Abstract
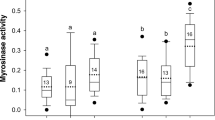
A Sebacinales species was recovered from a clone library made from a pooled rhizosphere sample of Nicotiana attenuata plants from 14 native populations. Axenic cultures of the related species, Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera, were used to examine their effects on plant performance. Inoculation of N. attenuata seeds with either fungus species stimulated seed germination and increased growth and stalk elongation. S. vermifera inoculated plants flowered earlier, produced more flowers and matured more seed capsules than did non-inoculated plants. Jasmonate treatment during rosette-stage growth, which slows growth and elicits herbivore resistance traits, erased differences in vegetative, but not reproductive performance resulting from S. vermifera inoculation. Total nitrogen and phosphorous contents did not differ between inoculated and control plants, suggesting that the performance benefits of fungal inoculation did not result from improvements in nutritional status. Since the expression of trypsin proteinase inhibitors (TPI), defensive proteins which confer resistance to attack from Manduca sexta larvae, incur significant growth and fitness costs for the plant, we examined the effect of S. vermifera inoculation on herbivore resistance and TPI activity. After 10 days of feeding on S. vermifera-inoculated plants, larval mass was 46% higher and TPI activity was 48% lower than that on non-inoculated plants. These results suggest that Sebacina spp. may interfere with defense signaling and allow plants to increase growth rates at the expense of herbivore resistance mediated by TPIs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen TR, Millar T, Berch SM, Berbee ML (2003) Culturing and direct DNA extraction find different fungi from the same ericoid mycorrhizal roots. New Phytol 160:255–272
Baldwin IT (2001) An ecologically motivated analysis of plant–herbivore interactions in native tobacco. Plant Physiol 127:1449–1458
Baldwin IT, Preston CA (1999) The eco-physiological complexity of plant responses to insect herbivores. Planta 208:137–145
Borowicz VA (2001) Do arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alter plant–pathogen relations? Ecology 82:3057–3068
Bubner B, Gase K, Baldwin IT (2004) Two-fold differences are the detection limit for determining transgene copy numbers in plants by real-time PCR. BMC Biotechnol 4:1–11
van Dam NM, Horn M, Mares M, Baldwin IT (2001) Ontogeny constrains systemic protease inhibitor response in Nicotiana attenuata. J Chem Ecol 27:547–568
Gange AC (2001) Species-specific responses of a root- and shoot-feeding insect to arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of its host plant. New Phytol 150:611–618
Gange AC, Nice HE (1997) Performance of the thistle gall fly, Urophora cardui, in relation to host plant nitrogen and mycorrhizal colonization. New Phytol 137:335–343
Gange AC, Stagg PG, Ward LK (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affect phytophagous insect specialism. Ecol Lett 5:11–15
Gardes M, Bruns TD (1993) ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes—application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol Ecol 2:113–118
Gehring CA, Whitham TG (1991) Herbivore-driven mycorrhizal mutualism in insect-susceptible pinyon pine. Nature 353:556–557
Gehring CA, Whitham TG (1995) Duration of herbivore removal and environmental-stress affect the ectomycorrhizae of pinyon pines. Ecology 76:2118–2123
Glawe GA, Zavala JA, Kessler A, Van Dam NM, Baldwin IT (2003) Ecological costs and benefits correlated with trypsin protease inhibitor production in Nicotiana attenuata. Ecology 84:79–90
Glen M, Tommerup IC, Bougher NL, O’Brien PA (2002) Are Sebacinaceae common and widespread ectomycorrhizal associates of Eucalyptus species in Australian forests? Mycorrhiza 12:243–247
Goverde M, van der Heijden MGA, Wiemken A, Sanders IR, Erhardt A (2000) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi influence life history traits of a lepidopteran herbivore. Oecologia 125:362–369
Grime JP, Mackey JML, Hillier SH, Read DJ (1987) Floristic diversity in a model system using experimental microcosms. Nature 328:420–422
Halitschke R, Baldwin IT (2003) Antisense LOX expression increases herbivore performance by decreasing defense responses and inhibiting growth-related transcriptional reorganization in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant J 36:794–807
Halitschke R, Schittko U, Pohnert G, Boland W, Baldwin IT (2001) Molecular interactions between the specialist herbivore Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera, Sphingidae) and its natural host Nicotiana attenuata. III. Fatty acid–amino acid conjugates in herbivore oral secretions are necessary and sufficient for herbivore-specific plant responses. Plant Physiol 125:711–717
Hause B, Maier W, Miersch O, Kramell R, Strack D (2002) Induction of jasmonate biosynthesis in arbuscular mycorrhizal barley roots. Plant Physiol 130:1213–1220
Hogeweg P, Hesper B (1984) The alignment of sets of sequences and the construction of phylogenetic trees: an integrated method. J Mol Evol 20:175–186
Käfer E (1977) Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergillus and its chromosomal aberrations. Adv Genet 19:33–131
Kaldorf M, Kuhn AJ, Schroder WH, Hildebrandt U, Bothe H (1999) Selective element deposits in maize colonized by a heavy metal tolerance conferring arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. J Plant Physiol 154:718–728
Karandashov V, Nagy R, Wegmuller S, Amrhein N, Bucher M (2004) Evolutionary conservation of a phosphate transporter in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6285–6290
Karban R, Baldwin IT (1997) Induced responses to herbivory. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Keinanen M, Oldham NJ, Baldwin IT (2001) Rapid HPLC screening of jasmonate-induced increases in tobacco alkaloids, phenolics, and diterpene glycosides in Nicotiana attenuata. J Agric Food Chem 49:3553–3558
Kessler A, Baldwin IT (2002) Plant responses to insect herbivory: the emerging molecular analysis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:299–328
Kottke I, Beiter A, Weiss M, Haug I, Oberwinkler F, Nebel M (2003) Heterobasidiomycetes form symbiotic associations with hepatics: Jungermanniales have sebacinoid mycobionts while Aneura pinguis (Metzgeriales) is associated with a Tulasnella species. Mycol Res 107:957–968
Krügel T, Lim M, Gase K, Halitschke R, Baldwin IT (2002) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Nicotiana attenuata, a model ecological expression system. Chemoecology 12:177–183
Kula AAR, Hartnett DC, Wilson GWT (2005) Effect of mycorrhizal symbiosis on tallgrass prairie plant–herbivore interactions. Ecol Lett 8:61–69
Kumari R, Kishan H, Bhoon YK, Varma A (2003) Colonization of cruciferous plants by Piriformospora indica. Curr Sci India 85:1672–1674
Little LR, Maun MA (1996) The “Ammophila problem” revisited: a role for mycorrhizal fungi. J Ecol 84:1–7
Lynds GY, Baldwin IT (1998) Fire, nitrogen, and defensive plasticity in Nicotiana attenuata. Oecologia 115:531–540
Marulanda A, Azcon R, Ruiz-Lozano JM (2003) Contribution of six arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates to water uptake by Lactuca sativa plants under drought stress. Physiol Plantarum 119:526–533
McCloud ES, Baldwin IT (1997) Herbivory and caterpillar regurgitants amplify the wound-induced increases in jasmonic acid but not nicotine in Nicotiana sylvestris. Planta 203:430–435
Norman JR, Atkinson D, Hooker JE (1996) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal-induced alteration to root architecture in strawberry and induced resistance to the root pathogen Phytophthora fragariae. Plant Soil 185:191–198
van der Peer Y, De Watcher R (1994) TREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput Appl Biosci 10:569–570
Peškan-Berghöfer T, Shahollari B, Giong PH, Hehl S, Markert C, Blanke V, Kost G, Varma A, Oelmüller R (2004) Association of Piriformospora indica with Arabidopsis thaliana roots represents a novel system to study beneficial plant–microbe interactions and involves early plant protein modifications in the endoplasmic reticulum and at the plasma membrane. Physiol Plantarum 122:465–477
Rai M, Acharya D, Singh A, Varma A (2001) Positive growth responses of the medicinal plants Spilanthes calva and Withania somnifera to inoculation by Piriformospora indica in a field trial. Mycorrhiza 11:123–128
Rausch C, Daram P, Brunner S, Jansa J, Laloi M, Leggewie G, Amrhein N, Bucher M (2001) A phosphate transporter expressed in arbuscule-containing cells in potato. Nature 414:462–466
Read DJ (1998) Biodiversity: plants on the web. Nature 396:22–23
Regvar M, Gogala N, Zalar P (1996) Effects of jasmonic acid on mycorrhizal Allium sativum. New Phytol 134:703–707
Regvar M, Gogala N, Znidarsic N (1997) Jasmonic acid effects mycorrhization of spruce seedlings with Laccaria laccata. Trees Struct Funct 11:511–514
Roda A, Halitschke R, Steppuhn A, Baldwin IT (2004) Individual variability in herbivore-specific elicitors from the plant’s perspective. Mol Ecol 13:2421–2433
Ruiz-Lozano JM, Azcón R (1995) Hyphal contribution to water uptake in mycorrhizal plants as affected by the fungal species and water status. Physiol Plantarum 95:472–478
Ruiz-Lozano JM, Azcón R, Palma JM (1996) Superoxide dismutase activity in arbuscular mycorrhizal Lactuca sativa plants subjected to drought stress. New Phytol 134:327–333
Ruiz-Lozano JM, Collados C, Barea JM, Azcón R (2001) Cloning of cDNAs encoding SODs from lettuce plants which show differential regulation by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis and by drought stress. J Exp Bot 52:2241–2242
Sahay NS, Varma A (1999) Piriformospora indica: a new biological hardening tool for micropropagated plants. FEMS Microbiol Lett 181:297–302
Schittko U, Hermsmeier D, Baldwin IT (2001) Molecular interactions between the specialist herbivore Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera, Sphingidae) and its natural host Nicotiana attenuata. II. Accumulation of plant mRNAs in response to insect-derived cues. Plant Physiol 125:701–710
Selosse MA, Bauer R, Moyersoen B (2002a) Basal hymenomycetes belonging to the Sebacinaceae are ectomycorrhizal on temperate deciduous trees. New Phytol 155:183–195
Selosse MA, Weiss M, Jany JL, Tillier A (2002b) Communities and populations of sebacinoid basidiomycetes associated with the achlorophyllous orchid Neottia nidus-avis (L.) LCM Rich. and neighbouring tree ectomycorrhizae. Mol Ecol 11:1831–1844
Smith SE, Read DJ (1997) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic, San Diego, CA, USA
Tajima F, Nei M (1984) Estimation of evolutionary distance between nucleotide-sequences. Mol Biol Evol 1:269–285
Taylor DL, Bruns TD, Szaro TM, Hodges SA (2003) Divergence in mycorrhizal specialization within Hexalectris spicata (Orchidaceae), a nonphotosynthetic desert orchid. Am J Bot 90:1168–1179
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Trotta A, Varese GC, Gnavi E, Fusconi A, Sampo S, Berta G (1996) Interactions between the soilborne root pathogen Phytophthora nicotianae var parasitica and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae in tomato plants. Plant Soil 185:199–209
Urban A, Weiss M, Bauer R (2003) Ectomycorrhizas involving sebacinoid mycobionts. Mycol Res 107:3–14
Varma A, Verma S, Sudha, Sahay N, Butehorn B, Franken P (1999) Piriformospora indica, a cultivable plant-growth-promoting root endophyte. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2741–2744
Verma S, Varma A, Rexer KH, Hassel A, Kost G, Sarbhoy A, Bisen P, Bütehorn B, Franken P (1998) Piriformospora indica, gen. et sp. nov., a new root-colonizing fungus. Mycologia 90:896–903
Vicari M, Hatcher PE, Ayres PG (2002) Combined effect of foliar and mycorrhizal endophytes on an insect herbivore. Ecology 83:2452–2464
Warcup JH (1988) Mycorrhizal associations of isolates of Sebacina vermifera. New Phytol 110:227–231
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setala H, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science 304:1629–1633
Weiss M, Selosse MA, Rexer KH, Urban A, Oberwinkler F (2004) Sebacinales: a hitherto overlooked cosm of heterobasidiomycetes with a broad mycorrhizal potential. Mycol Res 108:1003–1010
Zavala JA, Baldwin IT (2004) Fitness benefits of trypsin proteinase inhibitor expression in Nicotiana attenuata are greater than their costs when plants are attacked. BMC Ecol 4:11 (DOI 10.1186/1472-6785-4-11)
Zavala JA, Patankar AG, Gase K, Hui DQ, Baldwin IT (2004a) Manipulation of endogenous trypsin proteinase inhibitor production in Nicotiana attenuata demonstrates their function as antiherbivore defenses. Plant Physiol 134:1181–1190
Zavala JA, Patankar AG, Gase K, Baldwin IT (2004b) Constitutive and inducible trypsin proteinase inhibitor production incurs large fitness costs in Nicotiana attenuata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1607–1612
Acknowledgements
We thank the Max-Planck-Gesellschaft for financial support of this study and Prof. A. Varma and Dr. P. Franken for providing us with the two fungal clones.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Christian Koerner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barazani, O., Benderoth, M., Groten, K. et al. Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera increase growth performance at the expense of herbivore resistance in Nicotiana attenuata. Oecologia 146, 234–243 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-005-0193-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-005-0193-2