Abstract
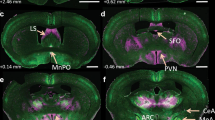
Angiotensin-II acts at its type-1 receptor (AT1R) in the brain to regulate body fluid homeostasis, sympathetic outflow and blood pressure. However, the role of the angiotensin type-2 receptor (AT2R) in the neural control of these processes has received far less attention, largely because of limited ability to effectively localize these receptors at a cellular level in the brain. The present studies combine the use of a bacterial artificial chromosome transgenic AT2R-enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) reporter mouse with recent advances in in situ hybridization (ISH) to circumvent this obstacle. Dual immunohistochemistry (IHC)/ISH studies conducted in AT2R-eGFP reporter mice found that eGFP and AT2R mRNA were highly co-localized within the brain. Qualitative analysis of eGFP immunoreactivity in the brain then revealed localization to neurons within nuclei that regulate blood pressure, metabolism, and fluid balance (e.g., NTS and median preoptic nucleus [MnPO]), as well as limbic and cortical areas known to impact stress responding and mood. Subsequently, dual IHC/ISH studies uncovered the phenotype of specific populations of AT2R-eGFP cells. For example, within the NTS, AT2R-eGFP neurons primarily express glutamic acid decarboxylase-1 (80.3 ± 2.8 %), while a smaller subset express vesicular glutamate transporter-2 (18.2 ± 2.9 %) or AT1R (8.7 ± 1.0 %). No co-localization was observed with tyrosine hydroxylase in the NTS. Although AT2R-eGFP neurons were not observed within the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus, eGFP immunoreactivity is localized to efferents terminating in the PVN and within GABAergic neurons surrounding this nucleus. These studies demonstrate that central AT2R are positioned to regulate blood pressure, metabolism, and stress responses.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbdAlla S, Lother H, Abdel-tawab AM, Quitterer U (2001) The angiotensin II AT2 receptor is an AT1 receptor antagonist. J Biol Chem 276:39721–39726. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105253200
Bacon SJ, Smith AD (1993) A monosynaptic pathway from an identified vasomotor centre in the medial prefrontal cortex to an autonomic area in the thoracic spinal cord. Neuroscience 54:719–728
Bader M, Ganten D (2008) Update on tissue renin-angiotensin systems. J Mol Med 86:615–621
Benicky J, Hafko R, Sanchez-Lemus E, Aguilera G, Saavedra JM (2012) Six commercially available angiotensin II AT1 receptor antibodies are non-specific. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:1353–1365. doi:10.1007/s10571-012-9862-y
Bosnyak S, Welungoda IK, Hallberg A, Alterman M, Widdop RE, Jones ES (2010) Stimulation of angiotensin AT2 receptors by the non-peptide agonist, Compound 21, evokes vasodepressor effects in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats. Br J Pharmacol 159:709–716. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00575.x
Breigeiron MK, Morris M, Lucion AB, Sanvitto GL (2002) Effects of angiotensin II microinjected into medial amygdala on male sexual behavior in rats. Horm Behav 41:267–274. doi:10.1006/hbeh.2002.1771
Cassis LA, Police SB, Yiannikouris F, Thatcher SE (2008) Local adipose tissue renin-angiotensin system. Curr Hypertens Rep 10:93–98
Cecconello AL, Raineki C, Sebben V, Lucion AB, Sanvitto GL (2010) Effect of acute stress on sexual behavior in female rats: participation of the central angiotensinergic system. Behav Brain Res 207:429–433. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2009.10.026
Chen AD, Zhang SJ, Yuan N, Xu Y, De W, Gao XY, Zhu GQ (2011) Angiotensin AT1 receptors in paraventricular nucleus contribute to sympathetic activation and enhanced cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in renovascular hypertensive rats. Exp Physiol 96:94–103. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2010.054353
Choi DC, Furay AR, Evanson NK, Ostrander MM, Ulrich-Lai YM, Herman JP (2007) Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis subregions differentially regulate hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity: implications for the integration of limbic inputs. J Neurosci 27:2025–2034. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.4301-06.2007
Ciriello J, Caverson MM, Li Z (2013) Effects of hypocretin and norepinephrine interaction in bed nucleus of the stria terminalis on arterial pressure. Neuroscience 255:278–291. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.09.032
Coleman CG, Anrather J, Iadecola C, Pickel VM (2009) Angiotensin II type 2 receptors have a major somatodendritic distribution in vasopressin-containing neurons in the mouse hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Neuroscience 163:129–142. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.06.032
Crestani CC, Alves FH, Gomes FV, Resstel LB, Correa FM, Herman JP (2013) Mechanisms in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis involved in control of autonomic and neuroendocrine functions: a review. Curr Neuropharmacol 11:141–159. doi:10.2174/1570159X11311020002
Cuadra AE, Shan Z, Sumners C, Raizada MK (2010) A current view of brain renin-angiotensin system: is the (pro)renin receptor the missing link? Pharmacol Ther 125:27–38
Danyel LA, Schmerler P, Paulis L, Unger T, Steckelings UM (2013) Impact of AT2-receptor stimulation on vascular biology, kidney function, and blood pressure. Integr Blood Press Control 6:153–161. doi:10.2147/IBPC.S34425
de Kloet AD, Krause EG, Woods SC (2010) The renin angiotensin system and the metabolic syndrome. Physiol Behav 100:525–534. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.03.018
de Kloet AD et al (2013) Angiotensin type 1a receptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus protect against diet-induced obesity. J Neurosci 33:4825–4833. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3806-12.2013
de Kloet AD, Pioquinto DJ, Nguyen D, Wang L, Smith JA, Hiller H (2014) CS Obesity induces neuroinflammation mediated by altered expression of the renin-angiotensin system in mouse forebrain nuclei. Physiol Behav 136:31–38
Egidy G, Friedman J, Viswanathan M, Wahl LM, Saavedra JM (1997) CGP-42112 partially activates human monocytes and reduces their stimulation by lipopolysaccharides. Am J Physiol 273:C826–C833
Eshima K, Hirooka Y, Shigematsu H, Matsuo I, Koike G, Sakai K, Takeshita A (2000) Angiotensin in the nucleus tractus solitarii contributes to neurogenic hypertension caused by chronic nitric oxide synthase inhibition. Hypertension 36:259–263
Fernandes KB, Crippa GE, Tavares RF, Antunes-Rodrigues J, Correa FM (2003) Mechanisms involved in the pressor response to noradrenaline injection into the cingulate cortex of unanesthetized rats. Neuropharmacology 44:757–763
Fernandes KB, Tavares RF, Correa FM (2005) The lateral septal area is involved in the pressor pathway activated by microinjection of norepinephrine into the rat brain cingulate cortex. Neuropharmacology 49:564–571. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.04.025
Fernandes KBP, Tavares RF, Pelosi GG, Corrêa FMA (2007) The paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus mediates the pressor response to noradrenergic stimulation of the medial prefrontal cortex in unanesthetized rats. Neurosci Lett 426:101–105. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.08.063
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (2008) The mouse brain: in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Elsevier, New York
Fuchtbauer L, Toft-Hansen H, Khorooshi R, Owens T (2010) Expression of astrocytic type 2 angiotensin receptor in central nervous system inflammation correlates with blood-brain barrier breakdown. J Mol Neurosci 42:89–98. doi:10.1007/s12031-010-9371-8
Gallo-Payet N, Guimond MO, Bilodeau L, Wallinder C, Alterman M, Hallberg A (2011) Angiotensin II, a neuropeptide at the frontier between endocrinology and neuroscience: is there a link between the angiotensin ii type 2 receptor and Alzheimer’s disease? Front Endocrinol 2:17. doi:10.3389/fendo.2011.00017
Gao J, Chao J, Parbhu KJ, Yu L, Xiao L, Gao F, Gao L (2012) Ontogeny of angiotensin type 2 and type 1 receptor expression in mice. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 13:341–352. doi:10.1177/1470320312443720
Gao J, Zhang H, Le KD, Chao J, Gao L (2011) Activation of central angiotensin type 2 receptors suppresses norepinephrine excretion and blood pressure in conscious rats. Am J Hypertens 24:724–730. doi:10.1038/ajh.2011.33
Gao J, Zucker IH, Gao L (2014) Activation of central angiotensin type 2 receptors by compound 21 improves arterial baroreflex sensitivity in rats with heart failure. Am J Hypertens. doi:10.1093/ajh/hpu044
Gao L, Wang W, Li H, Sumners C, Zucker IH (2008) Effects of angiotensin type 2 receptor overexpression in the rostral ventrolateral medulla on blood pressure and urine excretion in normal rats. Hypertension 51:521–527. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.101717
Gautron L, Rutkowski JM, Burton MD, Wei W, Wan Y, Elmquist JK (2013) Neuronal and nonneuronal cholinergic structures in the mouse gastrointestinal tract and spleen. J Comp Neurol 521:3741–3767. doi:10.1002/cne.23376
Grady EF, Sechi LA, Griffin CA, Schambelan M, Kalinyak JE (1991) Expression of AT2 receptors in the developing rat fetus. J Clin Invest 88:921–933. doi:10.1172/jci115395
Grove KL, Speth RC, Palmer AA, Ganong WF, Steele MK (1998) Angiotensin II receptor binding sites in the ventral portion of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis are reduced by interruption of the medial forebrain bundle. Brain Res 809:5–11
Guimaraes PS, Huber DA, Campagnole-Santos MJ, Schreihofer AM (2014) Development of attenuated baroreflexes in obese Zucker rats coincides with impaired activation of nucleus tractus solitarius. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 306:R681–R692. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00537.2013
Guyenet PG (2006) The sympathetic control of blood pressure nature reviews. Neuroscience 7:335–346. doi:10.1038/nrn1902
Hafko R, Villapol S, Nostramo R, Symes A, Sabban EL, Inagami T, Saavedra JM (2013) Commercially available angiotensin II At(2) receptor antibodies are nonspecific. PloS One 8:e69234. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069234
Hauser W, Johren O, Saavedra JM (1998) Characterization and distribution of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol 348:101–114
Hayes MR, Bradley L, Grill HJ (2009) Endogenous hindbrain glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation contributes to the control of food intake by mediating gastric satiation signaling. Endocrinology 150:2654–2659. doi:10.1210/en.2008-1479
Hein L, Barsh GS, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ, Kobilka BK (1995) Behavioural and cardiovascular effects of disrupting the angiotensin II type-2 receptor gene in mice. Nature 377:744–747
Herrera M, Sparks MA, Alfonso-Pecchio AR, Harrison-Bernard LM, Coffman TM (2013) Lack of specificity of commercial antibodies leads to misidentification of angiotensin type 1 receptor protein. Hypertension 61:253–258. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.203679
Heshmatian B, Parviz M, Karimian SM, Keshavarz M, Sohanaki H (2007) Cardiovascular response to renin substrate microinjection into the central nucleus of the amygdala of rats. Neuroreport 18:675–678. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e3280ba49d8
Ichiki T, Inagami T (1995) Expression, genomic organization, and transcription of the mouse angiotensin II type 2 receptor gene. Circ Res 76:693–700
Ichiki T et al (1995) Effects on blood pressure and exploratory behaviour of mice lacking angiotensin II type-2 receptor. Nature 377:748–750. doi:10.1038/377748a0
Israel A, Cierco M, Sosa B (2000a) Angiotensin AT(2) receptors mediate vasodepressor response to footshock in rats. Role of kinins, nitric oxide and prostaglandins. Eur J Pharmacol 394:103–108
Israel A, Sosa B, Gutierez CI (2000b) Brain AT(2) receptor mediate vasodepressor response to footshocks: role of kinins and nitric oxide. Brain Res Bull 51:339–343
Jessberger S, Toni N, Clemenson GD Jr, Ray J, Gage FH (2008) Directed differentiation of hippocampal stem/progenitor cells in the adult brain. Nat Neurosci 11:888–893. doi:10.1038/nn.2148
Jing F et al (2012) Direct stimulation of angiotensin II type 2 receptor enhances spatial memory. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:248–255. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2011.133
Johren O, Inagami T, Saavedra JM (1995) AT1A, AT1B, and AT2 angiotensin II receptor subtype gene expression in rat brain. Neuroreport 6:2549–2552
Joseph JP et al (2014) The angiotensin type 2 receptor agonist Compound 21 elicits cerebroprotection in endothelin-1 induced ischemic stroke. Neuropharmacology 81:134–141. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.044
Kádár A et al (2010) Distribution of hypophysiotropic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)-synthesizing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of the mouse. J Comp Neurol 518:3948–3961. doi:10.1002/cne.22432
Kostenis E et al (2005) G-protein-coupled receptor Mas is a physiological antagonist of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Circulation 111:1806–1813
Krause EG et al (2011) Blood-borne angiotensin II acts in the brain to influence behavioral and endocrine responses to psychogenic stress. J Neurosci 31:15009–15015. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0892-11.2011
Langlet F, Mullier A, Bouret SG, Prevot V, Dehouck B (2013) Tanycyte-like cells form a blood—cerebrospinal fluid barrier in the circumventricular organs of the mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 521:3389–3405. doi:10.1002/cne.23355
Lenkei Z, Palkovits M, Corvol P, Llorens-Cortes C (1996) Distribution of angiotensin II type-2 receptor (AT2) mRNA expression in the adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol 373:322–339. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960923)373:3<322:AID-CNE2>3.0.CO;2-4
Lenkei Z, Palkovits M, Corvol P, Llorens-Cortès C (1997) Expression of Angiotensin Type-1 (AT1) and Type-2 (AT2) Receptor mRNAs in the adult rat brain: a functional neuroanatomical review. Front Neuroendocrinol 18:383
Li Z, Iwai M, Wu L, Shiuchi T, Jinno T, Cui TX, Horiuchi M (2003) Role of AT2 receptor in the brain in regulation of blood pressure and water intake. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284:H116–H121. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00515.2002
Lienard F, Thornton SN, Martial FP, Mousseau MC, Galaverna O, Meile MJ, Nicolaidis S (1996) Effects of DOCA pretreatment on neuronal sensitivity and cell responsiveness to angiotensin II, in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the rat. Regul Pept 66:59–63
Llano Lopez LH et al (2012) Anxiolytic-like effect of losartan injected into amygdala of the acutely stressed rats. Pharmacol Rep 64:54–63
Masubuchi Y, Tsukamoto K, Isogai O, Yajima Y, Ito S, Saito S, Uchiyama T (2004) Effect of a high-salt diet on gamma-aminobutyric acid-mediated responses in the nucleus tractus solitarius of Sprague-Dawley rats. Brain Res Bull 64:221–226. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2004.07.009
McCarthy CA, Vinh A, Broughton BR, Sobey CG, Callaway JK, Widdop RE (2012) Angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation initiated after stroke causes neuroprotection in conscious rats. Hypertension 60:1531–1537. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.199646
McCarthy CA, Vinh A, Miller AA, Hallberg A, Alterman M, Callaway JK, Widdop RE (2014) Direct angiotensin AT2 receptor stimulation using a novel AT2 receptor agonist, compound 21 evokes neuroprotection in conscious hypertensive rats. PloS One 9:e95762. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095762
McKlveen JM, Myers B, Flak JN, Bundzikova J, Solomon MB, Seroogy KB, Herman JP (2013) Role of prefrontal cortex glucocorticoid receptors in stress and emotion. Biol Psychiatry 74:672–679. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.03.024
Millan MA, Jacobowitz DM, Aguilera G, Catt KJ (1991) Differential distribution of AT1 and AT2 angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat brain during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:11440–11444
Miyoshi M, Miyano K, Moriyama N, Taniguchi M, Watanabe T (2008) Angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced stimulation of rat microglial cells by suppressing nuclear factor kappaB and activator protein-1 activation. Eur J Neurosci 27:343–351. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.06014.x
Mo ZL, Katafuchi T, Muratani H, Hori T (1992) Effects of vasopressin and angiotensin II on neurones in the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus, in vitro. J Physiol 458:561–577
Mousa SA, Shaqura M, Schäper J, Treskatsch S, Habazettl H, Schäfer M, Abdul-Khaliq H (2011) Developmental expression of δ-opioid receptors during maturation of the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and sensory innervations of the neonatal heart: Early targets for opioid regulation of autonomic control. J Comp Neurol 519:957–971. doi:10.1002/cne.22560
Muller-Ribeiro FC, Zaretsky DV, Zaretskaia MV, Santos RA, DiMicco JA, Fontes MA (2012) Contribution of infralimbic cortex in the cardiovascular response to acute stress. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 303:R639–R650. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00573.2011
Mussa BM, Verberne AJ (2013) The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and regulation of pancreatic secretory function. Exp Physiol 98:25–37. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2012.066472
Northcott CA, Watts S, Chen Y, Morris M, Chen A, Haywood JR (2010) Adenoviral inhibition of AT1a receptors in the paraventricular nucleus inhibits acute increases in mean arterial blood pressure in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299:R1202–R1211. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00764.2009
Nuyt AM, Lenkei Z, Palkovits M, Corvol P, Llorens-Cortes C (1999) Ontogeny of angiotensin II type 2 receptor mRNA expression in fetal and neonatal rat brain. J Comp Neurol 407:193–206
Ohinata K, Fujiwata Y, Shingo F, Masaru I, Masatsugu H, Yoshikawa M (2009) Orally administered novokinin, an angiotensin AT2 receptor agonist, suppresses food intake via prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanism in mice. Peptides 30:1105–1108. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2009.03.003
Okuyama S, Sakagawa T, Chaki S, Imagawa Y, Ichiki T, Inagami T (1999) Anxiety-like behavior in mice lacking the angiotensin II type-2 receptor. Brain Res 821:150–159
Peters B et al (2012) A new transgenic rat model overexpressing the angiotensin II type 2 receptor provides evidence for inhibition of cell proliferation in the outer adrenal cortex. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 302:E1044–E1054. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00080.2011
Petrovich GD, Ross CA, Mody P, Holland PC, Gallagher M (2009) Central, but not basolateral, amygdala is critical for control of feeding by aversive learned cues. J Neurosci 29:15205–15212. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3656-09.2009
Plunkett LM, Saavedra JM (1985) Increased angiotensin II binding affinity in the nucleus tractus solitarius of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7721–7724
Polson JW, Dampney RA, Boscan P, Pickering AE, Paton JF (2007) Differential baroreflex control of sympathetic drive by angiotensin II in the nucleus tractus solitarii. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R1954–R1960. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00041.2007
Premer C, Lamondin C, Mitzey A, Speth RC, Brownfield MS (2013) Immunohistochemical localization of AT1a, AT1b, and AT2 angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat adrenal pituitary, and brain with a perspective commentary. Int J Hypertens 2013:175428. doi:10.1155/2013/175428
Qi Y et al (2012) Moderate cardiac-selective overexpression of angiotensin II type 2 receptor protects cardiac functions from ischaemic injury. Exp Physiol 97:89–101. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2011.060673
Reagan LP, Flanagan-Cato LM, Yee DK, Ma LY, Sakai RR, Fluharty SJ (1994) Immunohistochemical mapping of angiotensin type 2 (AT2) receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 662:45–59
Reis DG, Scopinho AA, Guimaraes FS, Correa FM, Resstel LB (2011) Behavioral and autonomic responses to acute restraint stress are segregated within the lateral septal area of rats. PloS One 6:e23171. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023171
Rodriguez-Pallares J, Rey P, Parga JA, Munoz A, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2008) Brain angiotensin enhances dopaminergic cell death via microglial activation and NADPH-derived ROS. Neurobiol Dis 31:58–73. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2008.03.003
Saavedra J, Pavel J (2006) The discovery of a novel macrophage binding site. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:507–524. doi:10.1007/s10571-006-9044-x
Saavedra JM, Ando H, Armando I, Baiardi G, Bregonzio C, Juorio A, Macova M (2005) Anti-stress and anti-anxiety effects of centrally acting angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonists. Regul Pept 128:227–238
Saha S, Drinkhill MJ, Moore JP, Batten TF (2005) Central nucleus of amygdala projections to rostral ventrolateral medulla neurones activated by decreased blood pressure. Eur J Neurosci 21:1921–1930. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04023.x
Sakai RR, McEwen BS, Fluharty SJ, Ma LY (2000) The amygdala: site of genomic and nongenomic arousal of aldosterone-induced sodium intake. Kidney Int 57:1337–1345. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00972.x
Santos RA, Ferreira AJ, Simoes ESAC (2008) Recent advances in the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-angiotensin(1-7)-Mas axis. Exp Physiol 93:519–527
Santos RA et al (2003) Angiotensin-(1-7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8258–8263
Scheuer DA (2010) Regulation of the stress response in rats by central actions of glucocorticoids. Exp Physiol 95:26–31. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2008.045971
Schulkin J, Marini J, Epstein AN (1989) A role for the medial region of the amygdala in mineralocorticoid-induced salt hunger. Behav Neurosci 103:179–185
Schwanhausser B et al (2011) Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 473:337–342. doi:10.1038/nature10098
Scopinho AA, Aguiar DC, Resstel LB, Guimaraes FS, Correa FM (2012) Brain pathways involved in the modulatory effects of noradrenaline in lateral septal area on cardiovascular responses. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:1147–1157. doi:10.1007/s10571-012-9840-4
Sevoz-Couche C, Brouillard C, Camus F, Laude D, De Boer SF, Becker C, Benoliel JJ (2013) Involvement of the dorsomedial hypothalamus and the nucleus tractus solitarii in chronic cardiovascular changes associated with anxiety in rats. J Physiol 591:1871–1887. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.247791
Shan Z et al (2013) Chronic knockdown of the nucleus of the solitary tract AT1 receptors increases blood inflammatory-endothelial progenitor cell ratio and exacerbates hypertension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension 61:1328–1333. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00156
Shao C, Yu L, Gao L (2014) Activation of angiotensin type 2 receptors partially ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male rats by islet protection. Endocrinology 155:793–804. doi:10.1210/en.2013-1601
Shao C, Zucker IH, Gao L (2013) Angiotensin type 2 receptor in pancreatic islets of adult rats: a novel insulinotropic mediator. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305:E1281–E1291. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00286.2013
Shi P et al (2010) Brain microglial cytokines in neurogenic hypertension. Hypertension 56:297–303
Siragy HM, de Gasparo M, Carey RM (2000) Angiotensin type 2 receptor mediates valsartan-induced hypotension in conscious rats. Hypertension 35:1074–1077
Stocker SD, Toney GM (2005) Median preoptic neurones projecting to the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus respond to osmotic, circulating Ang II and baroreceptor input in the rat. J Physiol 568:599–615. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.094425
Sumners C, Horiuchi M, Widdop RE, McCarthy C, Unger T, Steckelings UM (2013) Protective arms of the renin-angiotensin-system in neurological disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 40:580–588. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.12137
Sumners C, Tang W, Zelezna B, Raizada MK (1991) Angiotensin II receptor subtypes are coupled with distinct signal-transduction mechanisms in neurons and astrocytes from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7567–7571
Tavares RF, Antunes-Rodrigues J, de Aguiar Correa FM (2004) Pressor effects of electrical stimulation of medial prefrontal cortex in unanesthetized rats. J Neurosci Res 77:613–620. doi:10.1002/jnr.20195
Travers JB, Travers SP, Norgren R (1987) Gustatory neural processing in the hindbrain. Ann Rev Neurosci 10:595–632. doi:10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.003115
Tsukamoto K, Sved AF (1993) Enhanced gamma-aminobutyric acid-mediated responses in nucleus tractus solitarius of hypertensive rats. Hypertension 22:819–825
Vitela M, Mifflin SW (2001) γ-Aminobutyric acidb receptor-mediated responses in the nucleus tractus solitarius are altered in acute and chronic hypertension. Hypertension 37:619–622. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.37.2.619
Von Bohlen und Halbach O, Walther T, Bader M, Albrecht D (2001) Genetic deletion of angiotensin AT2 receptor leads to increased cell numbers in different brain structures of mice. Regul Pept 99:209–216
Wang H, Gallinat S, Li HW, Sumners C, Raizada MK, Katovich MJ (2004) Elevated blood pressure in normotensive rats produced by ‘knockdown’ of the angiotensin type 2 receptor. Exp Physiol 89:313–322. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2004.027359
Wang WZ, Gao L, Pan YX, Zucker IH, Wang W (2007) AT1 receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarii mediate the interaction between the baroreflex and the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in anesthetized rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R1137–R1145. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00590.2006
Wu CY et al (2013) Expression of angiotensin II and its receptors in activated microglia in experimentally induced cerebral ischemia in the adult rats. Mol Cell Biochem 382:47–58. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1717-4
Yan JB et al (2014) Natriorexigenic effect of DAMGO is decreased by blocking AT1 receptors in the central nucleus of the amygdala. Neuroscience 262:9–20. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.046
Ye S, Zhong H, Duong VN, Campese VM (2002) Losartan reduces central and peripheral sympathetic nerve activity in a rat model of neurogenic hypertension. Hypertension 39:1101–1106. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.0000018590.26853.c7
Yu L, Zheng M, Wang W, Rozanski GJ, Zucker IH, Gao L (2010) Developmental changes in AT1 and AT2 receptor-protein expression in rats. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 11:214–221. doi:10.1177/1470320310379065
Zardetto-Smith AM, Beltz TG, Johnson AK (1994) Role of the central nucleus of the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in experimentally-induced salt appetite. Brain research 645:123–134
Zhang Q, Yao F, O’Rourke ST, Qian SY, Sun C (2009) Angiotensin II enhances GABA(B) receptor-mediated responses and expression in nucleus tractus solitarii of rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297:H1837–H1844. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00354.2009
Zhang R, Jankord R, Flak JN, Solomon MB, D’Alessio DA, Herman JP (2010) Role of glucocorticoids in tuning hindbrain stress integration. J Neurosci 30:14907–14914. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0522-10.2010
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants HL-076803 (CS), HL-093186 (CS/DS), HL-096830 (EGK), T32-HL-083810 (ADdK), and F32-HL-116074 (ADdK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Kloet, A.D., Wang, L., Ludin, J.A. et al. Reporter mouse strain provides a novel look at angiotensin type-2 receptor distribution in the central nervous system. Brain Struct Funct 221, 891–912 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0943-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0943-1