Abstract
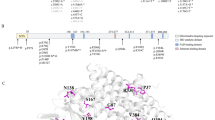
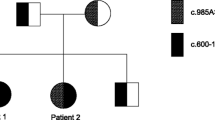
Short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (SBCADD) is an autosomal recessive disorder of l-isoleucine catabolism. Little is known about the clinical presentation associated with this enzyme defect, as it has been reported in only a limited number of patients. Because the presence of C5-carnitine in blood may indicate SBCADD, the disorder may be detected by MS/MS-based routine newborn screening. It is, therefore, important to gain more knowledge about the clinical presentation and the mutational spectrum of SBCADD. In the present study, we have studied two unrelated families with SBCADD, both with seizures and psychomotor delay as the main clinical features. One family illustrates the fact that affected individuals may also remain asymptomatic. In addition, the normal level of newborn blood spot C5-acylcarnitine in one patient underscores the fact that newborn screening by MS/MS currently lacks sensitivity in detecting SBCADD. Until now, seven mutations in the SBCAD gene have been reported, but only three have been tested experimentally. Here, we identify and characterize an IVS3+3A>G mutation (c.303+3A>G) in the SBCAD gene, and provide evidence that this mutation is disease-causing in both families. Using a minigene approach, we show that the IVS3+3A>G mutation causes exon 3 skipping, despite the fact that it does not appear to disrupt the consensus sequence of the 5′ splice site. Based on these results and numerous literature examples, we suggest that this type of mutation (IVS+3A>G) induces missplicing only when in the context of non-consensus (weak) 5′ splice sites. Statistical analysis of the sequences shows that the wild-type versions of 5′ splice sites in which +3A>G mutations cause exon skipping and disease are weaker on average than a random set of 5′ splice sites. This finding is relevant to the interpretation of the functional consequences of this type of mutation in other disease genes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaboshi, Ruiters J, Wanders R, Andresen B, Steiner R, Gibson KM (2001) Divergent phenotypes in siblings with confirmed 2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (2-MBCD) deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis (abstract) 24 (1):58
Andresen BS, Bross P, Udvari S, Kirk J, Gray G, Kmoch S, Chamoles N, Knudsen I, Winter V, Wilcken B, Yokota I, Hart K, Packman S, Harpey JP, Saudubray JM, Hale DE, Bolund L, Kolvraa S, Gregersen N (1997) The molecular basis of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency in compound heterozygous patients: is there correlation between genotype and phenotype? Hum Mol Genet 6:695–707
Andresen BS, Christensen E, Corydon TJ, Bross P, Pilgaard B, Wanders RJ, Ruiter JP, Simonsen H, Winter V, Knudsen I, Schroeder LD, Gregersen N, Skovby F (2000) Isolated 2-methylbutyrylglycinuria caused by short/branched-chain acyl- CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: identification of a new enzyme defect, resolution of its molecular basis, and evidence for distinct acyl-CoA dehydrogenases in isoleucine and valine metabolism. Am J Hum Genet 67:1095–1103
Aretz S, Uhlhaas S, Sun Y, Pagenstecher C, Mangold E, Caspari R, Moslein G, Schulmann K, Propping P, Friedl W (2004) Familial adenomatous polyposis: aberrant splicing due to missense or silent mutations in the APC gene. Hum Mutat 24:370–380
Ars E, Kruyer H, Morell M, Pros E, Serra E, Ravella A, Estivill X, Lazaro C (2003) Recurrent mutations in the NF1 gene are common among neurofibromatosis type 1 patients. J Med Genet 40:e82
Attanasio C, David A, Neerman-Arbez M (2003) Outcome of donor splice site mutations accounting for congenital afibrinogenemia reflects order of intron removal in the fibrinogen alpha gene (FGA). Blood 101:1851–1856
Baronciani L, Bianchi P, Zanella A (1998) Hematologically important mutations: red cell pyruvate kinase (2nd update). Blood Cells Mol Dis 24:273–279
Berger I, Shaag A, Anikster Y, Baumgartner ER, Bar-Meir M, Joseph A, Elpeleg ON (2001) Mutation analysis of the MCM gene in Israeli patients with mut(0) disease. Mol Genet Metab 73:107–110
Bidichandani SI, Shiach CR, Lanyon WG, Connor JM (1994) A novel splice donor mutation affecting position +3 in intron 6 of the factor VIII gene. Hum Mol Genet 3:651–653
Brackett JC, Sims HF, Rinaldo P, Shapiro S, Powell CK, Bennett MJ, Strauss AW (1995) Two alpha subunit donor splice site mutations cause human trifunctional protein deficiency. J Clin Invest 95:2076–2082
Brunak S, Engelbrecht J, Knudsen S (1991) Prediction of human mRNA donor and acceptor sites from the DNA sequence. J Mol Biol 220:49–65
Buraczynska M, Wu W, Fujita R, Buraczynska K, Phelps E, Andreasson S, Bennett J, Birch DG, Fishman GA, Hoffman DR, Inana G, Jacobson SG, Musarella MA, Sieving PA, Swaroop A (1997) Spectrum of mutations in the RPGR gene that are identified in 20% of families with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet 61:1287–1292
Burset M, Seledtsov IA, Solovyev VV (2000) Analysis of canonical and non-canonical splice sites in mammalian genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:4364–4375
Carstens RP, Fenton WA, Rosenberg LR (1991) Identification of RNA splicing errors resulting in human ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet 48:1105–1114
Cartegni L, Chew SL, Krainer AR (2002) Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: exonic mutations that affect splicing. Nat Rev Genet 3:285–298
Claes K, Machackova E, De Vos M, Poppe B, De Paepe A, Messiaen L (1999) Mutation analysis of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in the Belgian patient population and identification of a Belgian founder mutation BRCA1 IVS5 + 3A > G. Dis Markers 15:69–73
Claes K, Poppe B, Coene I, Paepe AD, Messiaen L (2004) BRCA1 and BRCA2 germline mutation spectrum and frequencies in Belgian breast/ovarian cancer families. Br J Cancer 90:1244–1251
Claes K, Vandesompele J, Poppe B, Dahan K, Coene I, De Paepe A, Messiaen L (2002) Pathological splice mutations outside the invariant AG/GT splice sites of BRCA1 exon 5 increase alternative transcript levels in the 5′ end of the BRCA1 gene. Oncogene 21:4171–4175
Cornejo-Roldan LR, Roessler E, Muenke M (1999) Analysis of the mutational spectrum of the FGFR2 gene in Pfeiffer syndrome. Hum Genet 104:425–431
Ensenauer R, Niederhoff H, Ruiter JP, Wanders RJ, Schwab KO, Brandis M, Lehnert W (2002) Clinical variability in 3-hydroxy-2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Ann Neurol 51:656–659
Fahsold R, Hoffmeyer S, Mischung C, Gille C, Ehlers C, Kucukceylan N, Abdel-Nour M, Gewies A, Peters H, Kaufmann D, Buske A, Tinschert S, Nurnberg P (2000) Minor lesion mutational spectrum of the entire NF1 gene does not explain its high mutability but points to a functional domain upstream of the GAP-related domain. Am J Hum Genet 66:790–818
Frischmeyer PA, Dietz HC (1999) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in health and disease. Hum Mol Genet 8:1893–1900
Fujita R, Buraczynska M, Gieser L, Wu W, Forsythe P, Abrahamson M, Jacobson SG, Sieving PA, Andreasson S, Swaroop A (1997) Analysis of the RPGR gene in 11 pedigrees with the retinitis pigmentosa type 3 genotype: paucity of mutations in the coding region but splice defects in two families. Am J Hum Genet 61:571–580
Gemignani F, Sazani P, Morcos P, Kole R (2002) Temperature-dependent splicing of beta-globin pre-mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 30:4592–4598
Gibson KM, Burlingame TG, Hogema B, Jakobs C, Schutgens RB, Millington D, Roe CR, Roe DS, Sweetman L, Steiner RD, Linck L, Pohowalla P, Sacks M, Kiss D, Rinaldo P, Vockley J (2000) 2-Methylbutyryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency: a new inborn error of L-isoleucine metabolism. Pediatr Res 47:830–833
Guldberg P, Henriksen KF, Thony B, Blau N, Guttler F (1994) Molecular heterogeneity of nonphenylketonuria hyperphenylalaninemia in 25 Danish patients. Genomics 21:453–455
Higuchi M, Wong C, Kochhan L, Olek K, Aronis S, Kasper CK, Kazazian HH Jr, Antonarakis SE (1990) Characterization of mutations in the factor VIII gene by direct sequencing of amplified genomic DNA. Genomics 6:65–71
Korman SH, Andresen BS, Zeharia A, Gutman A, Boneh A, Pitt JJ (2005) 2-Ethylhydracrylic Aciduria in short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Application to diagnosis and implications for the R-pathway of isoleucine oxidation. Clin Chem 51:610–617
Korman SH, Gutman A, Brooks R, Sinnathamby T, Gregersen N, Andresen BS (2004) Homozygosity for a severe novel medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) mutation IVS3-1G > C that leads to introduction of a premature termination codon by complete missplicing of the MCAD mRNA and is associated with phenotypic diversity ranging from sudden neonatal death to asymptomatic status. Mol Genet Metab 82:121–129
Kralovicova J, Houngninou-Molango S, Kramer A, Vorechovsky I (2004) Branch site haplotypes that control alternative splicing. Hum Mol Genet 13:3189–3202
Ladd AN, Cooper TA (2002) Finding signals that regulate alternative splicing in the post-genomic era. Genome Biol 3:8
Lerner MR, Boyle JA, Mount SM, Wolin SL, Steitz JA (1980) Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature 283:220–224
Lucchiari S, Donati MA, Parini R, Melis D, Gatti R, Bresolin N, Scarlato G, Comi GP (2002) Molecular characterisation of GSD III subjects and identification of six novel mutations in AGL. Hum Mutat 20:480
Matern D, He M, Berry SA, Rinaldo P, Whitley CB, Madsen PP, van Calcar SC, Lussky RC, Andresen BS, Wolff JA, Vockley J (2003) Prospective diagnosis of 2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in the Hmong population by newborn screening using tandem mass spectrometry. Pediatrics 112:74–78
Mulliken JB, Steinberger D, Kunze S, Muller U (1999) Molecular diagnosis of bilateral coronal synostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1603–1615
Neerman-Arbez M, de Moerloose P, Bridel C, Honsberger A, Schonborner A, Rossier C, Peerlinck K, Claeyssens S, Di Michele D, d’Oiron R, Dreyfus M, Laubriat-Bianchin M, Dieval J, Antonarakis SE, Morris MA (2000) Mutations in the fibrinogen alpha gene account for the majority of cases of congenital afibrinogenemia. Blood 96:149–152
Ohno K, Brengman JM, Felice KJ, Cornblath DR, Engel AG (1999) Congenital end-plate acetylcholinesterase deficiency caused by a nonsense mutation and an A–>G splice-donor-site mutation at position +3 of the collagenlike-tail-subunit gene (COLQ): how does G at position +3 result in aberrant splicing? Am J Hum Genet 65:635–644
Olpin SE, Pollitt RJ, McMenamin J, Manning NJ, Besley G, Ruiter JP, Wanders RJ (2002) 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in a 23-year-old man. J Inherit Metab Dis 25:477–482
Olschwang S, Laurent-Puig P, Groden J, White R, Thomas G (1993) Germ-line mutations in the first 14 exons of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. Am J Hum Genet 52:273–279
Pensotti V, Radice P, Presciuttini S, Calistri D, Gazzoli I, Grimalt PA, Mondini P, Buonsanti G, Sala P, Rossetti C, Ranzani GN, Bertario L, Pierotti MA (1997) Mean age of tumor onset in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) families correlates with the presence of mutations in DNA mismatch repair genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 19:135–142
Perrin-Vidoz L, Sinilnikova OM, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Lenoir GM, Mazoyer S (2002) The nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway triggers degradation of most BRCA1 mRNAs bearing premature termination codons. Hum Mol Genet 11:2805–2814
Pilia G, Uda M, Macis D, Frau F, Crisponi L, Balli F, Barbera C, Colombo C, Frediani T, Gatti R, Iorio R, Marazzi MG, Marcellini M, Musumeci S, Nebbia G, Vajro P, Ruffa G, Zancan L, Cao A, DeVirgilis S (1999) Jagged-1 mutation analysis in Italian Alagille syndrome patients. Hum Mutat 14:394–400
Purandare SM, Lanyon WG, Connor JM (1994) Characterisation of inherited and sporadic mutations in neurofibromatosis type-1. Hum Mol Genet 3:1109–1115
Reddy R, Henning D, Busch H (1981) Pseudouridine residues in the 5′-terminus of uridine-rich nuclear RNA I (U1 RNA). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 98:1076–1083
Reitsma PH, Bernardi F, Doig RG, Gandrille S, Greengard JS, Ireland H, Krawczak M, Lind B, Long GL, Poort SR (1995) Protein C deficiency: a database of mutations, 1995 update. On behalf of the subcommittee on plasma coagulation inhibitors of the scientific and standardization committee of the ISTH. Thromb Haemost 73:876–889
Richard MM, Erenberg G, Triggs-Raine BL (1995) An A to G mutation at the +3 position of intron 8 of the HEXA gene is associated with exon 8 skipping and Tay-Sachs disease. Biochem Mol Med 55:74–76
Robson CD, Mulliken JB, Robertson RL, Proctor MR, Steinberger D, Barnes PD, McFarren A, Muller U, Zurakowski D (2000) Prominent basal emissary foramina in syndromic craniosynostosis: correlation with phenotypic and molecular diagnoses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1707–1717
Roca X, Sachidanandam R, Krainer AR (2005) Determinants of the inherent strength of human 5′ splice sites. RNA 11:683–698
Roca X, Sachidanandam R, Krainer AR (2003) Intrinsic differences between authentic and cryptic 5′ splice sites. Nucleic Acids Res 31:6321–6333
Rogers J, Wall R (1980) A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77:1877–1879
Sarkany RP, Cox TM (1995) Autosomal recessive erythropoietic protoporphyria: a syndrome of severe photosensitivity and liver failure. QJM 88:541–549
Sass JO, Forstner R, Sperl W (2004) 2-Methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: impaired catabolism of isoleucine presenting as neurodegenerative disease. Brain Dev 26:12–14
Shapiro MB, Senapathy P (1987) RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 15:7155–7174
Spillantini MG, Murrell JR, Goedert M, Farlow MR, Klug A, Ghetti B (1998) Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:7737–7741
Tamary H, Dgany O, Toledano H, Shalev Z, Krasnov T, Shalmon L, Schechter T, Bercovich D, Attias D, Laor R, Koren A, Yaniv I (2004) Molecular characterization of three novel Fanconi anemia mutations in Israeli Arabs. Eur J Haematol 72:330–335
Tolnay M, Grazia SM, Rizzini C, Eccles D, Lowe J, Ellison D (2000) A new case of frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism resulting from an intron 10 +3-splice site mutation in the tau gene: clinical and pathological features. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 26:368–378
Tuddenham EG, Schwaab R, Seehafer J, Millar DS, Gitschier J, Higuchi M, Bidichandani S, Connor JM, Hoyer LW, Yoshioka A (1994) Haemophilia A: database of nucleotide substitutions, deletions, insertions and rearrangements of the factor VIII gene, second edition. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4851–4868
Wagner TM, Hirtenlehner K, Shen P, Moeslinger R, Muhr D, Fleischmann E, Concin H, Doeller W, Haid A, Lang AH, Mayer P, Petru E, Ropp E, Langbauer G, Kubista E, Scheiner O, Underhill P, Mountain J, Stierer M, Zielinski C, Oefner P (1999) Global sequence diversity of BRCA2: analysis of 71 breast cancer families and 95 control individuals of worldwide populations. Hum Mol Genet 8:413–423
Wang X, Poh-Fitzpatrick M, Chen T, Malavade K, Carriero D, Piomelli S (1995) Systematic screening for RNA with skipped exons—splicing mutations of the ferrochelatase gene. Biochem Biophys Acta 1271:358–362
Weil D, D’Alessio M, Ramirez F, Steinmann B, Wirtz MK, Glanville RW, Hollister DW (1989) Temperature-dependent expression of a collagen splicing defect in the fibroblasts of a patient with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem 264:16804–16809
Wilcken B, Wiley V, Hammond J, Carpenter K (2003) Screening newborns for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry. N Engl J Med 348:2304–2312
Wilkinson MF, Shyu AB (2002) RNA surveillance by nuclear scanning? Nat Cell Biol 4:144–147
Zeniou M, Gattoni R, Hanauer A, Stévenin J (2004) Delineation of the mechanisms of aberrant splicing caused by two unusual intronic mutations in the RSK2 gene involved in Coffin–Lowry syndrome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1214–1223
Zhuang Y, Weiner AM (1986) A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5′ splice site mutation. Cell 46:827–835
Zolezzi F, Valli M, Clementi M, Mammi I, Cetta G, Pignatti PF, Mottes M (1997) Mutation producing alternative splicing of exon 26 in the COL1A2 gene causes type IV osteogenesis imperfecta with intrafamilial clinical variability. Am J Med Genet 71:366–370
Zschocke J, Ruiter JP, Brand J, Lindner M, Hoffmann GF, Wanders RJ, Mayatepek E (2000) Progressive infantile neurodegeneration caused by 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: a novel inborn error of branched-chain fatty acid and isoleucine metabolism. Pediatr Res 48:852–855
Zytkovicz TH, Fitzgerald EF, Marsden D, Larson CA, Shih VE, Johnson DM, Strauss AW, Comeau AM, Eaton RB, Grady GF (2001) Tandem mass spectrometric analysis for amino, organic, and fatty acid disorders in newborn dried blood spots: a two-year summary from the New England newborn screening program. Clin Chem 47:1945–1955
Acknowledgments
We thank Henrik Simonsen, Statens Serum Institut, Copenhagen, for the MS/MS analysis of the newborn blood spot from patient 1. This work was supported by grants from The Danish Medical Research Council (Grant no. 22-01-0260), The Novo Nordic Foundation and the March of Dimes Foundation (Grant no.1-FY-2003-688).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madsen, P.P., Kibæk, M., Roca, X. et al. Short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency due to an IVS3+3A>G mutation that causes exon skipping. Hum Genet 118, 680–690 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-0070-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-0070-4