Abstract
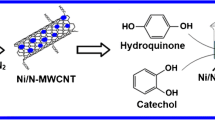
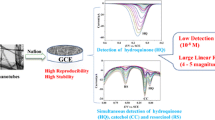
A glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and applied to the simultaneous determination of hydroquinone (HQ), catechol (CC), bisphenol A (BPA) and phenol by using square-wave voltammetry. The MWCNTs were deposited on the GCE and the AgNPs were then electrodeposited onto the MWCNT/GCE by the application of 10 potential sweep cycles using an AgNP colloidal suspension. The modified GCE was characterized by using SEM, which confirmed the presence of the AgNPs. The electrochemical behavior of the material was evaluated by using cyclic voltammetry, and by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy that employed hexacyanoferrate as an electrochemical probe. The results were compared to the performance of the unmodified GCE. The modified electrode has a lower charge-transfer resistance and yields an increased signal. The peaks for HQ (0.30 V), CC (0.40 V), BPA (0.74 V) and phenol (0.83 V; all versus Ag/AgCl) are well separated under optimized conditions, which facilitates their simultaneous determination. The oxidation current increases linearly with the concentrations of HQ, CC, BPA and phenol. Detection limits are in the order of 1 μM for all 4 species, and the sensor is highly stable and reproducible. The electrode was successfully employed with the simultaneous determination of HQ, CC, BPA and phenol in spiked tap water samples.

A glassy carbon electrode was modified with carbon nanotubes and silver nanoparticles and then successfully applied to the simultaneous determination of four phenolic compounds. The sensor showed high sensitivity in the detection of hydroquinone, catechol, bisphenol A and phenol in water samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ummethala R, Wenger D, Tedde SF et al (2016) Effect of substrate material on the growth and field emission characteristics of large-area carbon nanotube forests. J Appl Phys 119:44302. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4940418
Gooding JJ (2005) Nanostructuring electrodes with carbon nanotubes: a review on electrochemistry and applications for sensing. Electrochim Acta 50:3049–3060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2004.08.052
Moraes FC, Cabral MF, Mascaro LH, Machado SAS (2011) The electrochemical effect of acid functionalisation of carbon nanotubes to be used in sensors development. Surf Sci 605:435–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2010.11.014
Goulart LA, Mascaro LH (2016) GC electrode modified with carbon nanotubes and NiO for the simultaneous determination of bisphenol A, hydroquinone and catechol. Electrochim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.02.174
Zeng S, Yong K-T, Roy I et al (2011) A review on functionalized gold nanoparticles for biosensing applications. Plasmonics 6:491–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9228-1
Darvishi S, Karmizadeh F, Kharaziha M (2015) A facile one-step electrochemical synthesis of nickel nanoparticle/Graphene composites for non-enzymatic biosensor applications. Procedia Mater Sci 11:142–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.006
Jiang L, Gu S, Ding Y et al (2014) Facile and novel electrochemical preparation of a graphene–transition metal oxide nanocomposite for ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing of acetaminophen and phenacetin. Nano 6:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR03620K
Nantaphol S, Chailapakul O, Siangproh W (2015) Sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor using silver nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of cholesterol in bovine serum. Sensors Actuators B Chem 207:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.10.041
Pagnanelli F, Altimari P, Bellagamba M et al (2015) Pulsed electrodeposition of cobalt nanoparticles on copper: influence of the operating parameters on size distribution and morphology. Electrochim Acta 155:228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.12.112
Ingerslev F, Vaclavik E, Halling-Sørensen B (2003) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products - a source of endocrine disruption in the environment? Pure Appl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200375111881
Maffini MV, Rubin BS, Sonnenschein C, Soto AM (2006) Endocrine disruptors and reproductive health: the case of bisphenol-A. Mol Cell Endocrinol 254–255:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2006.04.033
Garoma T, Matsumoto SA, Wu Y, Klinger R (2010) Removal of bisphenol A and its reaction-intermediates from aqueous solution by ozonation. Ozone Sci Eng 32:338–343. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2010.508484
Lin T-M, Lee S-S, Lai C-S, Lin S-D (2006) Phenol burn. Burns 32:517–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2005.12.016
Flickinger CW (1976) The benzenediols: catechol, resorcinol and hydroquinone — a review of the industrial toxicology and current industrial exposure limits. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 37:596–606. https://doi.org/10.1080/0002889768507526
Bakker E (2004) Electrochemical sensors. Anal Chem 76:3285–3298. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac049580z
Hashemnia S, Khayatzadeh S, Hashemnia M (2012) Electrochemical detection of phenolic compounds using composite film of multiwall carbon nanotube/surfactant/tyrosinase on a carbon paste electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 16:473–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1355-2
Zhao G-H, Tang Y-T, Liu M-C et al (2007) Direct and simultaneous determination of phenol, hydroquinone and nitrophenol at boron-doped diamond film electrode. Chin J Chem 25:1445–1450. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.200790267
Ding Y-P, Liu W-L, Q-S W, Wang X-G (2005) Direct simultaneous determination of dihydroxybenzene isomers at C-nanotube-modified electrodes by derivative voltammetry. J Electroanal Chem 575:275–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2004.09.020
Zhang D, Peng Y, Qi H et al (2009) Application of multielectrode array modified with carbon nanotubes to simultaneous amperometric determination of dihydroxybenzene isomers. Sensors Actuators B Chem 136:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2008.11.010
Anu Prathap MU, Satpati B, Srivastava R (2013) Facile preparation of polyaniline/MnO2 nanofibers and its electrochemical application in the simultaneous determination of catechol, hydroquinone, and resorcinol. Sensors Actuators B Chem 186:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.05.076
Ma X, Liu Z, Qiu C et al (2013) Simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol based on glassy carbon electrode modified with gold-graphene nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 180:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-0949-z
Wang Y, Qu J, Li S et al (2015) Simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticles, ZnS/NiS@ZnS quantum dots and L-cysteine. Microchim Acta 182:2277–2283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1568-7
Peng J, Feng Y, Han X-X, Gao Z-N (2016) Simultaneous determination of bisphenol A and hydroquinone using a poly(melamine) coated graphene doped carbon paste electrode. Microchim Acta 183:2289–2296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1865-9
Campos AM, Raymundo-Pereira PA, Cincotto FH et al (2016) Sensitive determination of the endocrine disruptor bisphenol A at ultrathin film based on nanostructured hybrid material SiO2/GO/AgNP. J Solid State Electrochem 20:2503–2507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-015-3098-y
Yang L, Zhao H, Fan S et al (2014) A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and bisphenol A based on the ultrafine Pd nanoparticle@TiO2 functionalized SiC. Anal Chim Acta 852:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.08.037
Committee AM (1987) Recommendations for the definition, estimation and use of the detection limit. Analyst 112:199. https://doi.org/10.1039/an9871200199
de Moura MR, Mattoso LHC, Zucolotto V (2012) Development of cellulose-based bactericidal nanocomposites containing silver nanoparticles and their use as active food packaging. J Food Eng 109:520–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.10.030
Goulart LA, de Moraes FC, Mascaro LH (2016) Influence of the different carbon nanotubes on the development of electrochemical sensors for bisphenol A. Mater Sci Eng C 58:768–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.09.073
Balasubramanian K, Burghard M (2005) Chemically functionalized carbon nanotubes. Small 1:180–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200400118
Rawal R, Chawla S, Pundir CS (2011) Polyphenol biosensor based on laccase immobilized onto silver nanoparticles/multiwalled carbon nanotube/polyaniline gold electrode. Anal Biochem 419:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2011.07.028
Van der Horst C, Silwana B, Iwuoha E, Somerset V (2015) Synthesis and characterization of bismuth-silver nanoparticles for electrochemical sensor applications. Anal Lett 48:1311–1332. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2014.979357
Nasirizadeh N, Ghaani M, Shekari Z, Shateri-Khalilabad M (2016) Novel non enzymatic TBHQ modified electrochemical sensor for hydrogen peroxide determination in different beverage samples. J Braz Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20160037
Negash N, Alemu H, Tessema M (2014) Flow injection amperometric determination of phenol and Chlorophenols at Single Wall carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. Am J Anal Chem 5:188–198. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2014.53023
Kolvenbach B, Schlaich N, Raoui Z et al (2007) Degradation pathway of bisphenol A: does ipso substitution apply to phenols containing a quaternary -carbon structure in the para position? Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4776–4784. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00329-07
Hu Z, Leung C-F, Tsang Y-K et al (2011) A recyclable polymer-supported ruthenium catalyst for the oxidative degradation of bisphenol A in water using hydrogen peroxide. New J Chem 35:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NJ00583E
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge #2012/20926-2 and #2013/07296-2 São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), CNPq and CAPES for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic Supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2519 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goulart, L.A., Gonçalves, R., Correa, A.A. et al. Synergic effect of silver nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes on the simultaneous voltammetric determination of hydroquinone, catechol, bisphenol A and phenol. Microchim Acta 185, 12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2540-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2540-5