Abstract
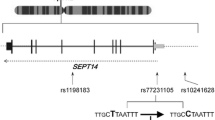
Inflammatory processes have been implicated in the cascade of events that lead to nerve cell death. In the nervous system, a number of genes involved in inflammation pathways are regulated post-transcriptionally via the interaction of their mRNAs with specific RNA-binding Hu proteins, the vertebrate homologues of the Drosophila ELAV (for embryonic lethal abnormal vision). The gene encoding ELAVL4, a member of the Hu family of proteins, is located 2 Mb from the chromosome 1p linkage region peak for age-at-onset (AAO) of Parkinson disease (PD) (LOD=3.41). Nine single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in ELAVL4 were genotyped for 266 multiplex families (1,223 samples). Additional genotyping in 377 singleton families was performed for a subset of five SNPs (SNPs 1–5) that were not in linkage disequilibrium. SNP 2 (located in the first intron of ELAVL4) showed a strong significant association with AAO of PD (P=0.006), and SNP 5 (a coding SNP in ELAVL4) showed a moderately significant association (P=0.035). Haplotype analysis revealed that the A-C haplotype at SNPs 2 and 3 has the strongest significant association with AAO (P=0.0001) among all combinations of two or three loci. The A-C haplotype remained significant for AAO after the inclusion of the C allele at SNP 5 to this haplotype (A-C-C haplotype, P=0.00018). Although SNP 5 was found to associate with PD risk in the early-onset subset of PD families (at least one affected with AAO <40 years, 60 families), we believe that it is a by-product of its association with AAO. Taken together, these results suggest a potential role for ELAVL4 as a modifier gene for AAO of PD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cookson WO (2000) GOLD—graphical overview of linkage disequilibrium. BioInformatics 16:182–183
Abecasis GR, Cardon LR, Cookson WO (2000) A general test of association for quantitative traits in nuclear families. Am J Hum Genet 66:279–292
Akamatsu W, Okano HJ, Osumi N, Inoue T, Nakamura S, Sakakibara S, Miura M, Matsuo N, Darnell RB, Okano H (1999) Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:9885–9890
Antic D, Keene JD (1997a) Embryonic lethal abnormal visual RNA-binding proteins involved in growth, differentiation, and posttranscriptional gene expression. Am J Hum Genet 61:273–278
Antic D, Keene JD (1997b) Embryonic lethal abnormal visual RNA-binding proteins involved in growth, differentiation, and posttranscriptional gene expression. Am J Hum Genet 61:273–278
Aranda-Abreu GE, Behar L, Chung S, Furneaux H, Ginzburg I (1999) Embryonic lethal abnormal vision-like RNA-binding proteins regulate neurite outgrowth and tau expression in PC12 cells. J Neurosci 19:6907–6917
Benner EJ, Mosley RL, Destache CJ, Lewis TB, Jackson-Lewis V, Gorantla S, Nemachek C, Green SR, Przedborski S, Gendelman HE (2004) Therapeutic immunization protects dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9435–9440
Benyahia B, Liblau R, Merle-Beral H, Tourani JM, Dalmau J, Delattre JY (1999) Cell-mediated autoimmunity in paraneoplastic neurological syndromes with anti-Hu antibodies. Ann Neurol 45:162–167
Brennan CM, Steitz JA (2001) HuR and mRNA stability. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:266–277
Campos AR, Grossman D, White K (1985) Mutant alleles at the locus elav in Drosophila melanogaster lead to nervous system defects: a developmental-genetic analysis. J Neurogenet 2:197–218
Cok SJ, Acton SJ, Morrison AR (2003) The proximal region of the 3′-untranslated region of cyclooxygenase-2 is recognized by a multimeric protein complex containing HuR, TIA-1, TIAR, and the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U. J Biol Chem 278:36157–36162
Cuadrado A, Navarro-Yubero C, Furneaux H, Kinter J, Sonderegger P, Munoz A (2002) HuD binds to three AU-rich sequences in the 3′-UTR of neuroserpin mRNA and promotes the accumulation of neuroserpin mRNA and protein. Nucleic Acids Res 30:2202–2211
Dalmau JO, Posner JB (1999) Paraneoplastic syndromes. Arch Neurol 56:405–408
Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W, Hong JS (2003) Novel anti-inflammatory therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:395–401
Good PJ (1995) A conserved family of elav-like genes in vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4557–4561
Griffin WS and Mrak RE (2002) Interleukin-1 in the genesis and progression of and risk for development of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. J Leukoc Biol 72:233–238
Grimaldi LM, Casadei VM, Ferri C, Veglia F, Licastro F, Annoni G, Biunno I, De Bellis G, Sorbi S, Mariani C, Canal N, Griffin WS, Franceschi M (2000) Association of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease with an interleukin-1alpha gene polymorphism. Ann Neurol 47:361–365
Horvath S, Xu X, Lake SL, Silverman EK, Weiss ST, Laird NM (2004) Family-based tests for associating haplotypes with general phenotype data: application to asthma genetics. Genet Epidemiol 26:61–69
Hunot S and Hirsch EC (2003) Neuroinflammatory processes in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53(suppl 3):S49–S58
King PH, Redden D, Palmgren JS, Nabors LB, Lennon VA (1999) Hu antigen specificities of ANNA-I autoantibodies in paraneoplastic neurological disease. J Autoimmun 13:435–443
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108
Laird NM, Horvath S, Xu X (2000) Implementing a unified approach to family-based tests of association. Genet Epidemiol 19 (suppl 1):S36–S42
Laliberte RE, Perregaux DG, Hoth LR, Rosner PJ, Jordan CK, Peese KM, Eggler JF, Dombroski MA, Geoghegan KF, Gabel CA (2003) Glutathione s-transferase omega 1–1 is a target of cytokine release inhibitory drugs and may be responsible for their effect on interleukin-1beta posttranslational processing. J Biol Chem 278:16567–16578
Levine TD, Gao F, King PH,rews LG, Keene JD (1993) Hel-N1: an autoimmune RNA-binding protein with specificity for 3′ uridylate-rich untranslated regions of growth factor mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol 13:3494–3504
Li YJ, Scott WK, Hedges DJ, Zhang F, Gaskell PC, Nance MA, Watts RL et al (2002) Age at onset in two common neurodegenerative diseases is genetically controlled. Am J Hum Genet 70:985–993
Li YJ, Oliveira SA, Xu P, Martin ER, Stenger JE, Hulette C, Scherzer CR et al (2004) Glutathione S-transferase omega-1 modifies age-at-onset of Alzheimer disease and Parkinson disease. Hum Mol Genet 13:573
Ma WJ, Chung S, Furneaux H (1997) The Elav-like proteins bind to AU-rich elements and to the poly(A) tail of mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3564–3569
Martin ER, Monks SA, Warren LL, Kaplan NL (2000) A test for linkage and association in general pedigrees: the pedigree disequilibrium test. Am J Hum Genet 67:146–154
Martin ER, Bass MP, Gilbert JR, Pericak-Vance MA, Hauser ER (2003) Genotype-based association test for general pedigrees: the genotype-PDT. Genet Epidemiol 25:203–213
Monks SA and Kaplan NL (2000) Removing the sampling restrictions from family-based tests of association for a quantitative-trait locus. Am J Hum Genet 66:576–592
Nabors LB, Gillespie GY, Harkins L, King PH (2001) HuR, a RNA stability factor, is expressed in malignant brain tumors and binds to adenine- and uridine-rich elements within the 3′ untranslated regions of cytokine and angiogenic factor mRNAs. Cancer Res 61:2154–2161
Perrone-Bizzozero N and Bolognani F (2002) Role of HuD and other RNA-binding proteins in neural development and plasticity. J Neurosci Res 68:121–126
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Ringheim GE, Conant K (2004) Neurodegenerative disease and the neuroimmune axis (Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, viral infections). J Neuroimmunol 147:43–49
Sakai K, Kitagawa Y, Hirose G (1999) Binding of neuronal ELAV-like proteins to the uridine-rich sequence in the 3’-untranslated region of tumor necrosis factor-alpha messenger RNA. FEBS Lett 446:157–162
Scott WK, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Lyons K, Pahwa R et al (2001) Complete genomic screen in Parkinson disease: evidence for multiple genes. JAMA 286:2239–2244
Sengupta S, Jang BC, Wu MT, Paik JH, Furneaux H, Hla T (2003) The RNA-binding protein HuR regulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem 278:25227–25233
Sully G, Dean JL, Wait R, Rawlinson L, Santalucia T, Saklatvala J, Clark AR (2004) Structural and functional dissection of a conserved destabilizing element of cyclo-oxygenase-2 mRNA: evidence against the involvement of AUF-1 [AU-rich element/poly(U)-binding/degradation factor-1], AUF-2, tristetraprolin, HuR (Hu antigen R) or FBP1 (far-upstream-sequence-element-binding protein 1). Biochem J 377:629–639
Szabo A, Dalmau J, Manley G, Rosenfeld M, Wong E, Henson J, Posner JB, and Furneaux HM (1991) HuD, a paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis antigen, contains RNA-binding domains and is homologous to Elav and Sex-lethal. Cell 67:325–333
Weiner HL, Selkoe DJ (2002) Inflammation and therapeutic vaccination in CNS diseases. Nature 420:879–884
Yao KM, Samson ML, Reeves R, White K (1993) Gene elav of Drosophila melanogaster: a prototype for neuronal-specific RNA binding protein gene family that is conserved in flies and humans. J Neurobiol 24:723–739
Zaykin D, Zhivotovsky L, Weir BS (1995) Exact tests for association between alleles at arbitrary numbers of loci. Genetica 96:169–178
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all of the families whose participation made this project possible. We thank the members of the PD Genetics collaboration Martha A. Nance, Ray L. Watts, Jean P. Hubble, William C. Koller, Kelly Lyons, Rajesh Pahwa, Matthew B. Stern, Amy Colcher, Bradley C. Hiner, Joseph Jankovic, William G. Ondo, Fred H. Allen Jr., Christopher G. Goetz, Gary W. Small, Donna Masterman, Frank Mastaglia and Jonathan L. Haines who contributed families to the study. We would also like to thank Dr. Eden Martin, Dr. Bill Scott, Dr. Jack Keen, and Dr. Peter King for helpful discussions on this work. This research was supported by the NIH/NINDS R01 NS311530-10 and P50-NS-039764 grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noureddine, M.A., Qin, XJ., Oliveira, S.A. et al. Association between the neuron-specific RNA-binding protein ELAVL4 and Parkinson disease. Hum Genet 117, 27–33 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-1259-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-1259-2