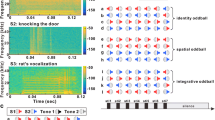
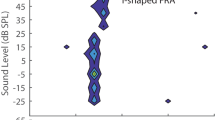
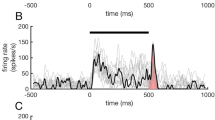
Abstract
Rapid behavioral responses to unexpected events in the acoustic environment are critical for survival. Stimulus-specific adaptation (SSA) is the process whereby some auditory neurons respond better to rare stimuli than to repetitive stimuli. Most experiments on SSA have been performed under anesthesia, and it is unknown if SSA sensitivity is altered by the anesthetic agent. Only a direct comparison can answer this question. Here, we recorded extracellular single units in the inferior colliculus of awake and anesthetized mice under an oddball paradigm that elicits SSA. Our results demonstrate that SSA is similar, but not identical, in the awake and anesthetized preparations. The differences are mostly due to the higher spontaneous activity observed in the awake animals, which also revealed a high incidence of inhibitory receptive fields. We conclude that SSA is not an artifact of anesthesia and that spontaneous activity modulates neuronal SSA differentially, depending on the state of arousal. Our results suggest that SSA may be especially important when nervous system activity is suppressed during sleep-like states. This may be a useful survival mechanism that allows the organism to respond to danger when sleeping.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolafia JM, Vergara R, Arnold MM, Reig R, Sanchez-Vives MV (2011) Cortical auditory adaptation in the awake rat and the role of potassium currents. Cereb Cortex 21:977–990. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq163
Anderson LA, Christianson GB, Linden JF (2009) Stimulus-specific adaptation occurs in the auditory thalamus. J Neurosci 29:7359–7363. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0793-09.2009
Antunes FM, Malmierca MS (2011) Effect of auditory cortex deactivation on stimulus-specific adaptation in the medial geniculate body. J Neurosci 31:17306–17316. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1915-11.2011
Antunes FM, Malmierca MS (2014) An overview of stimulus-specific adaptation in the auditory thalamus. Brain Topogr. doi:10.1007/s10548-013-0342-6
Antunes FM, Nelken I, Covey E, Malmierca MS (2010) Stimulus-specific adaptation in the auditory thalamus of the anesthetized rat. PLoS One 5:e14071. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014071
Astikainen P, Stefanics G, Nokia M, Lipponen A, Cong F, Penttonen M, Ruusuvirta T (2011) Memory-based mismatch response to frequency changes in rats. PLoS One 6:e24208. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024208
Ayala YA, Malmierca MS (2013) Stimulus-specific adaptation and deviance detection in the inferior colliculus. Front Neural Circuits 6:89. doi:10.3389/fncir.2012.00089. eCollection 2012
Ayala YA, Perez-Gonzalez D, Duque D, Nelken I, Malmierca MS (2013) Frequency discrimination and stimulus deviance in the inferior colliculus and cochlear nucleus. Front Neural Circuits 6:119. doi:10.3389/fncir.2012.00119. eCollection 2012
Bryant JL, Roy S, Heck DH (2009) A technique for stereotaxic recordings of neuronal activity in awake, head-restrained mice. J Neurosci Methods 178:75–79. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.11.014
Buran BN, von Trapp G, Sanes DH (2014) Behaviorally gated reduction of spontaneous discharge can improve detection thresholds in auditory cortex. J Neurosci 34:4076–4081. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4825-13.2014
Castro-Alamancos MA (2004) Absence of rapid sensory adaptation in neocortex during information processing states. Neuron 41:455–464
Clement EA, Richard A, Thwaites M, Ailon J, Peters S, Dickson CT (2008) Cyclic and sleep-like spontaneous alternations of brain state under urethane anaesthesia. PLoS One 3:e2004. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002004
Chandrasekaran B, Kraus N (2010) The scalp-recorded brainstem response to speech: neural origins and plasticity. Psychophysiology 47(2):236–246. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00928.x
Chung S, Li X, Nelson SB (2002) Short-term depression at thalamocortical synapses contributes to rapid adaptation of cortical sensory responses in vivo. Neuron 34:437–446
Chung Y, Hancock KE, Nam SI, Delgutte B (2014) Coding of electric pulse trains presented through cochlear implants in the auditory midbrain of awake rabbit: comparison with anesthetized preparations. J Neurosci 34:218–231. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2084-13.2014
Dhruv NT, Carandini M (2014) Cascaded effects of spatial adaptation in the early visual system. Neuron 81:529–535. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.11.025
Duque D, Malmierca MS, Caspary DM (2014) Modulation of stimulus-specific adaptation by GABAA receptor activation or blockade in the medial geniculate body of the anaesthetized rat. J Physiol 592:729–743. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2013.261941
Duque D, Perez-Gonzalez D, Ayala YA, Palmer AR, Malmierca MS (2012) Topographic distribution, frequency, and intensity dependence of stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus of the rat. J Neurosci 32:17762–17774. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3190-12.2012
Ehret G (1979) Quantitative analysis of nerve fibre densities in the cochlea of the house mouse (Mus musculus). J Comp Neurol 183(1):73–88. doi:10.1002/cne.901830107
Escera C, Malmierca MS (2014) The auditory novelty system: an attempt to integrate human and animal research. Psychophysiology 51:111–123. doi:10.1111/psyp.12156
Egorova M, Ehret G, Vartanian I, Esser KH (2001) Frequency response areas of neurons in the mouse inferior colliculus. I. Threshold and tuning characteristics. Exp Brain Res 140:145–161
Faure PA, Fremouw T, Casseday JH, Covey E (2003) Temporal masking reveals properties of sound-evoked inhibition in duration-tuned neurons of the inferior colliculus. J Neurosci 23:3052–3065
Fishman YI, Steinschneider M (2012) Searching for the mismatch negativity in primary auditory cortex of the awake monkey: deviance detection or stimulus specific adaptation? J Neurosci 32:15747–15758. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2835-12.2012
Fitzpatrick DC, Kuwada S, Batra R, Trahiotis C (1995) Neural responses to simple simulated echoes in the auditory brain stem of the unanesthetized rabbit. J Neurophysiol 74:2469–2486
Franklin K, Paxinos G (2007) The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, New York
Goldstein MH Jr, Abeles M (1975) Note on tonotopic organization of primary auditory cortex in the cat. Brain Res 100(1):188–191
Grimm S, Escera C, Slabu L, Costa-Faidella J (2011) Electrophysiological evidence for the hierarchical organization of auditory change detection in the human brain. Psychophysiology 48:377–384. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01073.x
Hara K, Harris RA (2002) The anesthetic mechanism of urethane: the effects on neurotransmitter-gated ion channels. Anesth Analg 94:313–318 (table of contents)
Hernandez O, Espinosa N, Perez-Gonzalez D, Malmierca MS (2005) The inferior colliculus of the rat: a quantitative analysis of monaural frequency response areas. Neuroscience 132:203–217
Hernández O, Rees A, Malmierca MS (2006) A GABAergic component in the commissure of the inferior colliculus in rat. Neuroreport 17:1611–1614
Holmstrom LA, Eeuwes LB, Roberts PD, Portfors CV (2010) Efficient encoding of vocalizations in the auditory midbrain. J Neurosci 30:802–819. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1964-09.2010
Ito T, Bishop DC, Oliver DL (2009) Two classes of GABAergic neurons in the inferior colliculus. J Neurosci 29(44):13860–13869. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3454-09.2009
Izquierdo MA, Gutiérrez-Conde PM, Merchán MA, Malmierca MS (2008) Non-plastic reorganization of frequency coding in the inferior colliculus of the rat following noise-induced hearing loss. Neuroscience 154:355–369. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.057
Jones S, Mill R, Denham S, Klump G (2012) Stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus of the awake gerbil in response to Markov chain tone sequences. ARO Midwinter Meeting, abstr 795, San Diego, USA
Jung F, Stephan KE, Backes H, Moran R, Gramer M, Kumagai T, Graf R, Endepols H, Tittgemeyer M (2013) Mismatch responses in the awake rat: evidence from epidural recordings of auditory cortical fields. PLoS One 8:e63203. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063203
King AJ, Nelken I (2009) Unraveling the principles of auditory cortical processing: can we learn from the visual system? Nat Neurosci 12(6):698–701. doi:10.1038/nn.2308
Klein C, von der Behrens W, Gaese BH (2014) Stimulus-specific adaptation in field potentials and neuronal responses to frequency-modulated tones in the primary auditory cortex. Brain Topogr. doi:10.1007/s10548-014-0376-4
Kuwada S, Batra R, Stanford TR (1989) Monaural and binaural response properties of neurons in the inferior colliculus of the rabbit: effects of sodium pentobarbital. J Neurophysiol 61:269–282
Loewy DH, Campbell KB, Bastien C (1996) The mismatch negativity to frequency deviant stimuli during natural sleep. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 98:493–501
Lumani A, Zhang H (2010) Responses of neurons in the rat’s dorsal cortex of the inferior colliculus to monaural tone bursts. Brain Res 1351:115–129. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.06.066
Maggi CA, Meli A (1986) Suitability of urethane anesthesia for physiopharmacological investigations in various systems. Part 1: general considerations. Experientia 42:109–114
Malmierca MS (2003) The structure and physiology of the rat auditory system: an overview. Int Rev Neurobiol 56:147–211
Malmierca MS, Ryugo DK (2011) Auditory system. The mouse nervous system, 1st edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 607–645
Malmierca MS, Hernandez O, Rees A (2005) Intercollicular commissural projections modulate neuronal responses in the inferior colliculus. Eur J Neurosci 21(10):2701–2710. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04103.x
Malmierca MS, Cristaudo S, Perez-Gonzalez D, Covey E (2009) Stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus of the anesthetized rat. J Neurosci 29:5483–5493
Malmierca MS, Izquierdo MA, Cristaudo S, Hernández O, Pérez-González D, Covey E, Oliver DL (2008) A discontinuous tonotopic organization in the inferior colliculus of the rat. J Neurosci 28:4767–4776. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0238-08.2008
Malmierca MS, Sanchez-Vives MV, Escera C, Bendixen A (2014) Neuronal adaptation, novelty detection and regularity encoding in audition. Front Syst Neurosci 8:111. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2014.00111
Merrill EG, Ainsworth A (1972) Glass-coated platinum-plated tungsten microelectrodes. Med Biol Eng 10:662–672
Moroni F, Corradetti R, Casamenti F, Moneti G, Pepeu G (1981) The release of endogenous GABA and glutamate from the cerebral cortex in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 316:235–239
Muniak MA, Mayko ZM, Ryugo DK, Portfors CV (2012) Preparation of an awake mouse for recording neural responses and injecting tracers. J Vis Exp. doi:10.3791/3755
Näätänen R, Gaillard AW, Mantysalo S (1978) Early selective-attention effect on evoked potential reinterpreted. Acta Psychol (Amst) 42:313–329
Nakamura T, Michie PT, Fulham WR, Todd J, Budd TW, Schall U, Hunter M, Hodgson DM (2011) Epidural auditory event-related potentials in the rat to frequency and duration deviants: evidence of mismatch negativity? Front Psychol 2:367. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00367. eCollection 2011
Nir Y, Vyazovskiy VV, Cirelli C, Banks MI, Tononi G (2013) Auditory responses and stimulus-specific adaptation in rat auditory cortex are preserved across NREM and REM sleep. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bht328
Pagliardini S, Funk GD, Dickson CT (2013) Breathing and brain state: urethane anesthesia as a model for natural sleep. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 188:324–332. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2013.05.035
Pagliardini S, Greer JJ, Funk GD, Dickson CT (2012) State-dependent modulation of breathing in urethane-anesthetized rats. J Neurosci 32:11259–11270. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0948-12.2012
Perez-Gonzalez D, Malmierca MS (2012) Variability of the time course of stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus. Front Neural Circuits 6:107. doi:10.3389/fncir.2012.00107. eCollection 2012
Pérez-González D, Malmierca MS (2014) Adaptation in the auditory system: an overview. Front Integr Neurosci 8:19. doi:10.3389/fnint.2014.00019
Pérez-González D, Malmierca MS, Covey E (2005) Novelty detector neurons in the mammalian auditory midbrain. Eur J Neurosci 22:2879–2885
Perez-Gonzalez D, Hernandez O, Covey E, Malmierca MS (2012) GABA(A)-mediated inhibition modulates stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus. PLoS One 7:e34297. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034297 [Erratum in: PLoS One. 2012;7(8). doi:10.1371/annotation/883c90e9-2108-449f-a652-2cbf25ba6456]
Peruzzi D, Bartlett E, Smith PH, Oliver DL (1997) A monosynaptic GABAergic input from the inferior colliculus to the medial geniculate body in rat. J Neurosci 17(10):3766–3777
Portfors CV, Roberts PD, Jonson K (2009) Over-representation of species-specific vocalizations in the awake mouse inferior colliculus. Neuroscience 162:486–500. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.04.056
Portfors CV, Mayko ZM, Jonson K, Cha GF, Roberts PD (2011) Spatial organization of receptive fields in the auditory midbrain of awake mouse. Neuroscience 193:429–439. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.025
Rechtschaffen A, Hauri P, Zeitlin M (1966) Auditory awakening thresholds in REM and NREM sleep stages. Percept Motor Skills 22:927–942
Rees A, Sarbaz A, Malmierca MS, Le Beau FE (1997) Regularity of firing of neurons in the inferior colliculus. J Neurophysiol 77:2945–2965
Richardson BD, Hancock KE, Caspary DM (2013) Stimulus-specific adaptation in auditory thalamus of young and aged awake rats. J Neurophysiol 110:1892–1902. doi:10.1152/jn.00403.2013
Roberts PD, Portfors CV (2008) Design principles of sensory processing in cerebellum-like structures. Early stage processing of electrosensory and auditory objects. Biol Cybern 98:491–507. doi:10.1007/s00422-008-0217-1
Ruby P, Caclin A, Boulet S, Delpuech C, Morlet D (2008) Odd sound processing in the sleeping brain. J Cogn Neurosci 20:296–311. doi:10.1162/jocn.2008.20023
Sceniak MP, Maciver MB (2006) Cellular actions of urethane on rat visual cortical neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol 95:3865–3874
Shiramatsu TI, Kanzaki R, Takahashi H (2013) Cortical mapping of mismatch negativity with deviance detection property in rat. PLoS One 8:e82663. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0082663. eCollection 2012
Skoe E, Chandrasekaran B, Spitzer ER, Wong PC, Kraus N (2013a) Human brainstem plasticity: the interaction of stimulus probability and auditory learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 109C:82–93. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2013.11.011
Skoe E, Kraus N (2010) Auditory brain stem response to complex sounds: a tutorial. Ear Hear 31(3):302–324. doi:10.1097/AUD.0b013e3181cdb272
Skoe E, Krizman J, Spitzer E, Kraus N (2013b) The auditory brainstem is a barometer of rapid auditory learning. Neuroscience 243:104–114. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.03.009
Slabu L, Escera C, Grimm S, Costa-Faidella J (2010) Early change detection in humans as revealed by auditory brainstem and middle-latency evoked potentials. Eur J Neurosci 32:859–865. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07324.x
Sloan TB (1998) Anesthetic effects on electrophysiologic recordings. J Clin Neurophysiol: Off Publ Am Electroencephalogr Soc 15(3):217–226
Song P, Wang N, Wang H, Xie Y, Jia J, Li H (2011) Pentobarbital anesthesia alters neural responses in the precedence effect. Neurosci Lett 498:72–77. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.04.066
Stabler SE, Palmer AR, Winter IM (1996) Temporal and mean rate discharge patterns of single units in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of the anesthetized guinea pig. J Neurophysiol 76:1667–1688
Stiebler I, Ehret G (1985) Inferior colliculus of the house mouse. I. A quantitative study of tonotopic organization, frequency representation, and tone-threshold distribution. J Comp Neurol 238(1):65–76. doi:10.1002/cne.902380106
Ter-Mikaelian M, Sanes DH, Semple MN (2007) Transformation of temporal properties between auditory midbrain and cortex in the awake Mongolian gerbil. J Neurosci 27:6091–6102
Thomas JM, Morse C, Kishline L, O’Brien-Lambert A, Simonton A, Miller KE, Covey E (2012) Stimulus-specific adaptation in specialized neurons in the inferior colliculus of the big brown bat, Eptesicus fuscus. Hear Res 291:34–40
Tikhonravov D, Neuvonen T, Pertovaara A, Savioja K, Ruusuvirta T, Naatanen R, Carlson S (2008) Effects of an NMDA-receptor antagonist MK-801 on an MMN-like response recorded in anesthetized rats. Brain Res 1203:97–102. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.006
Tollin DJ, Populin LC, Yin TC (2004) Neural correlates of the precedence effect in the inferior colliculus of behaving cats. J Neurophysiol 92:3286–3297
Ulanovsky N, Las L, Nelken I (2003) Processing of low-probability sounds by cortical neurons. Nat Neurosci 6:391–398
von der Behrens W, Bauerle P, Kossl M, Gaese BH (2009) Correlating stimulus-specific adaptation of cortical neurons and local field potentials in the awake rat. J Neurosci 29:13837–13849. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3475-09.2009
Winer JA, Saint Marie RL, Larue DT, Oliver DL (1996) GABAergic feedforward projections from the inferior colliculus to the medial geniculate body. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(15):8005–8010
Willott JF, Parham K, Hunter KP (1988) Response properties of inferior colliculus neurons in young and very old CBA/J mice. Hear Res 37:1–14
Young ED, Brownell WE (1976) Responses to tones and noise of single cells in dorsal cochlear nucleus of unanesthetized cats. J Neurophysiol 39:282–300
Zhao L, Liu Y, Shen L, Feng L, Hong B (2011) Stimulus-specific adaptation and its dynamics in the inferior colliculus of rat. Neuroscience 181:163–174. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.01.060
Zook JM, Winer JA, Pollak GD, Bodenhamer RD (1985) Topology of the central nucleus of the mustache bat’s inferior colliculus: correlation of single unit properties and neuronal architecture. J Comp Neurol 231(4):530–546
Acknowledgments
We are most grateful to Drs. Flora Antunes, Nell Cant, Douglas Oliver, Alan Palmer and Christine Portfors for their critical and valuable comments on a previous version of this manuscript. We also thank Mr. Javier Nieto and Dr. David Pérez-González for their help and assistance in the analysis of the data. Financial support was provided by the Spanish MEC (BFU2013-43608-P), to MSM; DD held a fellowship from the Spanish MEC (BES-2010-035649). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duque, D., Malmierca, M.S. Stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus of the mouse: anesthesia and spontaneous activity effects. Brain Struct Funct 220, 3385–3398 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0862-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0862-1