Abstract
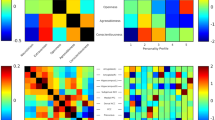
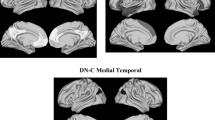
Recent neuroimaging studies have provided evidence that different dimensions of human personality may be associated with specific structural neuroanatomic correlates. Identifying brain correlates of a situation-independent personality structure would require evidence of a stable default mode of brain functioning. In this study, we investigated the correlates of the Big Five personality dimensions (Extraversion, Neuroticism, Openness/Intellect, Agreeableness, and Conscientiousness) and the default mode network (DMN). Forty-nine healthy adults completed the NEO-Five Factor. The results showed that the Extraversion (E) and Agreeableness (A) were positively correlated with activity in the midline core of the DMN, whereas Neuroticism (N), Openness (O), and Conscientiousness (C) were correlated with the parietal cortex system. Activity of the anterior cingulate cortex was positively associated with A and negatively with C. Regions of the parietal lobe were differentially associated with each personality dimension. The present study not only confirms previous functional correlates regarding the Big Five personality dimensions, but it also expands our knowledge showing the association between different personality dimensions and specific patterns of brain activation at rest.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
All variables but Conscientiousness followed a normal distribution sample with p < 0.05 in both tests (K–S and S-W) – here we included only S-W test.
References
Adelstein JS, Shehzad Z, Mennes M, Deyoung CG, Zuo XN, Kelly C, Margulies DS, Bloomfield A, Gray JR, Castellanos FX, Milham MP (2011) Personality is reflected in the brain’s intrinsic functional architecture. PLoS One 6(11):e27633. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027633
Andrews-Hanna JR, Reidler JS, Sepulcre J, Poulin R, Buckner RL (2010) Functional-anatomic fractionation of the brain’s default network. Neuron 65(4):550–562. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.02.005
Beckmann CF, DeLuca M, Devlin JT, Smith SM (2005) Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360(1457):1001–1013. doi:10.1098/rstb.2005.1634
Behrmann M, Geng JJ, Shomstein S (2004) Parietal cortex and attention. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14(2):212–217. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2004.03.012
Buckner RL, Andrews-Hanna JR, Schacter DL (2008) The brain’s default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1124:1–38
Calhoun VD, Adali T, Pearlson GD, Pekar JJ (2001a) A method for making group inferences from functional MRI data using independent component analysis. Hum Brain Mapp 14:140–151
Calhoun VD, Adali T, Pearlson GD, Pekar JJ (2001b) Spatial and temporal independent component analysis of functional MRI data containing a pair of task-related waveforms. Hum Brain Mapp 13:43–53
Cavanna AE, Trimble MR (2006) The precuneus: a review of its functional anatomy and behavioural correlates. Brain: J Neurol 129(Pt 3):564–583. doi:10.1093/brain/awl004
Chan SW, Harmer CJ, Goodwin GM, Norbury R (2008) Risk for depression is associated with neural biases in emotional categorisation. Neuropsychologia 46(12):2896–2903. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.05.030
Cherkassky VL, Kana RK, Keller TA, Just MA (2006) Functional connectivity in baseline resting-state network in autism. Neuroreport 17:1687–1690
Correa N, Adali T, Li Y, Calhoun V (2005) Comparison of blind source separation algorithms for FMRI using a new Matlab toolbox: GIFT. Proc IEEE Int Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process 5:401–404
Costa PT, McCrae RR (1992) Revised NEO personality inventory (NEOPI- R) and the NEO five-factor inventory (NEO-FFI) professional manual. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa, FL
Costa PT, McCrae RR (1995) Domains and facets: hierarchical personality assessment using the revised NEO personality inventory. J Pers Assess 64:21–50
Deckersbach T, Miller KK, Klibanski A, Fischman A, Dougherty DD, Blais MA, Herzog DB, Rauch SL (2006) Regional cerebral brain metabolism correlates of neuroticism and extraversion. Depress Anxiety 23(3):133–138. doi:10.1002/da.20152
DeYoung CG (2010) Personality neuroscience and the biology of traits. Soc Pers Psychol Compass 4(12):1165–1180
DeYoung CG, Hirsh JB, Shane MS, Papademetris X, Rajeevan N, Gray JR (2010) Testing predictions from personality neuroscience. Psychol Sci 21(6):820
Fleeson W, Noftle EE (2009) In favor of the synthetic resolution to the person-situation debate. J Res Pers 43(2):150–154
Garavan H, Ross TJ, Stein EA (1999) Right hemispheric dominance of inhibitory control: an event-related functional MRI study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(14):8301–8306
Greene DJ, Colich N, Iacoboni M, Zaidel E, Bookheimer SY, Dapretto M (2011) Atypical neural networks for social orienting in autism spectrum disorders. Neuroimage 56(1):354–362. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.02.031
Greicius MD, Krasnow B, Reiss AL, Menon V (2003) Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(1):253–258. doi:10.1073/pnas.0135058100
Gusnard DA, Akbudak E, Shulman GL, Raichle ME (2001) Medial prefrontal cortex and self-referential mental activity: relation to a default mode of brain function. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Johnson DL, Wiebe JS, Gold SM, Andreasen NC, Hichwa RD, Watkins GL, Boles Ponto LL (1999) Cerebral blood flow and personality: a positron emission tomography study. Am J Psychiatry 156(2):252–257
Johnson MK, Raye CL, Mitchell KJ, Touryan SR, Greene EJ, Nolen-Hoeksema S (2006) Dissociating medial frontal and posterior cingulate activity during self-reflection. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 1(1):56–64. doi:10.1093/scan/nsl004
Kehoe EG, Toomey JM, Balsters JH, Bokde AL (2011) Personality modulates the effects of emotional arousal and valence on brain activation. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. doi:10.1093/scan/nsr059
Kennedy DP, Courchesne E (2008) The intrinsic functional organisation of the brain is altered in autism. Neuroimage 39:1877–1885
Kim SH, Hwang JH, Park HS, Kim SE (2008) Resting brain metabolic correlates of neuroticism and extraversion in young men. Neuroreport 19(8):883–886. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e328300080f
Krebs RM, Schott BH, Duzel E (2009) Personality traits are differentially associated with patterns of reward and novelty processing in the human substantia nigra/ventral tegmental area. Biol Psychiatry 65(2):103–110. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.08.019
Kunisato Y, Okamoto Y, Okada G, Aoyama S, Nishiyama Y, Onoda K, Yamawaki S (2011) Personality traits and the amplitude of spontaneous low-frequency oscillations during resting state. Neurosci Lett 492(2):109–113. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.01.067
Lane RD, Reiman EM, Axelrod B, Yun LS, Holmes A, Schwartz GE (1998) Neural correlates of levels of emotional awareness. Evidence of an interaction between emotion and attention in the anterior cingulate cortex. J Cogn Neurosci 10(4):525–535
Mason MF, Norton MI, Van Horn JD, Wegner DM, Grafton ST, Macrae CN (2007) Wandering minds: the default network and stimulus independent thought. Science 315:393–395
Mischel W (1968) Personality and assessment. John Wiley, New York
Raichle ME, Snyder AZ (2007) A default mode of brain function: a brief history of an evolving idea. Neuroimage 37(4):1083–1090. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.041 (discussion 1097–1089)
Raichle ME, MacLeod AM, Snyder AZ, Powers WJ, Gusnard DA, Shulman GL (2001) A default mode of brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:676–682
Ryman SG, Gasparovic C, Bedrick EJ, Flores RA, Marshall AN, Jung RE (2011) Brain biochemistry and personality: a magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. PLoS One 6(11):e26758. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026758
Sohn MH, Ursu S, Anderson JR, Stenger VA, Carter CS (2000) The role of prefrontal cortex and posterior parietal cortex in task switching. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(24):13448–13453. doi:10.1073/pnas.240460497
Sutin AR, Beason-Held LL, Resnick SM, Costa PT (2009) Sex differences in resting-state neural correlates of openness to experience among older adults. Cereb Cortex 19(12):2797–2802. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp066
van der Linden D, Nijenhuis J, Bakker AB (2010) The general factor of personality: a meta-analysis of big five intercorrelations and a criterion-related validity study. J Res Personal 44(3):315–327
Volkow ND, Tomasi D, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Telang F, Goldstein RZ, Alia-Klein N, Woicik P, Wong C, Logan J, Millard J, Alexoff D (2011) Positive emotionality is associated with baseline metabolism in orbitofrontal cortex and in regions of the default network. Mol Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/mp.2011.30
Wei L, Duan X, Yang Y, Liao W, Gao Q, Ding JR, Zhang Z, Zeng W, Li Y, Lu G, Chen H (2011) The synchronization of spontaneous BOLD activity predicts extraversion and neuroticism. Brain Res 1419:68–75. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.08.060
Wei L, Duan X, Zheng C, Wang S, Gao Q, Zhang Z, Lu G, Chen H (2012) Specific frequency bands of amplitude low-frequency oscillation encodes personality. Hum Brain Mapp. doi:10.1002/hbm.22176
Wright CI, Williams D, Feczko E, Barrett LF, Dickerson BC, Schwartz CE, Wedig MM (2006) Neuroanatomical correlates of extraversion and neuroticism. Cereb Cortex 16(12):1809–1819. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj118
Zhou Y, Liang M, Tian L, Wang K, Hao Y, Liu H, Liu Z, Jiang T (2007) Functional disintegration in paranoid schizophrenia using resting-state fMRI. Schizophr Res 97:194–205
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by PIC/IC/83290/2007, which is supported by FEDER (POFC—COMPETE) and FCT. The authors acknowledge Jaime Rocha for his discussions on neuroimaging.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Sampaio and J. M. Soares share equal first authorship.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sampaio, A., Soares, J.M., Coutinho, J. et al. The Big Five default brain: functional evidence. Brain Struct Funct 219, 1913–1922 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0610-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0610-y