Abstract
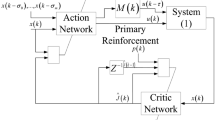
In this paper, an online adaptive optimal control problem of a class of continuous-time Markov jump linear systems (MJLSs) is investigated by using a parallel reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm with completely unknown dynamics. Before collecting and learning the subsystems information of states and inputs, the exploration noise is firstly added to describe the actual control input. Then, a novel parallel RL algorithm is used to parallelly compute the corresponding N coupled algebraic Riccati equations by online learning. By this algorithm, we will not need to know the dynamic information of the MJLSs. The convergence of the proposed algorithm is also proved. Finally, the effectiveness and applicability of this novel algorithm is illustrated by two simulation examples.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krasovskii NN, Lidskii EA (1961) Analysis design of controller in systems with random attributes—part 1. Autom Remote Control 22:1021–1025
Luan X, Huang B, Liu F (2018) Higher order moment stability region for Markov jump systems based on cumulant generating function. Automatica 93:389–396
Zhang L, Boukas EK (2009) Stability and stabilization of Markovian jump linear systems with partly unknown transition probabilities. Automatica 45(2):463–468
Shi P, Li F (2015) A survey on Markovian jump systems: modeling and design. Int J Control Autom Syst 13(1):1–16
Wang Y, Xia Y, Shen H, Zhou P (2017) SMC design for robust stabilization of nonlinear Markovian jump singular systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control. https://doi.org/10.1109/tac.2017.2720970(In Press)
Li H, Shi P, Yao D, Wu L (2016) Observer-based adaptive sliding mode control for nonlinear Markovian jump systems. Automatica 64(1):133–142
Kao Y, Xie J, Wang C, Karimi HR (2015) A sliding mode approach to H∞ non-fragile observer-based control design for uncertain Markovian neutral-type stochastic systems. Automatica 52:218–226
Shi P, Liu M, Zhang L (2015) Fault-tolerant sliding mode observer synthesis of Markovian jump systems using quantized measurements. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 62(9):5910–5918
Ma Y, Jia X, Liu D (2016) Robust finite-time H∞ control for discrete-time singular Markovian jump systems with time-varying delay and actuator saturation. Appl Comput Math 286:213–227
Mao Z, Jiang B, Shi P (2007) H∞ fault detection filter design for networked control systems modelled by discrete Markovian jump systems. IET Control Theory Appl 1(5):1336–1343
Shi P, Li F, Wu L, Lim CC (2017) Neural network-based passive filtering for delayed neutral-type semi-markovian jump systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(9):2101–2114
Li F, Wu L, Shi P, Lim CC (2015) State estimation and sliding mode control for semi-Markovian jump systems with mismatched uncertainties. Automatica 51:385–393
Ma H, Liang H, Zhu Q, Ahn CK (2018) Adaptive dynamic surface control design for uncertain nonlinear strict-feedback systems with unknown control direction and disturbances. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2018.2855170(In Press)
Ma H, Zhou Q, Bai L, Liang H (2018) Observer-based adaptive fuzzy fault-tolerant control for stochastic nonstrict-feedback nonlinear systems with input quantization. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2018.2833872(In Press)
Tao G (2003) Adaptive control design and analysis. Wiley-IEEE Press, Hoboken
Kleinman D (1968) On an iterative technique for Riccati equation computations. IEEE Trans Autom Control 13(1):114–115
Lu L, Lin W (1993) An iterative algorithm for the solution of the discrete-time algebraic Riccati equation. Linear Algebra Appl 188–189(1):465–488
Costa OLV, Aya JCC (1999) Temporal difference methods for the maximal solution of discrete-time coupled algebraic Riccati equations. In: Proceedings of the american control conference, San Diego. IEEE Press, pp 1791–1795
Gajic Z, Borno I (1975) Lyapunov iterations for optimal control of jump linear systems at steady state. IEEE Trans Autom Control 40(11):1971–1975
He W, Dong Y, Sun C (2016) Adaptive neural impedance control of a robotic manipulator with input saturation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 46(3):334–344
Shen H, Men Y, Wu Z, Park JH (2017) Nonfragile H∞ control for fuzzy Markovian jump systems under fast sampling singular perturbation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2017.2758381(In Press)
Xu Y, Lu R, Peng H, Xie K, Xue A (2017) Asynchronous dissipative state estimation for stochastic complex networks with quantized jumping coupling and uncertain measurements. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(2):268–277
Cheng J, Park JH, Karimi HR (2018) A flexible terminal approach to sampled-data exponentially synchronization of Markovian neural networks with time-varying delayed signals. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(8):2232–2244
Zhai D, An L, Li X, Zhang Q (2018) Adaptive fault-tolerant control for nonlinear systems with multiple sensor faults and unknown control directions. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(9):4436–4446
Zhai D, An L, Ye D, Zhang Q (2018) Adaptive reliable H∞ static output feedback control against Markovian jumping sensor failures. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(3):631–644
Liu D, Wei Q, Yan P (2015) Generalized policy iteration adaptive dynamic programming for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 45(12):1577–1591
Wei Q, Liu D (2014) Stable iterative adaptive dynamic programming algorithm with approximation errors for discrete-time nonlinear systems. Neural Comput Appl 24(6):1355–1367
Liang Y, Zhang H, Xiao G, Jiang H (2018) Reinforcement learning-based online adaptive controller design for a class of unknown nonlinear discrete-time systems with time delays. Neural Comput Appl 30(6):1733–1745
Lewis FL, Vrabie D (2009) Reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for feedback control. IEEE Circuits Syst Mag 9(3):32–50
Vrabie D, Lewis FL (2011) Adaptive dynamic programming for online solution of a zero-sum differential game. IET Control Theory Appl 9(3):353–360
Vrabie D, Lewis FL (2009) Adaptive optimal control algorithm for continuous-time nonlinear systems based on policy iteration. In: Proceedings of the 48th IEEE conference on decision and control, Shanghai, pp 73–79
Guo W, Si J, Liu F, Mei S (2018) Policy approximation in policy iteration approximate dynamic programming for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(7):2794–2807
Kiumarsi B, Lewis FL, Modares H, Karimpour A, Naghibi-Sistani MB (2014) Reinforcement Q-learning for optimal tracking control of linear discrete-time systems with unknown dynamics. Automatica 50(4):1167–1175
Liu YJ, Li S, Tong CT, Chen CLP (2019) Adaptive reinforcement learning control based on neural approximation for nonlinear discrete-time systems with unknown nonaffine dead-zone input. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(1):295–305
Wu HN, Luo B (2013) Simultaneous policy update algorithms for learning the solution of linear continuous-time H∞ state feedback control. Inf Sci 222(11):472–485
Mu C, Wang D, He H (2017) Data-driven finite-horizon approximate optimal control for discrete-time nonlinear systems using iterative HDP approach. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2017.2752845(In Press)
He X, Huang T, Yu J, Li C, Zhang Y (2017) A continuous-time algorithm for distributed optimization based on multiagent networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2017.2780194(In Press)
Yang X, He H, Liu Y (2017) Adaptive dynamic programming for robust neural control of unknown continuous-time nonlinear systems. IET Control Theory Appl 11(14):2307–2316
Xu W, Huang Z, Zuo L, He H (2017) Manifold-based reinforcement learning via locally linear reconstruction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(4):934–947
Alipour MM, Razavi SN, Derakhshi MRF, Balafar MA (2018) A hybrid algorithm using a genetic algorithm and multiagent reinforcement learning heuristic to solve the traveling salesman problem. Neural Comput Appl 30(9):2935–2951
Zhu Y, Zhao D (2015) A data-based online reinforcement learning algorithm satisfying probably approximately correct principle. Neural Comput Appl 26(4):775–787
Tang L, Liu Y, Tong S (2014) Adaptive neural control using reinforcement learning for a class of robot manipulator. Neural Comput Appl 25(1):135–141
Mu C, Ni Z, Sun C, He H (2017) Air-breathing hypersonic vehicle tracking control based on adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(3):584–598
Xie X, Yue D, Hu S (2017) Fault estimation observer design of discrete-time nonlinear systems via a joint real-time scheduling law. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 45(7):1451–1463
He S, Song J, Ding Z, Liu F (2015) Online adaptive optimal control for continuous-time Markov jump linear systems using a novel policy iteration algorithm. IET Control Theory Appl 9(10):1536–1543
Song J, He S, Liu F, Niu Y, Ding Z (2016) Data-driven policy iteration algorithm for optimal control of continuous-time Itô stochastic systems with Markovian jumps. IET Control Theory Appl 10(12):1431–1439
Song J, He S, Ding Z, Liu F (2016) A new iterative algorithm for solving H∞ control problem of continuous-time Markovian jumping linear systems based on online implementation. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 26(17):3737–3754
Gajic Z, Borno I (2000) General transformation for block diagonalization of weakly coupled linear systems composed of N-subsystems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Fundam Theory Appl 47(6):909–912
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61673001, 61722306, the Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Anhui Province under Grant 1608085J05, the Key Support Program of University Outstanding Youth Talent of Anhui Province under Grant gxydZD2017001, the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61833007 and the 111 Project under Grant B12018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Zhang, M., Fang, H. et al. Reinforcement learning and adaptive optimization of a class of Markov jump systems with completely unknown dynamic information. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 14311–14320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04180-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04180-2