Abstract
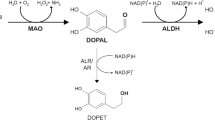
Evidence suggests that aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH; E.C. 1.2.1.3) gene, protein expression and activity are substantially decreased in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). This holds especially true for cytosolic ALDH1A1, while mitochondrial ALDH2 is increased in the putamen of PD. Similarly, in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) several studies in genetic, transcriptomic, protein and animal models suggest ALDH involvement in the neurodegeneration processes. Such data are in line with findings of increased toxic aldehydes, like for example malondialdehyde, nonenal, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde and others. Genetic, transcriptomic and protein alterations may contribute to such data. Also in vitro and in vivo experimental work points to an important role of ALDH in the pathology of neurodegenerative disorders. Aims at investigating dysfunctions of aldehyde detoxification are suitable to define genetic/molecular targets for new therapeutic strategies balancing amine metabolism in devastating disorders like PD and probably also AD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agid Y, Javoy F, Youdim MB (1973) Monoamine oxidase and aldehyde dehydrogenase activity in the striatum of rats after 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the nigrostriatal pathway. Br J Pharmacol 48(1):175–178
Alvarez-Lopez MJ, Castro-Freire M, Cosin-Tomas M, Sanchez-Roige S, Lalanza JF, Del Valle J, Parrizas M, Camins A, Pallas M, Escorihuela RM, Kaliman P (2013) Long-term exercise modulates hippocampal gene expression in senescent female mice. J Alzheimers Dis 33(4):1177–1190. doi:10.3233/JAD-121264
Anderson DW, Schray RC, Duester G, Schneider JS (2011) Functional significance of aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH1A1 to the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Res 1408:81–87. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.06.051
Bai J, Mei Y (2011) Overexpression of aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 attenuates neurotoxicity induced by 4-hydroxynonenal in cultured primary hippocampal neurons. Neurotox Res 19(3):412–422. doi:10.1007/s12640-010-9183-1
Black W, Vasiliou V (2009) The aldehyde dehydrogenase gene superfamily resource center. Hum Genomics 4(2):136–142
Black WJ, Stagos D, Marchitti SA, Nebert DW, Tipton KF, Bairoch A, Vasiliou V (2009) Human aldehyde dehydrogenase genes: alternatively spliced transcriptional variants and their suggested nomenclature. Pharmacogenet Genomics 19(11):893–902. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283329023
Budas GR, Disatnik MH, Chen CH, Mochly-Rosen D (2010) Activation of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) confers cardioprotection in protein kinase C epsilon (PKCvarepsilon) knockout mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol 48(4):757–764. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.10.030
Dedek J, Baumes R, Tien-Duc N, Gomeni R, Korf J (1979) Turnover of free and conjugated (sulphonyloxy) dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid in rat striatum. J Neurochem 33(3):687–695
Duncan RJ, Sourkes TL, Boucher R, Poirier LJ, Roberge A (1972) Aldehyde dehydrogenase and monoamine oxidase in the striatum of cats with nigrostriatal lesions. J Neurochem 19(8):2007–2010
Durrenberger PF, Grünblatt E, Fernando FS, Monoranu CM, Evans J, Riederer P, Reynolds R, Dexter DT (2012) Inflammatory Pathways in Parkinson’s Disease; A BNE Microarray Study. Parkinsons Dis 2012:214714. doi:10.1155/2012/214714
Fishman-Jacob T, Youdim MB, Mandel SA (2010) Silencing/overexpressing selected genes as a model of sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 7(1–3):108–111. doi:10.1159/000285517
Fitzmaurice AG, Rhodes SL, Lulla A, Murphy NP, Lam HA, O’Donnell KC, Barnhill L, Casida JE, Cockburn M, Sagasti A, Stahl MC, Maidment NT, Ritz B, Bronstein JM (2013) Aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition as a pathogenic mechanism in Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(2):636–641. doi:10.1073/pnas.1220399110
Fitzmaurice AG, Rhodes SL, Cockburn M, Ritz B, Bronstein JM (2014) Aldehyde dehydrogenase variation enhances effect of pesticides associated with Parkinson disease. Neurology 82(5):419–426. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000083
Galter D, Buervenich S, Carmine A, Anvret M, Olson L (2003) ALDH1 mRNA: presence in human dopamine neurons and decreases in substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease and in the ventral tegmental area in schizophrenia. Neurobiol Dis 14(3):637–647
Goedde HW, Agarwal DP, Fritze G, Meier-Tackmann D, Singh S, Beckmann G, Bhatia K, Chen LZ, Fang B, Lisker R et al (1992) Distribution of ADH2 and ALDH2 genotypes in different populations. Hum Genet 88(3):344–346
Goldstein DS, Sullivan P, Holmes C, Miller GW, Alter S, Strong R, Mash DC, Kopin IJ, Sharabi Y (2013) Determinants of buildup of the toxic dopamine metabolite DOPAL in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 126(5):591–603. doi:10.1111/jnc.12345
Grünblatt E (2012) Parkinson’s disease: molecular risk factors. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(Suppl 1):S45–S48. doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(11)70016-5
Grünblatt E, Mandel S, Jacob-Hirsch J, Zeligson S, Amariglo N, Rechavi G, Li J, Ravid R, Roggendorf W, Riederer P, Youdim MB (2004) Gene expression profiling of parkinsonian substantia nigra pars compacta; alterations in ubiquitin-proteasome, heat shock protein, iron and oxidative stress regulated proteins, cell adhesion/cellular matrix and vesicle trafficking genes. J Neural Transm 111(12):1543–1573
Grünblatt E, Zehetmayer S, Jacob CP, Muller T, Jost WH, Riederer P (2010) Pilot study: peripheral biomarkers for diagnosing sporadic Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm. doi:10.1007/s00702-010-0509-1
Jackson B, Brocker C, Thompson DC, Black W, Vasiliou K, Nebert DW, Vasiliou V (2011) Update on the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene (ALDH) superfamily. Hum Genomics 5(4):283–303
Komatsu M, Shibata N, Ohnuma T, Kuerban B, Tomson K, Toda A, Tagata Y, Nakada T, Shimazaki H, Arai H (2014) Polymorphisms in the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and dopamine beta hydroxylase genes are not associated with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 121(4):427–432. doi:10.1007/s00702-013-1112-z
Kong D, Kotraiah V (2012) Modulation of aldehyde dehydrogenase activity affects (±)-4-hydroxy-2E-nonenal (HNE) toxicity and HNE-protein adduct levels in PC12 cells. J Mol Neurosci 47(3):595–603. doi:10.1007/s12031-011-9688-y
Kotraiah V, Pallares D, Toema D, Kong D, Beausoleil E (2013) Identification of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 modulators using virtual screening. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 28(3):489–494. doi:10.3109/14756366.2011.653353
Lamensdorf I, Eisenhofer G, Harvey-White J, Hayakawa Y, Kirk K, Kopin IJ (2000) Metabolic stress in PC12 cells induces the formation of the endogenous dopaminergic neurotoxin, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde. J Neurosci Res 60(4):552–558
Larson HN, Weiner H, Hurley TD (2005) Disruption of the coenzyme binding site and dimer interface revealed in the crystal structure of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase “Asian” variant. J Biol Chem 280(34):30550–30556. doi:10.1074/jbc.M502345200
Legros H, Dingeval MG, Janin F, Costentin J, Bonnet JJ (2004) Toxicity of a treatment associating dopamine and disulfiram for catecholaminergic neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells: relationships with 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde formation. Neurotoxicology 25(3):365–375. doi:10.1016/S0161-813X(03)00148-7
Maes OC, Schipper HM, Chertkow HM, Wang E (2009) Methodology for discovery of Alzheimer’s disease blood-based biomarkers. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64(6):636–645. doi:10.1093/gerona/glp045
Mandel SA, Fishman T, Youdim MB (2007) Gene and protein signatures in sporadic Parkinson’s disease and a novel genetic model of PD. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13(Suppl 3):S242–S247. doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(08)70009-9
Mandel SA, Fishman-Jacob T, Youdim MB (2012) Genetic reduction of the E3 ubiquitin ligase element, SKP1A and environmental manipulation to emulate cardinal features of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(Suppl 1):S177–S179. doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(11)70055-4
Marchitti SA, Brocker C, Stagos D, Vasiliou V (2008) Non-P450 aldehyde oxidizing enzymes: the aldehyde dehydrogenase superfamily. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4(6):697–720. doi:10.1517/17425255.4.6.697
Maring JA, Deitrich RA, Little R (1985) Partial purification and properties of human brain aldehyde dehydrogenases. J Neurochem 45(6):1903–1910
Meyer MJ, Mosely DE, Amarnath V, Picklo MJ Sr (2004) Metabolism of 4-hydroxy-trans-2-nonenal by central nervous system mitochondria is dependent on age and NAD+ availability. Chem Res Toxicol 17(9):1272–1279. doi:10.1021/tx049843k
Michel TM, Gsell W, Kasbauer L, Tatschner T, Sheldrick AJ, Neuner I, Schneider F, Grünblatt E, Riederer P (2010) Increased activity of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) in the putamen of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease: a human postmortem study. J Alzheimers Dis 19(4):1295–1301. doi:10.3233/JAD-2010-1326
Michel TM, Kasbauer L, Gsell W, Jecel J, Sheldrick AJ, Cortese M, Nickl-Jockschat T, Grünblatt E, Riederer P (2014) Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(Suppl 1):S68–S72. doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(13)70018-X
Molochnikov L, Rabey JM, Dobronevsky E, Bonucelli U, Ceravolo R, Frosini D, Grünblatt E, Riederer P, Jacob C, Aharon-Peretz J, Bashenko Y, Youdim MB, Mandel SA (2012) A molecular signature in blood identifies early Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 7:26. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-7-26
Ohsawa I, Nishimaki K, Yasuda C, Kamino K, Ohta S (2003) Deficiency in a mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase increases vulnerability to oxidative stress in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 84(5):1110–1117
Ohsawa I, Nishimaki K, Murakami Y, Suzuki Y, Ishikawa M, Ohta S (2008) Age-dependent neurodegeneration accompanying memory loss in transgenic mice defective in mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 activity. J Neurosci 28(24):6239–6249. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4956-07.2008
Ohta S, Ohsawa I (2006) Dysfunction of mitochondria and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: on defects in the cytochrome c oxidase complex and aldehyde detoxification. J Alzheimers Dis 9(2):155–166
Picklo MJ, Olson SJ, Markesbery WR, Montine TJ (2001) Expression and activities of aldo-keto oxidoreductases in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60(7):686–695
Ryzlak MT, Pietruszko R (1987) Purification and characterization of aldehyde dehydrogenase from human brain. Arch Biochem Biophys 255(2):409–418
Rzhetsky A, Ayala FJ, Hsu LC, Chang C, Yoshida A (1997) Exon/intron structure of aldehyde dehydrogenase genes supports the “introns-late” theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(13):6820–6825
Scherzer CR, Eklund AC, Morse LJ, Liao Z, Locascio JJ, Fefer D, Schwarzschild MA, Schlossmacher MG, Hauser MA, Vance JM, Sudarsky LR, Standaert DG, Growdon JH, Jensen RV, Gullans SR (2007) Molecular markers of early Parkinson’s disease based on gene expression in blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(3):955–960. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610204104
Serrano-Pozo A, Gomez-Isla T, Growdon JH, Frosch MP, Hyman BT (2013) A phenotypic change but not proliferation underlies glial responses in Alzheimer disease. Am J Pathol 182(6):2332–2344. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.02.031
Shoeb M, Ansari NH, Srivastava SK, Ramana KV (2014) 4-hydroxynonenal in the pathogenesis and progression of human diseases. Curr Med Chem 21(2):230–237
Solito R, Corti F, Chen CH, Mochly-Rosen D, Giachetti A, Ziche M, Donnini S (2013) Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 activation prevents beta-amyloid-induced endothelial cell dysfunction and restores angiogenesis. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 9):1952–1961. doi:10.1242/jcs.117184
Song BJ, Abdelmegeed MA, Yoo SH, Kim BJ, Jo SA, Jo I, Moon KH (2011) Post-translational modifications of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase and biomedical implications. J Proteomics 74(12):2691–2702. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2011.05.013
Stewart MJ, Malek K, Crabb DW (1996) Distribution of messenger RNAs for aldehyde dehydrogenase 1, aldehyde dehydrogenase 2, and aldehyde dehydrogenase 5 in human tissues. J Investig Med 44(2):42–46
Stott SR, Barker RA (2014) Time course of dopamine neuron loss and glial response in the 6-OHDA striatal mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 39(6):1042–1056. doi:10.1111/ejn.12459
Strickland KC, Holmes RS, Oleinik NV, Krupenko NI, Krupenko SA (2011) Phylogeny and evolution of aldehyde dehydrogenase-homologous folate enzymes. Chem Biol Interact 191(1–3):122–128. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2010.12.025
Tanzi RE, Bertram L (2001) New frontiers in Alzheimer’s disease genetics. Neuron 32(2):181–184
Vasiliou V, Pappa A, Estey T (2004) Role of human aldehyde dehydrogenases in endobiotic and xenobiotic metabolism. Drug Metab Rev 36(2):279–299. doi:10.1081/DMR-120034001
Werner CJ, Heyny-von Haussen R, Mall G, Wolf S (2008) Proteome analysis of human substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Proteome Sci 6:8. doi:10.1186/1477-5956-6-8
Wey MC, Fernandez E, Martinez PA, Sullivan P, Goldstein DS, Strong R (2012) Neurodegeneration and motor dysfunction in mice lacking cytosolic and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenases: implications for Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 7(2):e31522. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031522
Wood PL, Khan MA, Moskal JR (2007) The concept of “aldehyde load” in neurodegenerative mechanisms: cytotoxicity of the polyamine degradation products hydrogen peroxide, acrolein, 3-aminopropanal, 3-acetamidopropanal and 4-aminobutanal in a retinal ganglion cell line. Brain Res 1145:150–156. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.10.004
Yoshida A, Huang IY, Ikawa M (1984) Molecular abnormality of an inactive aldehyde dehydrogenase variant commonly found in Orientals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81(1):258–261
Yoval-Sanchez B, Rodriguez-Zavala JS (2012) Differences in susceptibility to inactivation of human aldehyde dehydrogenases by lipid peroxidation byproducts. Chem Res Toxicol 25(3):722–729. doi:10.1021/tx2005184
Zhang M, Shoeb M, Goswamy J, Liu P, Xiao TL, Hogan D, Campbell GA, Ansari NH (2010) Overexpression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 reduces oxidation-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Neurosci Res 88(3):686–694. doi:10.1002/jnr.22230
Conflict of interest
The authors declare neither competing financial interests regarding this review nor conflicts of interest in respect to the content of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grünblatt, E., Riederer, P. Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 123, 83–90 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1320-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1320-1