Abstract
Purpose
Controversy remains exist for the effect of adjuvant chemotherapy (ACT) among stage IB lung adenocarcinoma patients. This study aimed to investigate the predictive value of the current lung adenocarcinoma classification system on benefit of ACT among patients with stage IB lung adenocarcinoma.
Methods
A total of 928 pathological stage IB invasive adenocarcinoma patients with R0 resection were included in this study. Based on the predominant growth pattern present in the tumor, invasive adenocarcinomas with mixed histologic components were classified into five subtypes: lepidic (LEP), acinar (ACN), papillary (PAP), micropapillary (MIP) and solid (SOL). These five histologic subtypes were collapsed into three groups (LEP, ACN/PAP and SOL/MIP). Disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were analyzed to evaluate benefit from ACT in patients with different histologic patterns using the Kaplan–Meier approach and multivariable Cox models.
Results
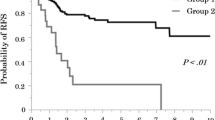
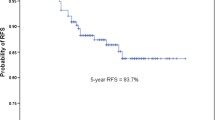
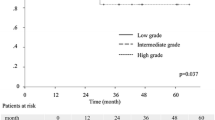
For all stage IB invasive adenocarcinoma patients, SOL/MIP subgroup presented the worst prognosis, and LEP subgroup showed approximately 100 % 5-year survival. ACT was associated with a better DFS (HR, 0.70; 95 % CI 0.51–0.96, p = .026) for all stage IB patients. In SOL/MIP subgroup, patients could benefit from ACT for a significant improved DFS (HR, 0.81; 95 % CI 0.49–1.35; p = .030), but not for OS (HR, 0.39; 95 % CI 0.12–1.30, p = .111). In ACN/PAP subgroup, there was no significant benefit from ACT for both DFS (HR, 0.76; 95 % CI 0.54–1.08, p = .125) and OS (HR, 0.81; 95 % CI 0.49–1.35, p = .421).
Conclusions
SOL/MIP predominant pattern was predictive for ACT benefit for DFS among invasive lung adenocarcinoma patients in stage IB.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bueno R et al (2015) Validation of a molecular and pathological model for five-year mortality risk in patients with early stage lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 10:67–73. doi:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000365
Campos-Parra AD, Aviles A, Contreras-Reyes S, Rojas-Marin CE, Sanchez-Reyes R, Borbolla-Escoboza RJ, Arrieta O (2014) Relevance of the novel IASLC/ATS/ERS classification of lung adenocarcinoma in advanced disease. The European Respiratory Journal 43:1439–1447. doi:10.1183/09031936.00138813
Coutinho D, Goncalves A, Antunes A, Campainha S, Miranda J, Barroso A (2016) Adjuvant chemotherapy in stage IB non-small cell lung carcinoma: a survival analysis. Revista portuguesa de pneumologia 22:123–125. doi:10.1016/j.rppnen.2015.09.005
Donington JS (2016) An additional step toward personalization of surgical care for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 34:295–296. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.64.7578
Ettinger DS et al (2015) Non-small cell lung cancer, version 6.2015. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw JNCCN 13:515–524
Friboulet L et al (2013) ERCC1 isoform expression and DNA repair in non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med 368:1101–1110. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1214271
Goldstraw P et al (2007) The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol 2:706–714. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31812f3c1a
Goldstraw P et al (2016) The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 11:39–51. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2015.09.009
Huang Q et al (2016) Identification and validation of lymphovascular invasion as a prognostic and staging factor in node-negative esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 11:583–592. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2015.12.109
Hung JJ, Jeng WJ, Chou TY, Hsu WH, Wu KJ, Huang BS, Wu YC (2013) Prognostic value of the new International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society lung adenocarcinoma classification on death and recurrence in completely resected stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg 258:1079–1086. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828920c0
Li Z et al (2009) Analysis of the T descriptors and other prognosis factors in pathologic stage I non-small cell lung cancer in China. J Thorac Oncol 4:702–709. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181a5269d
Park SY et al (2013) Efficacy of platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy in T2aN0 stage IB non-small cell lung cancer. J Cardiothorac Surg 8:151. doi:10.1186/1749-8090-8-151
Pignon JP et al (2008) Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: a pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group. J Clin Oncol 26:3552–3559. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.13.9030
Pirker R (2014) Adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 3:305–310. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.09.13
Russell PA, Wright GM (2016) Predominant histologic subtype in lung adenocarcinoma predicts benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in completely resected patients: discovery of a holy grail? Ann Transl Med 4:16. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.10.21
Shim HS et al (2015) Unique Genetic and Survival Characteristics of Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. J Thorac Oncol 10:1156–1162. doi:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000579
Takahashi Y, Eguchi T, Bains S, Adusumilli PS (2016) Significance of IASLC/ATS/ERS classification for early-stage lung adenocarcinoma patients in predicting benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Transl Med 4:66. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.10.40
Travis WD et al (2011) International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 6:244–285. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221
Tsao MS et al (2015) Subtype classification of lung adenocarcinoma predicts benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in patients undergoing complete resection. J Clin Oncol 33:3439–3446. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.58.8335
Warth A et al (2012) The novel histologic International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification system of lung adenocarcinoma is a stage-independent predictor of survival. J Clin Oncol 30:1438–1446. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.37.2185
Wilcox JE (2006) DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med 355:2590 (author reply 2591)
Xu CH et al (2015) Prognostic value of the new International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification in stage IB lung adenocarcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 41:1430–1436. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2015.06.004
Yanagawa N, Shiono S, Abiko M, Ogata SY, Sato T, Tamura G (2013) New IASLC/ATS/ERS classification and invasive tumor size are predictive of disease recurrence in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 8:612–618. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318287c3eb
Yoshida T et al (2013) Solid predominant histology predicts EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor response in patients with EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139:1691–1700. doi:10.1007/s00432-013-1495-0
Yoshizawa A et al (2011) Impact of proposed IASLC/ATS/ERS classification of lung adenocarcinoma: prognostic subgroups and implications for further revision of staging based on analysis of 514 stage I cases. Mod Pathol 24:653–664. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.232
Yoshizawa A et al (2013) Validation of the IASLC/ATS/ERS lung adenocarcinoma classification for prognosis and association with EGFR and KRAS gene mutations: analysis of 440 Japanese patients. J Thorac Oncol 8:52–61. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182769aa8
Zhang J, Wu J, Tan Q, Zhu L, Gao W (2013) Why do pathological stage IA lung adenocarcinomas vary from prognosis?: a clinicopathologic study of 176 patients with pathological stage IA lung adenocarcinoma based on the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification. J Thorac Oncol 8:1196–1202. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31829f09a7
Zhang Y et al (2014) The prognostic and predictive value of solid subtype in invasive lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 4:7163. doi:10.1038/srep07163
Zhu ZH et al (2009) Three immunomarker support vector machines-based prognostic classifiers for stage IB non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:1091–1099. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.6991
Authors’ contribution
Dr Haiquan Chen is the guarantor of the manuscript. Dr Jizhuang Luo contributed to conception and study design, acquisition and analysis of data, and writing and revision of the manuscript. Dr Qingyuan Huang contributed to conception and study design, acquisition and analysis of data, and writing and revision of the manuscript. Dr Rui. Wang contributed to conception and study design, acquisition and analysis of data, and writing and revision of the manuscript. Dr Baohui Han contributed to conception and study design, acquisition and analysis of data, and revision of the manuscript. Dr Jie Zhang contributed to acquisition of data. Dr Heng Zhao contributed to acquisition of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Wentao Fang contributed to analysis of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Qingqian Luo contributed to analysis of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Jun Yang contributed to acquisition of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Yunhai Yang contributed to acquisition of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Lei Zhu contributed to analysis of data. Dr Tianxiang Chen contributed to acquisition of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Xinghua Cheng contributed to acquisition of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Yiyang Wang contributed to acquisition of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Jiajie Zheng contributed to analysis of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Han Wu contributed to acquisition of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Weicong Xia contributed to analysis of data and revision of the manuscript. Dr Haiquan Chen contributed to conception and study design, analysis of data and review and revision of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81330056, 81401886, 81401891, 81422029 and 81372525) and Shen-kang Center Project (SKMB1201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient to allow their biological samples to be genetically analyzed.
Additional information
Jizhuang Luo, Qingyuan Huang and Rui Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, J., Huang, Q., Wang, R. et al. Prognostic and predictive value of the novel classification of lung adenocarcinoma in patients with stage IB. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 2031–2040 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2192-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2192-6