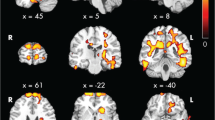
Abstract
Background
This study aimed to determine stroke incidence and assess the association between stroke and neurocognitive functioning in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods
Data was derived from the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) cohort study. Stroke incidence was calculated after confirming self-reports of stroke occurrence by chart review. Each participant with stroke was matched with three stroke-free participants and performance on selected neurocognitive measures was compared. Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were used to compare neurocognitive test scores. Effect size (ES) was estimated using a modified version of Cohen’s U3 metric that measures the excess percentage of the stroke group worse than the median of the control group.
Results
Of 891 subjects, five (0.56%) had a confirmed stroke prior to study entry. Median time at risk was 15.7 years [interquartile range, 12.5–18.4]. Estimated incidence rate of history of stroke was 36.8 per 100,000 children per year (95% confidence interval 15.3, 88.5). Controls and subjects with stroke were similar in age, CKD duration, race, and maternal education. ES for many of the neurocognitive comparisons was moderate to large. Subjects in the CKID cohort with a history of stroke had lower scores on spatial span reverse, spatial span forward, and design fluency, and worse parent ratings on BRIEF Metacognition Index compared to a matched sample of children with CKD without stroke.
Conclusions
Children with CKD have an increased incidence of prior ischemic stroke compared to the general pediatric population. A stroke history was associated with poorer performance on neurocognitive measures.

Graphical abstract
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Xu J, Arias E (2014) Mortality in the United States, 2013. NCHS Data Brief 178:1–8
Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Delling FN, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Ferguson JF, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Lutsey PL, Mackey JS, Matchar DB, Matsushita K, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, O'Flaherty M, Palaniappan LP, Pandey A, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Ritchey MD, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sampson UKA, Satou GM, Shah SH, Spartano NL, Tirschwell DL, Tsao CW, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P, American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee (2018) Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 137:e67–e492. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558
CDC (2017) 10 Leading Causes of Death by Age Group United States. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/images/lc-charts/leading_causes_of_death_by_age_group_2017_1100w850h.jpg. Accessed December 3, 2019
Ferriero DM, Fullerton HJ, Bernard TJ, Billinghurst L, Daniels SR, DeBaun MR, de Veber G, Ichord RN, Jordan LC, Massicotte P, Meldau J, Roach ES, Smith ER, American Heart Association Stroke Council and Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing (2019) Management of Stroke in neonates and children: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 50:e51–e96. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000183
Lehman LL, Khoury JC, Taylor JM, Yeramaneni S, Sucharew H, Alwell K, Moomaw CJ, Peariso K, Flaherty M, Khatri P, Broderick JP, Kissela BM, Kleindorfer DO (2018) Pediatric stroke rates over 17 years: report from a population-based study. J Child Neurol 33:463–467. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073818767039
Mallick AA, Ganesan V, Kirkham FJ, Fallon P, Hedderly T, McShane T, Parker AP, Wassmer E, Wraige E, Amin S, Edwards HB, Tilling K, O'Callaghan FJ (2014) Childhood arterial ischaemic stroke incidence, presenting features, and risk factors: a prospective population-based study. Lancet Neurol 13:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70290-4
Fullerton HJ, Wu YW, Zhao S, Johnston SC (2003) Risk of stroke in children: ethnic and gender disparities. Neurology 61:189–194
Agrawal N, Johnston SC, Wu YW, Sidney S, Fullerton HJ (2009) Imaging data reveal a higher pediatric stroke incidence than prior US estimates. Stroke 40:3415–3421. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.564633
Sacco RL, Kasner SE, Broderick JP, Caplan LR, Connors JJ, Culebras A, Elkind MS, George MG, Hamdan AD, Higashida RT, Hoh BL, Janis LS, Kase CS, Kleindorfer DO, Lee JM, Moseley ME, Peterson ED, Turan TN, Valderrama AL, Vinters HV; American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity and Metabolism (2013) An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 44:2064–2089. doi:https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e318296aeca
Kirkham FJ, Prengler M, Hewes DK, Ganesan V (2000) Risk factors for arterial ischemic stroke in children. J Child Neurol 15:299–307
Ganesan V, Prengler M, McShane MA, Wade AM, Kirkham FJ (2003) Investigation of risk factors in children with arterial ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 53:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10423
Lo W, Stephens J, Fernandez S (2009) Pediatric stroke in the United States and the impact of risk factors. J Child Neurol 24:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073808322665
Mackay MT, Wiznitzer M, Benedict SL, Lee KJ, Deveber GA, Ganesan V, International Pediatric Stroke Study Group (2011) Arterial ischemic stroke risk factors: the International Pediatric Stroke Study. Ann Neurol 69:130–140. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22224
Numis AL, Fox CK (2014) Arterial ischemic stroke in children: risk factors and etiologies. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 14:422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-013-0422-8
Kupferman JC, Zafeiriou DI, Lande MB, Kirkham FJ, Pavlakis SG (2017) Stroke and hypertension in children and adolescents. J Child Neurol 32:408–417. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073816685240
Toyoda K, Ninomiya T (2014) Stroke and cerebrovascular diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. Lancet Neurol 13:823–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70026-2
Tonelli M, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani R (2016) Epidemiology and mechanisms of uremia-related cardiovascular disease. Circulation 133:518–536. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018713
Seliger SL, Gillen DL, Longstreth WT Jr, Kestenbaum B, Stehman-Breen CO (2003) Elevated risk of stroke among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 64:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00101.x
Wu CL, Tsai CC, Kor CT, Tarng DC, Lian Ie B, Yang TH, Chiu PF, Chang CC (2016) Stroke and risks of development and progression of kidney diseases and end-stage renal disease: a nationwide population-based cohort study. PLoS One 11:e0158533. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158533
Hailpern SM, Melamed ML, Cohen HW, Hostetter TH (2007) Moderate chronic kidney disease and cognitive function in adults 20 to 59 years of age: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2205–2213. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006101165
Douven E, Schievink SH, Verhey FR, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Aalten P, Staals J, Kohler S (2016) The cognition and affect after stroke - a prospective evaluation of risks (CASPER) study: rationale and design. BMC Neurol 16:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-016-0588-1
Bugnicourt JM, Godefroy O, Chillon JM, Choukroun G, Massy ZA (2013) Cognitive disorders and dementia in CKD: the neglected kidney-brain axis. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2012050536
Hajek CA, Yeates KO, Anderson V, Mackay M, Greenham M, Gomes A, Lo W (2014) Cognitive outcomes following arterial ischemic stroke in infants and children. J Child Neurol 29:887–894. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073813491828
Studer M, Boltshauser E, Capone Mori A, Datta A, Fluss J, Mercati D, Hackenberg A, Keller E, Maier O, Marcoz JP, Ramelli GP, Poloni C, Schmid R, Schmitt-Mechelke T, Wehrli E, Heinks T, Steinlin M (2014) Factors affecting cognitive outcome in early pediatric stroke. Neurology 82:784–792. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000162
Hooper SR, Gerson AC, Butler RW, Gipson DS, Mendley SR, Lande MB, Shinnar S, Wentz A, Matheson M, Cox C, Furth SL, Warady BA (2011) Neurocognitive functioning of children and adolescents with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1824–1830. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.09751110
Ruebner RL, Laney N, Kim JY, Hartung EA, Hooper SR, Radcliffe J, Furth SL (2015) Neurocognitive dysfunction in children, adolescents, and young adults with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.08.025
Hartung EA, Kim JY, Laney N, Hooper SR, Radcliffe J, Port AM, Gur RC, Furth SL (2016) Evaluation of neurocognition in youth with CKD using a novel computerized neurocognitive battery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11:39–46. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.02110215
Chen K, Didsbury M, van Zwieten A, Howell M, Kim S, Tong A, Howard K, Nassar N, Barton B, Lah S, Lorenzo J, Strippoli G, Palmer S, Teixeira-Pinto A, Mackie F, McTaggart S, Walker A, Kara T, Craig JC, Wong G (2018) Neurocognitive and educational outcomes in children and adolescents with CKD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 13:387–397. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.09650917
Steinberg A, Efrat R, Pomeranz A, Drukker A (1985) Computerized tomography of the brain in children with chronic renal failure. Int J Pediatr Nephrol 6:121–126
Baxter P, Gardner-Medwin D, Green SH, Moss C (1993) Congenital livedo reticularis and recurrent stroke-like episodes. Dev Med Child Neurol 35:917–921
Bodas P, Huang A, O'Riordan MA, Sedor JR, Dell KM (2013) The prevalence of hypertension and abnormal kidney function in children with sickle cell disease -a cross sectional review. BMC Nephrol 14:237. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-14-237
Caksen H, Odabas D, Akbayram S, Faik Oner A, Arslan S, Cesur Y, Uner A (2003) Silent stroke in a case of beta-thalassemia major associated with chronic renal failure and diabetes mellitus. J Child Neurol 18:798–800
Qvist E, Pihko H, Fagerudd P, Valanne L, Lamminranta S, Karikoski J, Sainio K, Ronnholm K, Jalanko H, Holmberg C (2002) Neurodevelopmental outcome in high-risk patients after renal transplantation in early childhood. Pediatr Transplant 6:53–62
Valanne L, Qvist E, Jalanko H, Holmberg C, Pihko H (2004) Neuroradiologic findings in children with renal transplantation under 5 years of age. Pediatr Transplant 8:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1397-3142.2003.00125.x
Furth SL, Cole SR, Moxey-Mims M, Kaskel F, Mak R, Schwartz G, Wong C, Munoz A, Warady BA (2006) Design and methods of the chronic kidney disease in children (CKiD) prospective cohort study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:1006–1015. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.01941205
Lezak MDHD, Bigler ED, Tranel D (2012) Neuropsychological assessment, 5th edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences 2nd edn. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NY
Moodalbail DG, Reiser KA, Detre JA, Schultz RT, Herrington JD, Davatzikos C, Doshi JJ, Erus G, Liu HS, Radcliffe J, Furth SL, Hooper SR (2013) Systematic review of structural and functional neuroimaging findings in children and adults with CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1429–1448. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.11601112
Grelli KN, Gindville MC, Walker CH, Jordan LC (2016) Association of blood pressure, blood glucose, and temperature with neurological outcome after childhood stroke. JAMA Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0992
Nathanson S, Kwon T, Elmaleh M, Charbit M, Launay EA, Harambat J, Brun M, Ranchin B, Bandin F, Cloarec S, Bourdat-Michel G, Pietrement C, Champion G, Ulinski T, Deschenes G (2010) Acute neurological involvement in diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1218–1228. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.08921209
Khalid M, Andreoli S (2018) Extrarenal manifestations of the hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC HUS). Pediatr Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-4105-1
Gallo EG, Gianantonio CA (1995) Extrarenal involvement in diarrhoea-associated haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 9:117–119
Signorini E, Lucchi S, Mastrangelo M, Rapuzzi S, Edefonti A, Fossali E (2000) Central nervous system involvement in a child with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 14:990–992
DiMario FJ Jr, Bronte-Stewart H, Sherbotie J, Turner ME (1987) Lacunar infarction of the basal ganglia as a complication of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. MRI and clinical correlations. Clin Pediatr 26:586–590. https://doi.org/10.1177/000992288702601106
Trevathan E, Dooling EC (1987) Large thrombotic strokes in hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J Pediatr 111:863–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80207-x
Hahn JS, Havens PL, Higgins JJ, O'Rourke PP, Estroff JA, Strand R (1989) Neurological complications of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J Child Neurol 4:108–113. https://doi.org/10.1177/088307388900400206
Lopez M, Huete I, Hernandez M (2017) Acute cerebrovascular events associated to hemolytic uremic syndrome: description of two pediatric cases. Rev Chil Pediatr 88:640–646. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0370-41062017000500011
Cimolai N, Morrison BJ, Carter JE (1992) Risk factors for the central nervous system manifestations of gastroenteritis-associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Pediatrics 90:616–621
Eisenhauer PB, Jacewicz MS, Conn KJ, Koul O, Wells JM, Fine RE, Newburg DS (2004) Escherichia coli Shiga toxin 1 and TNF-alpha induce cytokine release by human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Microb Pathog 36:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2003.11.004
Acknowledgments
Data reviewed in this manuscript were collected by the Chronic Kidney Disease in children prospective cohort study (CKiD) with clinical coordinating centers (Principal Investigators) at Children’s Mercy Hospital and the University of Missouri-Kansas City (Bradley Warady, MD) and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (Susan Furth, MD, PhD), Central Biochemistry Laboratory (George Schwartz, MD) at the University of Rochester Medical Center, and data coordinating center (Alvaro Muñoz, PhD and Derek Ng, PhD) at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Funding
The CKiD is funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, with additional funding from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (U01-DK-66143, U01-DK-66174, U01-DK-082194, and U01-DK66116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial disclosure
The authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PPTX 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kupferman, J.C., Matheson, M.B., Lande, M.B. et al. Increased history of ischemic stroke and decreased neurocognitive performance in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 35, 1315–1321 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04503-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04503-9