250. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.01980.x
Wikesjo UM, Huang YH, Xiropaidis AV, Sorensen RG, Rohrer MD, Prasad HS, Wozney JM, Hall J (2008) Bone formation at recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2-coated titanium implants in the posterior maxilla (type IV bone) in non-human primates. J Clin Periodontol 35(11):992–1000. doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01322.x
Sykaras N, Triplett RG, Nunn ME, Iacopino AM, Opperman LA (2001) Effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on bone regeneration and osseointegration of dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 12(4):339–349
Leknes KN, Yang J, Qahash M, Polimeni G, Susin C, Wikesjo UM (2012) Alveolar ridge augmentation using implants coated with recombinant human growth/differentiation factor-5 (rhGDF-5). radiographic observations. Clin Oral Implants Res 24(11):1185–1191. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02564.x
Schliephake H (2013) Clinical efficacy of growth factors to enhance tissue repair in oral and maxillofacial reconstruction: a systematic review. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. doi:10.1111/cid.12114
Currey JD (1999) The design of mineralised hard tissues for their mechanical functions. J Exp Biol 202(Pt 23):3285–3294
Donnelly E, Boskey AL, Baker SP, van der Meulen MC (2010) Effects of tissue age on bone tissue material composition and nanomechanical properties in the rat cortex. J Biomed Mater Res A 92(3):1048–1056. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32442
Mulder L, Koolstra JH, den Toonder JMJ, van Eijden TMGJ (2007) Intratrabecular distribution of tissues stiffness and mineralization in developing trabecular bone. Bone 41(2):256–265
Mulder L, Koolstra JH, den Toonder JM, van Eijden TM (2008) Relationship between tissue stiffness and degree of mineralization of developing trabecular bone. J Biomed Mater Res A 84(2):508–515
Ruffoni D, Fratzl P, Roschger P, Klaushofer K, Weinkamer R (2007) The bone mineralization density distribution as a fingerprint of the mineralization process. Bone 40(5):1308–1319
Hoffler CE, Guo XE, Zysset PK, Goldstein SA (2005) An application of nanoindentation technique to measure bone tissue lamellae properties. J Biomech Eng 127(7):1046–1053
Rho JY, Tsui TY, Pharr GM (1997) Elastic properties of human cortical and trabecular lamellar bone measured by nanoindentation. Biomaterials 18(20):1325–1330
Kim DG, Huja SS, Navalgund A, D'Atri A, Tee B, Reeder S, Ri Lee H (2013b) Effect of estrogen deficiency on regional variation of a viscoelastic tissue property of bone. J Biomech 46(1):110–115. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2012.10.013
Kim DG, Huja SS, Lee HR, Tee BC, Hueni S (2010) Relationships of viscosity with contact hardness and modulus of bone matrix measured by nanoindentation. J Biomech Eng 132(2):024502. doi:10.1115/1.4000936
Kim DG, Elias K (2014) Handbook of nanomaterials properties. In: Bhushan B, Luo D, Schricker SR, Sigmund W, Zauscher S (eds) Elastic, viscoelastic, and fracture properties of bone tissue measured by nanoindentation. Springer, Berlin, pp. 1321–1341
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (2004) Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J Mater Res 19(1):3–20. doi:10.1557/jmr.2004.19.1.3
Fischer-Cripps AC (2004) A simple phenomenological approach to nanoindentation creep. Mat Sci Eng A-Struct 385(1–2):74–82. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2004.04.070
Huja SS, Fernandez SA, Hill KJ, Gulati P (2007) Indentation modulus of the alveolar process in dogs. J Dent Res 86(3):237–241
Rho JY, Pharr GM (1999) Effects of drying on the mechanical properties of bovine femur measured by nanoindentation. J Mater Sci Mater Med 10(8):485–488
Hoffler CE, Moore KE, Kozloff K, Zysset PK, Brown MB, Goldstein SA (2000) Heterogeneity of bone lamellar-level elastic moduli. Bone 26(6):603–609
Lakes RS (1999) Viscoelastic solid. CRC Press, New York, p. 267
Kim DG, Navalgund AR, Tee BC, Noble GJ, Hart RT, Lee HR (2012) Increased variability of bone tissue mineral density resulting from estrogen deficiency influences creep behavior in a rat vertebral body. Bone 51(5):868–875. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2012.08.124
Donnelly E, Williams RM, Downs SA, Dickinson ME, Baker SP, van der Meulen MCH (2006) Quasistatic and dynamic nanomechanical properties of cancellous bone tissue relate to collagen content and organization. J Mater Res 21(8):2106–2117. doi:10.1557/Jmr.2006.0259
Isaksson H, Malkiewicz M, Nowak R, Helminen HJ, Jurvelin JS (2010a) Rabbit cortical bone tissue increases its elastic stiffness but becomes less viscoelastic with age. Bone 47(6):1030–1038. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2010.08.015
Isaksson H, Nagao S, Malkiewicz M, Julkunen P, Nowak R, Jurvelin JS (2010b) Precision of nanoindentation protocols for measurement of viscoelasticity in cortical and trabecular bone. J Biomech 43(12):2410–2417. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.04.017
Poiate IA, de Vasconcellos AB, de Santana RB, Poiate E (2009) Three-dimensional stress distribution in the human periodontal ligament in masticatory, parafunctional, and trauma loads: finite element analysis. J Periodontol 80(11):1859–1867. doi:10.1902/jop.2009.090220
Ona M, Wakabayashi N (2006) Influence of alveolar support on stress in periodontal structures. J Dent Res 85(12):1087–1091
Iezzi G, Degidi M, Shibli JA, Vantaggiato G, Piattelli A, Perrotti V (2013) Bone response to dental implants after a 3- to 10-year loading period: a histologic and histomorphometric report of four cases. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 33(6):755–761. doi:10.11607/prd.1257
Jager IL (2005) A model for the stability and creep of organic materials. J Biomech 38(7):1459–1467
Gupta HS, Krauss S, Kerschnitzki M, Karunaratne A, Dunlop JW, Barber AH, Boesecke P, Funari SS, Fratzl P (2013) Intrafibrillar plasticity through mineral/collagen sliding is the dominant mechanism for the extreme toughness of antler bone. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 28:366–382. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.03.020
Oyen ML, Ko CC (2007) Examination of local variations in viscous, elastic, and plastic indentation responses in healing bone. J Mater Sci Mater Med 18(4):623–628
Pathak S, Swadener JG, Kalidindi SR, Courtland HW, Jepsen KJ, Goldman HM (2011) Measuring the dynamic mechanical response of hydrated mouse bone by nanoindentation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4(1):34–43. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2010.09.002
Acknowledgments
The project described was, in part, supported by American Association of Orthodontists Foundation Award (Kim, D-G). The authors would like to thank Kathy L. Elias and Cheol-Woo Park who helped collecting data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DG., Kwon, HJ., Jeong, YH. et al. Mechanical properties of bone tissues surrounding dental implant systems with different treatments and healing periods. Clin Oral Invest 20, 2211–2220 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1734-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1734-2