Abstract
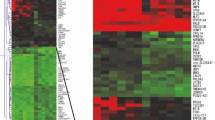
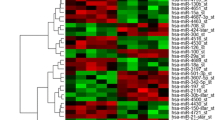
In this study, we used microRNA (miRNA) microarrays in an unbiased screen for aberrantly expressed miRNAs in seminoma, a primitive type of germ cell tumor. Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) surgical samples from 11 cases of normal testicular tissue resected for nonneoplastic causes and from 11 cases of seminoma were assessed for miRNA expression. Normal testicular tissue and seminoma were paired by race. We found 112 miRNAs to be differentially expressed between seminoma and normal testicular tissue; 52 miRNAs were overexpressed, and 60, downregulated in seminoma. We did not observe significant differences between black and white populations in our race-paired study. The upregulation of the expression of hsa-mir-21, hsa-mir-372, hsa-mir-373, has-mir-221, and hsa-mir-222 was validated by reverse transcription and real-time PCR. Hsa-mir-372 was upregulated around 1,270-fold (95 % confidence interval (CI) 525.2–3,064.8; p = 8.1e-5 by Mann–Whitney U test). Hsa-mir-373 was upregulated around 1,530-fold (95 % CI 620.5–3,785.6; p = 8.0e-5 by Mann–Whitney U test), consistent with previous reports, indicating that the miRNAs in FFPE are well preserved, and FFPE can be a valuable source for the miRNA study of seminoma. In addition, expression of hsa-mir-21 (12.2-fold, 0.0095), hsa-mir-221 (3.8-fold, 0.014) and hsa-mir-222 (3.8-fold, 0.019) was found elevated in seminoma compared to normal testicular tissue.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGlynn KA, Devesa SS, Sigurdson AJ et al (2003) Trends in the incidence of testicular germ cell tumors in the United States. Cancer 97(1):63–70
Iczkowski KA, Butler SL (2006) New immunohistochemical markers in testicular tumors. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 28(4):181–187
Cowland JB, Hother C, Gronbaek K (2007) MicroRNAs and cancer. APMIS 115(10):1090–1106
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M et al (2006) A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell 124(6):1169–1181
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J et al (2007) Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 120(5):1046–1054
Palmer RD, Murray MJ, Saini HK et al (2010) Malignant germ cell tumors display common microRNA profiles resulting in global changes in expression of messenger RNA targets. Cancer Res 70(7):2911–2923
Skakkebaek NE (1972) Possible carcinoma-in-situ of the testis. Lancet 2(7776):516–517
Heidenreich A, Weissbach L, Holtl W et al (2001) Organ sparing surgery for malignant germ cell tumor of the testis. J Urol 166(6):2161–2165
Di Vizio D, Cito L, Boccia A et al (2005) Loss of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN marks the transition from intratubular germ cell neoplasias (ITGCN) to invasive germ cell tumors. Oncogene 24(11):1882–1894
Tang F, Hajkova P, Barton SC et al (2006) MicroRNA expression profiling of single whole embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 34(2):e9
Lehmann U (2010) MicroRNA-profiling in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens. Methods Mol Biol 667:113–125
Liu A, Xu X (2011) MicroRNA isolation from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Methods Mol Biol 724:259–267
Luzna P, Gregar J, Uberall I et al (2011) Changes of microRNAs-192, 196a and 203 correlate with Barrett’s esophagus diagnosis and its progression compared to normal healthy individuals. Diagn Pathol 6(1):114
Niyazi M, Zehentmayr F, Niemoller OM et al (2011) MiRNA expression patterns predict survival in glioblastoma. Radiat Oncol 6:153
Snowdon J, Zhang X, Childs T et al (2011) The microRNA-200 family is upregulated in endometrial carcinoma. PLoS One 6(8):e22828
Tetzlaff MT, Liu A, Xu X et al (2007) Differential expression of miRNAs in papillary thyroid carcinoma compared to multinodular goiter using formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissues. Endocr Pathol 18(3):163–173
Gillis AJ, Stoop HJ, Hersmus R et al (2007) High-throughput microRNAome analysis in human germ cell tumours. J Pathol 213(3):319–328
Suh MR, Lee Y, Kim JY et al (2004) Human embryonic stem cells express a unique set of microRNAs. Dev Biol 270(2):488–498
Judson RL, Babiarz JE, Venere M et al (2009) Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs promote induced pluripotency. Nat Biotechnol 27(5):459–461
Wang Y, Baskerville S, Shenoy A et al (2008) Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs regulate the G1-S transition and promote rapid proliferation. Nat Genet 40(12):1478–1483
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M et al (2007) A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Adv Exp Med Biol 604:17–46
Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T, Housman DE (1993) p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell 74(6):957–967
Lutzker SG (1998) P53 tumour suppressor gene and germ cell neoplasia. APMIS 106(1):85–89
Port M, Glaesener S, Ruf C et al (2011) Micro-RNA expression in cisplatin resistant germ cell tumor cell lines. Mol Cancer 10:52
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M et al (2008) The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 10(2):202–210
Rentoft M, Fahlen J, Coates PJ et al (2011) miRNA analysis of formalin-fixed squamous cell carcinomas of the tongue is affected by age of the samples. Int J Oncol 38(1):61–69
Siebolts U, Varnholt H, Drebber U et al (2009) Tissues from routine pathology archives are suitable for microRNA analyses by quantitative PCR. J Clin Pathol 62(1):84–88
Li S, Liang Z, Xu L, Zou F (2012) MicroRNA-21: a ubiquitously expressed pro-survival factor in cancer and other diseases. Mol Cell Biochem 360(1–2):147–158
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65(14):6029–6033
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A et al (2008) Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283(2):1026–1033
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA et al (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27(15):2128–2136
Nagao Y, Hisaoka M, Matsuyama A et al (2012) Association of microRNA-21 expression with its targets, PDCD4 and TIMP3, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 25(1):112–121
Niu Z, Goodyear SM, Rao S et al (2011) MicroRNA-21 regulates the self-renewal of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(31):12740–12745
Elmen J, Lindow M, Silahtaroglu A et al (2008) Antagonism of microRNA-122 in mice by systemically administered LNA-antimiR leads to up-regulation of a large set of predicted target mRNAs in the liver. Nucleic Acids Res 36(4):1153–1162
Krutzfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R et al (2005) Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature 438(7068):685–689
Felicetti F, Errico MC, Segnalini P, Mattia G, Care A (2008) MicroRNA-221 and −222 pathway controls melanoma progression. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 8(11):1759–1765
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA et al (2007) Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J 26(15):3699–3708
Liang Y (2008) An expression meta-analysis of predicted microRNA targets identifies a diagnostic signature for lung cancer. BMC Med Genomics 1:61
Miller TE, Ghoshal K, Ramaswamy B et al (2008) MicroRNA-221/222 confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer by targeting p27Kip1. J Biol Chem 283(44):29897–29903
Zhao JJ, Lin J, Yang H et al (2008) MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates estrogen receptor alpha and is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 283(45):31079–31086
Garofalo M, Di Leva G, Romano G et al (2009) miR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell 16(6):498–509
Zhang C, Kang C, Wang P et al (2011) MicroRNA-221 and −222 regulate radiation sensitivity by targeting the PTEN pathway. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 80(1):240–248
Acknowledgments
We thank Aihua Liu for the technical support.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bing, Z., Master, S.R., Tobias, J.W. et al. MicroRNA expression profiles of seminoma from paraffin-embedded formalin-fixed tissue. Virchows Arch 461, 663–668 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1325-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1325-9