Abstract
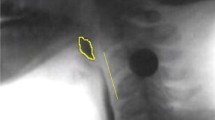
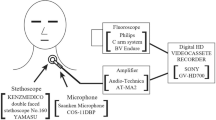
This study was designed to further our understanding of a potentially significant clinical event of negative nasal airflow near the end of the respiratory pause (inhibition) to accommodate swallowing. This negative flow, referred to as “SNIF,” or swallow noninspiratory flow, occurs at the onset of airway reestablishment at the conclusion of the oropharyngeal swallow. Using simultaneous digital video fluoroscopic and nasal respiratory airflow recordings on 82 healthy adults (21–97 years old), the objectives of this study were to determine (1) the frequency of occurrence of SNIF during a 5-ml natural cup-drinking task, (2) differences in SNIF occurrence by age group, and (3) the temporal relationship between SNIF and other swallowing events. Results revealed that for most participants SNIF was observed in both swallowing trials. There was a statistically significant difference in SNIF occurrence by age category, with SNIF observed less frequently in the oldest participants. The peak onset of SNIF is closely related to the first release of contact between the soft palate and tongue base with the posterior pharyngeal wall and opening of the laryngeal vestibule. Based on this, and in agreement with previous investigators, we suggest that this negative flow may be related to a partial vacuum established by the relaxation of pharyngeal contraction near the conclusion of the pharyngeal swallow. The more frequent occurrence of SNIF in younger adults and less in older adults suggests a reduction in pharyngeal pressure associated with healthy aging.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodsky MB, McFarland DH, Dozier TS, Blair J, Ayers C, Michel Y, Gillespie MB, Day TA, Martin-Harris B. Respiratory-swallow phase patterns and their relationship to swallowing impairment in patients treated for oropharyngeal cancer. Head Neck. 2010;32:481–9.
Dozier TS, Brodsky MB, Michel Y, Walters BC Jr, Martin-Harris B. Coordination of swallowing and respiration in normal sequential cup swallows. Laryngoscope. 2006;116:1489–93.
Martin BJ, Logemann JA, Shaker R, Dodds WJ. Coordination between respiration and swallowing: Respiratory phase relationships and temporal integration. J Appl Physiol. 1994;76:714–23.
Martin BJW. The influence of deglutition on respiration. Evanston, IL: Northwestern University; 1991.
Martin-Harris B, Brodsky MB, Michel Y, Ford CL, Walters B, Heffner J. Breathing and swallowing dynamics across the adult lifespan. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;131:762–70.
Martin-Harris B, Brodsky MB, Price CC, Michel Y, Walters B. Temporal coordination of pharyngeal and laryngeal dynamics with breathing during swallowing: single liquid swallows. J Appl Physiol. 2003;94:1735–43.
Martin-Harris B, Michel Y, Castell DO. Physiologic model of oropharyngeal swallowing revisited. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;133:234–40.
Palmer JB, Hiiemae KM. Eating and breathing: Interactions between respiration and feeding on solid food. Dysphagia. 2003;18:169–78.
Paydarfar D, Gilbert RJ, Poppel CS, Nassab PF. Respiratory phase resetting and airflow changes induced by swallowing in humans. J Physiol (Lond). 1995;483:273–88.
Perlman AL, Ettema SL, Barkmeier J. Respiratory and acoustic signals associated with bolus passage during swallowing. Dysphagia. 2000;15:89–94.
Perlman AL, He X, Barkmeier J, Van Leer E. Bolus location associated with videofluoroscopic and respirodeglutometric events. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2005;48:21–33.
McFarland DH, Lund JP, Gagner M. Effects of posture on the coordination of respiration and swallowing. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:2431–7.
McFarland DH, Lund JP. Modification of mastication and respiration during swallowing in the adult human. J Neurophysiol. 1995;74:1509–17.
McFarland DH, Lund JP. An investigation of the coupling between respiration, mastication, and swallowing in the awake rabbit. J Neurophysiol. 1993;69:95–108.
Doty RW, Bosma JF. An electromyographic analysis of reflex deglutition. J Neurophysiol. 1956;19:44–60.
Hårdemark Cedborg AI, Sundman E, Bodén K, Hedström HW, Kuylenstierna R, Ekberg O, Eriksson LI. Co-ordination of spontaneous swallowing with respiratory airflow and diaphragmatic and abdominal muscle activity in healthy adult humans. Exp Physiol. 2009;94:459–68.
Vantrappen G, Hellemans J. Studies on the normal deglutition complex. Dig Dis Sci. 1967;12:255–66.
Hirst LJ, Ford GA, Gibson GJ, Wilson JA. Swallow-induced alterations in breathing in normal older people. Dysphagia. 2002;17:152–61.
McConnel FM. Analysis of pressure generation and bolus transit during pharyngeal swallowing. Laryngoscope. 1988;98:71–8.
Sokol EM, Heitmann P, Wolf BS, Cohen BR. Simultaneous cineradiographic and manometric study of the pharynx, hypopharynx, and cervical esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1966;51:960–74.
Feroah TR, Forster HV, Fuentes CG, Lang IM, Beste D, Martino P, Pan L, Rice T. Effects of spontaneous swallows on breathing in awake goats. J Appl Physiol. 2002;92:1923–35.
Atkinson M, Kramer P, Wyman S, Ingelfinger F. The dynamics of swallow. I. Normal pharyngeal mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1957;36:581–98.
Kahrilas PJ, Dodds WJ, Dent J, Logemann JA, Shaker R. Upper esophageal sphincter function during deglutition. Gastroenterology. 1988;95:52–62.
Odanaka T. Studies on the swallow respiration. J Physiol Soc Jpn. 1952;14:114–9.
Yamamoto T. Experimental studies for swallowing respiration. Otologica (Kyoto). 1956;49:346–61.
Kawasaki M, Ogura JH, Takenouchi S. Neurophysiologic observations of normal deglutition. I. Its relationship to the respiratory cycle. Laryngoscope. 1964;74:1747–65.
Butler S, Stuart A, Wilhelm E, Rees C, Williamson J, Kritchevsky S. The effects of aspiration status, liquid type, and bolus volume on pharyngeal peak pressure in healthy older adults. Dysphagia. doi:10.1007/s00455-010-9290-4.
Meier-Ewert HK, Van Herwaarden MA, Gideon RM, Castell JA, Achem S, Castell DO. Effect of age on differences in upper esophageal sphincter and pharynx pressures between patients with dysphagia and control subjects. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:35–40.
Tracy JF, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Jacob P, Kobara M, Krugler C. Preliminary observations on the effects of age on oropharyngeal deglutition. Dysphagia. 1989;4:90–4.
Shaw DW, Cook IJ, Gabb M, Holloway RH, Simula ME, Panagopoulos V, Dent J. Influence of normal aging on oral-pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter function during swallowing. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1995;268:G389–96.
Lee J, Steele CM, Chau T. Classification of healthy and abnormal swallows based on accelerometry and nasal airflow signals. Artif Intell Med. 2011;52:17–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brodsky, M.B., McFarland, D.H., Michel, Y. et al. Significance of Nonrespiratory Airflow During Swallowing. Dysphagia 27, 178–184 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-011-9350-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-011-9350-4