Abstract
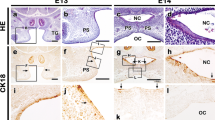
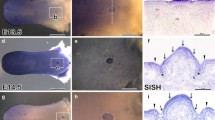
The molecular mechanisms for epithelial differentiation have been studied by observing skin development in embryogenesis, but the early signaling modulations involved in tongue epithelial differentiation are not completely understood. Based on the gene expression patterns of the Fgf signaling molecules and previous results from Fgf10 and Fgfr2b knockout mice, it was hypothesized that there would be fundamental signaling interactions through the epithelial Fgfr2b and its mesenchymal ligand Fgf10 to regulate tongue epithelium differentiation. To elucidate these reciprocal interactions in tongue epithelial differentiation, this study employed an in vitro tongue organ culture system with antisense-oligodeoxynucleotides (AS-ODNs) and recombinant protein-soaked bead implantation for the loss-of-function and gain-of-function studies. Functional analysis of Fgf signaling revealed precise reciprocal interactions, which showed that mesenchymal Fgf10 rather than Fgf7 modulates tongue epithelial differentiation via Fgfr2b in a temporal- and spatial-specific manner.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aszterbaum M, Menon GK, Feingold KR, Williams ML (1992) Ontogeny of the epidermal barrier to water loss in the rat: correlation of function with stratum corneum structure and lipid content. Pediatr Res 31:308–317
Dhouailly D, Olivera-Martinez I, Fliniaux I, Missier S, Viallet JP, Thelu J (2004) Skin field formation: morphogenetic events. Int J Dev Biol 48:85–91
Eswarakumar VP, Lax I, Schlessinger J (2005) Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:139–149
Finch PW, Cunha GR, Rubin JS, Wong J, Ron D (1995) Pattern of keratinocyte growth factor and keratinocyte growth factor receptor expression during mouse fetal development suggests a role in mediating morphogenetic mesenchymal-epithelial interactions. Dev Dyn 203:223–240
Guo L, Yu QC, Fuchs E (1993) Targeting expression of keratinocyte growth factor to keratinocytes elicits striking changes in epithelial differentiation in transgenic mice. EMBO J 12:973–986
Guo L, Degenstein L, Fuchs E (1996) Keratinocyte growth factor is required for hair development but not for wound healing. Genes Dev 10:165–175
Hardman MJ, Sisi P, Banbury DN, Byrne C (1998) Patterned acquisition of skin barrier function during development. Development 125:1541–1552
Hoffman MP, Kidder BL, Steinberg ZL, Lakhani S, Ho S, Kleinman HK, Larsen M (2002) Gene expression profiles of mouse submandibular gland development: FGFR1 regulates branching morphogenesis in vitro through BMP- and FGF-dependent mechanisms. Development 129:5767–5778
Huang L, Pu Y, Alam S, Birch L, Prins GS (2005) The role of Fgf10 signaling in branching morphogenesis and gene expression of the rat prostate gland: lobe-specific suppression by neonatal estrogens. Dev Biol 278:396–414
Jahoda CA, Horne KA, Oliver RF (1984) Induction of hair growth by implantation of cultured dermal papilla cells. Nature 311:560–562
Johnson DE, Williams LT (1993) Structural and functional diversity in the FGF receptor multigene family. Adv Cancer Res 60:1–41
Jonker L, Kist R, Aw A, Wappler I, Peters H (2004) Pax9 is required for filiform papilla development and suppresses skin-specific differentiation of the mammalian tongue epithelium. Mech Dev 121:1313–1322
Kettunen P, Laurikkala J, Itaranta P, Vainio S, Itoh N, Thesleff I (2000) Associations of FGF-3 and FGF-10 with signaling networks regulating tooth morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 219:322–332
Kim JY, Mochizuki T, Akita K, Jung HS (2003) Morphological evidence of the importance of epithelial tissue during mouse tongue development. Exp Cell Res 290:217–226
Kim JY, Cho SW, Lee MJ, Hwang HJ, Lee JM, Lee SI, Muramatsu T, Shimono M, Jung HS (2005) Inhibition of connexin 43 alters Shh and Bmp-2 expression patterns in embryonic mouse tongue. Cell Tissue Res 320:409–415
Kim JY, Lee MJ, Cho KW, Lee JM, Kim YJ, Kim JY, Jung HI, Cho JY, Cho SW, Jung HS (2009) Shh and ROCK1 modulate the dynamic epithelial morphogenesis in circumvallate papilla development. Dev Biol 325:273–280
Maas-Szabowski N, Shimotoyodome A, Fusenig NE (1999) Keratinocyte growth regulation in fibroblast cocultures via a double paracrine mechanism. J Cell Sci 112:1843–1853
Mailleux AA, Tefft D, Ndiaye D, Itoh N, Thiery JP, Warburton D, Bellusci S (2001) Evidence that SPROUTY2 functions as an inhibitor of mouse embryonic lung growth and morphogenesis. Mech Dev 102:81–94
Marshall D, Hardman MJ, Byrne C (2000) SPRR1 gene induction and barrier formation occur as coordinated moving fronts in terminally differentiating epithelia. J Invest Dermatol 114:967–975
Mason IJ, Fuller-Pace F, Smith R, Dickson C (1994) FGF-7 (keratinocyte growth factor) expression during mouse development suggests roles in myogenesis, forebrain regionalisation and epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. Mech Dev 45:15–30
McKeehan WL, Wang F, Kan M (1998) The heparan sulfate-fibroblast growth factor family: diversity of structure and function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 59:135–176
Miralles F, Czernichow P, Ozaki K, Itoh N, Scharfmann R (1999) Signaling through fibroblast growth factor receptor 2b plays a key role in the development of the exocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6267–6272
Nie Y, Vigues S, Hobbs JR, Conn GL, Munger SD (2005) Distinct contributions of T1R2 and T1R3 taste receptor subunits to the detection of sweet stimuli. Curr Biol 15:1948–1952
Ornitz DM, Xu J, Colvin JS, McEwen DG, MacArthur CA, Coulier F, Gao G, Goldfarb M (1996) Receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family. J Biol Chem 271:15292–15297
Orr-Urtreger A, Bedford MT, Burakova T, Arman E, Zimmer Y, Yayon A, Givol D, Lonai P (1993) Developmental localization of the splicing alternatives of fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 (FGFR2). Dev Biol 158:475–486
Park WY, Miranda B, Lebeche D, Hashimoto G, Cardoso WV (1998) FGF-10 is a chemotactic factor for distal epithelial buds during lung development. Dev Biol 201:125–134
Peters KG, Werner S, Chen G, Williams LT (1992) Two FGF receptor genes are differentially expressed in epithelial and mesenchymal tissues during limb formation and organogenesis in the mouse. Development 114:233–243
Petiot A, Conti FJ, Grose R, Revest JM, Hodivala-Dilke KM, Dickson C (2003) A crucial role for Fgfr2-IIIb signalling in epidermal development and hair follicle patterning. Development 130:5493–5501
Pispa J, Thesleff I (2003) Mechanisms of ectodermal organogenesis. Dev Biol 262:195–205
Post M, Souza P, Liu J, Tseu I, Wang J, Kuliszewski M, Tanswell AK (1996) Keratinocyte growth factor and its receptor are involved in regulating early lung branching. Development 122:3107–3115
Rice R, Spencer-Dene B, Connor EC, Gritli-Linde A, McMahon AP, Dickson C, Thesleff I, Rice DP (2004) Disruption of Fgf10/Fgfr2b-coordinated epithelial-mesenchymal interactions causes cleft palate. J Clin Invest 113:1692–1700
Roop D (1995) Defects in the barrier. Science 267:474–475
Steinberg Z, Myers C, Heim VM, Lathrop CA, Rebustini IT, Stewart JS, Larsen M, Hoffman MP (2005) FGFR2b signaling regulates ex vivo submandibular gland epithelial cell proliferation and branching morphogenesis. Development 132:1223–1234
Tao H, Shimizu M, Kusumoto R, Ono K, Noji S, Ohuchi H (2005) A dual role of FGF10 in proliferation and coordinated migration of epithelial leading edge cells during mouse eyelid development. Development 132:3217–3230
Veltmaat JM, Relaix F, Le LT, Kratochwil K, Sala FG, van Veelen W, Rice R, Spencer-Dene B, Mailleux AA, Rice DP, Thiery JP, Bellusci S (2006) Gli3-mediated somitic Fgf10 expression gradients are required for the induction and patterning of mammary epithelium along the embryonic axes. Development 133:2325–2335
Williams ML, Feingold KR (1998) Barrier function of neonatal skin. J Pediatr 133:467–468
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wern-Joo Sohn and Hye-In Jung: contributed equally to this work.
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (R13-2008-009-01002-0)", and by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD)” (KRF-2007-E00124).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohn, WJ., Jung, HI., Choi, MA. et al. Reciprocal interactions of Fgf10/Fgfr2b modulate the mouse tongue epithelial differentiation. Cell Tissue Res 345, 265–273 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1204-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1204-8