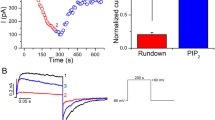
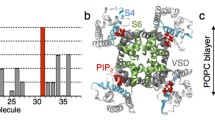
Abstract
Phosphoinositides, such as phosphatidylinositol-bisphosphate (PIP2), control the activity of many ion channels in yet undefined ways. Inwardly, rectifying potassium (Kir) channels were the first shown to be dependent on direct interactions with phosphoinositides. Alterations in channel-PIP2 interactions affect Kir single-channel gating behavior. Aberrations in channel-PIP2 interactions can lead to human disease. As the activity of all Kir channels depends on their interactions with phosphoinositides, future research will aim to understand the molecular events that occur from phosphoinositide binding to channel gating. The determination of atomic resolution structures for several mammalian and bacterial Kir channels provides great promise towards this goal. We have mapped onto the three-dimensional channel structure the position of basic residues identified through mutagenesis studies that contribute to the sensitivity of a Kir channel to PIP2. The localization of these putative PIP2-interacting residues relative to the channel’s permeation pathway has given rise to a testable model, which could account for channel activation by PIP2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham MR, Jahangir A, Alekseev AE, Terzic A (1999) Channelopathies of inwardly rectifying potassium channels. FASEB J 13:1901–1910
Adrian RH, Chandler WK, Hodgkin AL (1970) Slow changes in potassium permeability in skeletal muscle. J Physiol 208:645–668
Aguilar-Bryan L, Nichols CG, Wechsler SW, Clement JP 4th, Boyd AE 3rd, Gonzalez G, Herrera-Sosa H, Nguy K, Bryan J, Nelson DA (1995) Cloning of the beta cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science 268:423–426
Ammala C, Moorhouse A, Gribble F, Ashfield R, Proks P, Smith PA, Sakura H, Coles B, Ashcroft SJ, Ashcroft FM (1996) Promiscuous coupling between the sulphonylurea receptor and inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Nature 379:545–548
Armstrong CM (1969) Inactivation of the potassium conductance and related phenomena caused by quaternary ammonium ion injection in squid axons. J Gen Physiol 54:553–575
Bichet D, Haass FA, Jan LY (2003) Merging functional studies with structures of inward-rectifier K+ channels. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:957–967
Bond CT, Pessia M, Xia XM, Lagrutta A, Kavanaugh MP, Adelman JP (1994) Cloning and expression of a family of inward rectifier potassium channels. Recept Channels 2:183–191
Bredt DS, Wang TL, Cohen NA, Guggino WB, Snyder SH (1995) Cloning and expression of two brain-specific inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6753–6757
Chan KW, Langan MN, Sui JL, Kozak JA, Pabon A, Ladias JA, Logothetis DE (1996) A recombinant inwardly rectifying potassium channel coupled to GTP-binding proteins. J Gen Physiol 107:381–397
Clement JP 4th, Kunjilwar K, Gonzalez G, Schwanstecher M, Panten U, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J (1997) Association and stoichiometry of K(ATP) channel subunits. Neuron 18:827–838
Cohen NA, Sha Q, Makhina EN, Lopatin AN, Linder ME, Snyder SH, Nichols CG (1996) Inhibition of an inward rectifier potassium channel (Kir2.3) by G-protein βγ subunits. J Biol Chem 271:32301–32305
Dascal N, Schreibmayer W, Lim NF, Wang W, Chavkin C, DiMagno L, Labarca C, Kieffer BL, Gaveriaux-Ruff C, Trollinger D (1993) Atrial G protein-activated K+ channel: expression cloning and molecular properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10235–10239
Davies NP, Imbrici P, Fialho D, Herd C, Bilsland LG, Weber A, Mueller R, Hilton-Jones D, Ealing J, Boothman BR, Giunti P, Parsons LM, Thomas M, Manzur AY, Jurkat-Rott K, Lehmann-Horn F, Chinnery PF, Rose M, Kullmann DM, Hanna MG (2005) Andersen–Tawil syndrome: new potassium channel mutations and possible phenotypic variation. Neurology 65:1083–1089
Derst C, Konrad M, Kockerling A, Karolyi L, Deschenes G, Daut J, Karschin A, Seyberth HW (1997) Mutations in the ROMK gene in antenatal Bartter syndrome are associated with impaired K+ channel function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 230:641–645
Donaldson MR, Jensen JL, Tristani-Firouzi M, Tawil R, Bendahhou S, Suarez WA, Cobo AM, Poza JJ, Behr E, Wagstaff J, Szepetowski P, Pereira S, Mozaffar T, Escolar DM, Fu YH, Ptacek LJ (2003) PIP2 binding residues of Kir2.1 are common targets of mutations causing Andersen syndrome. Neurology 60:1811–1816
Doring F, Derst C, Wischmeyer E, Karschin C, Schneggenburger R, Daut J, Karschin A (1998) The epithelial inward rectifier channel Kir7.1 displays unusual K+ permeation properties. J Neurosci 18:8625–8636
Doyle DA, Morais Cabral J, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (1998) The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 280:69–77
Du X, Zhang H, Lopes C, Mirshahi T, Rohacs T, Logothetis DE (2004) Characteristic interactions with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate determine regulation of Kir channels by diverse modulators. J Biol Chem 279:37271–37281
Durell SR, Guy HR (2001) A family of putative Kir potassium channels in prokaryotes. BMC Evol Biol 1:14
Fakler B, Brandle U, Glowatzki E, Zenner HP, Ruppersberg JP (1994) Kir2.1 inward rectifier K+ channels are regulated independently by protein kinases and ATP hydrolysis. Neuron 13:1413–1420
Fan Z, Makielski JC (1997) Anionic phospholipids activate ATP-sensitive potassium channels. J Biol Chem 272:5388–5395
Gosset P, Ghezala GA, Korn B, Yaspo ML, Poutska A, Lehrach H, Sinet PM, Creau N (1997) A new inward rectifier potassium channel gene (KCNJ15) localized on chromosome 21 in the Down syndrome chromosome region 1 (DCR1). Genomics 44:237–241
Gribble FM, Tucker SJ, Ashcroft FM (1997) The essential role of the Walker A motifs of SUR1 in KATP channel activation by Mg-ADP and diazoxide. EMBO J 16:1145–1152
Hagiwara S, Jaffe LA (1979) Electrical properties of egg cell membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng 8:385–416
Hagiwara S, Yoshii M (1979) Effects of internal potassium and sodium on the anomalous rectification of the starfish egg as examined by internal perfusion. J Physiol 292:251–265
He C, Yan X, Zhang H, Mirshahi T, Jin T, Huang A, Logothetis DE (2002) Identification of critical residues controlling G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channel activity through interactions with the βγ subunits of G proteins. J Biol Chem 277:6088–6096
He C, Zhang H, Mirshahi T, Logothetis DE (1999) Identification of a potassium channel site that interacts with G protein βγ subunits to mediate agonist-induced signaling. J Biol Chem 274:12517–12524
Hebert SC, Desir G, Giebisch G, Wang W (2005) Molecular diversity and regulation of renal potassium channels. Physiol Rev 85:319–371
Hilgemann DW, Ball R (1996) Regulation of cardiac Na+,Ca2+ exchange and KATP potassium channels by PIP2. Science 273:956–959
Hilgemann DW, Feng S, Nasuhoglu C (2001) The complex and intriguing lives of PIP2 with ion channels and transporters. Sci STKE 2001:RE19
Ho K, Nichols CG, Lederer WJ, Lytton J, Vassilev PM, Kanazirska MV, Hebert SC (1993) Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature 362:31–38
Hodgkin AL, Horowicz P (1959) The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol 148:127–160
Huang CL, Feng S, Hilgemann DW (1998) Direct activation of inward rectifier potassium channels by PIP2 and its stabilization by G βγ. Nature 391:803–806
Huang CL, Jan YN, Jan LY (1997) Binding of the G protein βγ subunit to multiple regions of G protein-gated inward-rectifying K+ channels. FEBS Lett 405:291–298
Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Clement JP 4th, Namba N, Inazawa J, Gonzalez G, Aguilar-Bryan L, Seino S, Bryan J (1995) Reconstitution of IKATP: an inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor. Science 270:1166–1170
Inagaki N, Tsuura Y, Namba N, Masuda K, Gonoi T, Horie M, Seino Y, Mizuta M, Seino S (1995) Cloning and functional characterization of a novel ATP-sensitive potassium channel ubiquitously expressed in rat tissues, including pancreatic islets, pituitary, skeletal muscle, and heart. J Biol Chem 270:5691–5694
Inanobe A, Matsuura T, Nakagawa A, Kurachi Y (2007) Structural diversity in the cytoplasmic region of G protein-gated inward rectifier K+ channels. Channels 1:39–45
Inanobe A, Morishige KI, Takahashi N, Ito H, Yamada M, Takumi T, Nishina H, Takahashi K, Kanaho Y, Katada T (1995) G beta gamma directly binds to the carboxyl terminus of the G protein-gated muscarinic K+ channel, GIRK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 212:1022–1028
Ishihara K, Hiraoka M (1994) Gating mechanism of the cloned inward rectifier potassium channel from mouse heart. J Membr Biol 142:55–64
Ishii K, Yamagishi T, Taira N (1994) Cloning and functional expression of a cardiac inward rectifier K+ channel. FEBS Lett 338:107–111
Jiang Y, Lee A, Chen J, Cadene M, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (2002) Crystal structure and mechanism of a calcium-gated potassium channel. Nature 417:515–522
Jiang Y, Lee A, Chen J, Cadene M, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (2002) The open pore conformation of potassium channels. Nature 417:523–526
Jin T, Peng L, Mirshahi T, Rohacs T, Chan KW, Sanchez R, Logothetis DE (2002) The beta gamma subunits of G proteins gate a K+ channel by pivoted bending of a transmembrane segment. Mol Cell 10:469–481
Jin T, Logothetis DE (2004) Effects of altered channel-PIP2 interactions on single-channel kinetics of inwardly rectifying Kir channels. Biophys J 439A–440A
Katz B (1949) Les constantes électriques de la membrane du muscle. Archives des Sciences Physiologiques 3:285–299
Krapivinsky G, Gordon EA, Wickman K, Velimirovic B, Krapivinsky L, Clapham DE (1995) The G-protein-gated atrial K+ channel IKACh is a heteromultimer of two inwardly rectifying K+-channel proteins. Nature 374:135–141
Krapivinsky G, Medina I, Eng L, Krapivinsky L, Yang Y, Clapham DE (1998) A novel inward rectifier K+ channel with unique pore properties. Neuron 20:995–1005
Kubo Y, Baldwin TJ, Jan YN, Jan LY (1993) Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature 362:127–133
Kubo Y, Reuveny E, Slesinger PA, Jan YN, Jan LY (1993) Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature 364:802–806
Kunkel MT, Peralta EG (1995) Identification of domains conferring G protein regulation on inward rectifier potassium channels. Cell 83:443–449
Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Antcliff JF, Rahman T, Lowe ED, Zimmer J, Cuthbertson J, Ashcroft FM, Ezaki T, Doyle DA (2003) Crystal structure of the potassium channel KirBac1.1 in the closed state. Science 300:1922–1926
Kurachi Y (1985) Voltage-dependent activation of the inward-rectifier potassium channel in the ventricular cell membrane of guinea-pig heart. J Physiol 366:365–385
Leech CA, Stanfield PR (1981) Inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres and its dependence on membrane potential and external potassium. J Physiol 319:295–309
Lesage F, Duprat F, Fink M, Guillemare E, Coppola T, Lazdunski M, Hugnot JP (1994) Cloning provides evidence for a family of inward rectifier and G-protein coupled K+ channels in the brain. FEBS Lett 353:37–42
Leung YM, Zeng WZ, Liou HH, Solaro CR, Huang CL (2000) Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and intracellular pH regulate the ROMK1 potassium channel via separate but interrelated mechanisms. J Biol Chem 275:10182–10189
Logothetis DE, Kurachi Y, Galper J, Neer EJ, Clapham DE (1987) The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature 325:321–326
Logothetis DE, Lupyan D, Rosenhouse-Dantsker A (2007) Diverse Kir modulators act in close proximity to residues implicated in phosphoinositide binding. J Physiol (in press)
Lopatin AN, Makhina EN, Nichols CG (1994) Potassium channel block by cytoplasmic polyamines as the mechanism of intrinsic rectification. Nature 372:366–369
Lopes CM, Zhang H, Rohacs T, Jin T, Yang J, Logothetis DE (2002) Alterations in conserved Kir channel-PIP2 interactions underlie channelopathies. Neuron 34:933–944
Mark MD, Herlitze S (2000) G-protein mediated gating of inward-rectifier K+ channels. Eur J Biochem 267:5830–5836
Matsuda H, Saigusa A, Irisawa H (1987) Ohmic conductance through the inwardly rectifying K channel and blocking by internal Mg2+. Nature 325:156–159
Nakamura N, Suzuki Y, Sakuta H, Ookata K, Kawahara K, Hirose S (1999) Inwardly rectifying K+ channel Kir7.1 is highly expressed in thyroid follicular cells, intestinal epithelial cells and choroid plexus epithelial cells: implication for a functional coupling with Na+,K+-ATPase. Biochem J 342(Pt 2):329–336
Newman EA (1993) Inward-rectifying potassium channels in retinal glial (Muller) cells. J Neurosci 13:3333–3345
Nichols CG, Lederer WJ (1991) Adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol 261:H1675–H1686
Nishida M, MacKinnon R (2002) Structural basis of inward rectification: cytoplasmic pore of the G protein-gated inward rectifier GIRK1 at 1.8 A resolution. Cell 111:957–965
Noma A (1983) ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature 305:147–148
Ohira M, Seki N, Nagase T, Suzuki E, Nomura N, Ohara O, Hattori M, Sakaki Y, Eki T, Murakami Y, Saito T, Ichikawa H, Ohki M (1997) Gene identification in 1.6-Mb region of the Down syndrome region on chromosome 21. Genome Res 7:47–58
Oliva C, Cohen IS, Pennefather P (1990) The mechanism of rectification of iK1 in canine Purkinje myocytes. J Gen Physiol 96:299–318
Partiseti M, Collura V, Agnel M, Culouscou JM, Graham D (1998) Cloning and characterization of a novel human inwardly rectifying potassium channel predominantly expressed in small intestine. FEBS Lett 434:171–176
Pearson WL, Dourado M, Schreiber M, Salkoff L, Nichols CG (1999) Expression of a functional Kir4 family inward rectifier K+ channel from a gene cloned from mouse liver. J Physiol 514:639–653
Pegan S, Arrabit C, Slesinger PA, Choe S (2006) Andersen’s syndrome mutation effects on the structure and assembly of the cytoplasmic domains of Kir2.1. Biochemistry 45:8599–8606
Pegan S, Arrabit C, Zhou W, Kwiatkowski W, Collins A, Slesinger PA, Choe S (2005) Cytoplasmic domain structures of Kir2.1 and Kir3.1 show sites for modulating gating and rectification. Nat Neurosci 8:279–287
Perier F, Radeke CM, Vandenberg CA (1994) Primary structure and characterization of a small-conductance inwardly rectifying potassium channel from human hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:6240–6244
Pessia M, Tucker SJ, Lee K, Bond CT, Adelman JP (1996) Subunit positional effects revealed by novel heteromeric inwardly rectifying K+ channels. EMBO J 15:2980–2987
Phillips LR, Nichols CG (2003) Ligand-induced closure of inward rectifier Kir6.2 channels traps spermine in the pore. J Gen Physiol 122:795–804
Plaster NM, Tawil R, Tristani-Firouzi M, Canun S, Bendahhou S, Tsunoda A, Donaldson MR, Iannaccone ST, Brunt E, Barohn R, Clark J, Deymeer F, George AL Jr, Fish FA, Hahn A, Nitu A, Ozdemir C, Serdaroglu P, Subramony SH, Wolfe G et al (2001) Mutations in Kir2.1 cause the developmental and episodic electrical phenotypes of Andersen’s syndrome. Cell 105:511–519
Proks P, Antcliff JF, Ashcroft FM (2003) The ligand-sensitive gate of a potassium channel lies close to the selectivity filter. EMBO Rep 4:70–75
Raab-Graham KF, Radeke CM, Vandenberg CA (1994) Molecular cloning and expression of a human heart inward rectifier potassium channel. Neuroreport 5:2501–2505
Rohacs T, Chen J, Prestwich GD, Logothetis DE (1999) Distinct specificities of inwardly rectifying K+ channels for phosphoinositides. J Biol Chem 274:36065–36072
Rohacs T, Lopes C, Mirshahi T, Jin T, Zhang H, Logothetis DE (2002) Assaying phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate regulation of potassium channels. Methods Enzymol 345:71–92
Rohacs T, Lopes CM, Jin T, Ramdya PP, Molnar Z, Logothetis DE (2003) Specificity of activation by phosphoinositides determines lipid regulation of Kir channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:745–750
Rohacs T, Lopes CM, Michailidis I, Logothetis DE (2005) PI(4,5)P2 regulates the activation and desensitization of TRPM8 channels through the TRP domain. Nat Neurosci 8:626–634
Ruppersberg JP (2000) Intracellular regulation of inward rectifier K+ channels. Pflügers Arch 441:1–11
Sakmann B, Noma A, Trautwein W (1983) Acetylcholine activation of single muscarinic K+ channels in isolated pacemaker cells of the mammalian heart. Nature 303:250–253
Salvatore L, D’Adamo MC, Polishchuk R, Salmona M, Pessia M (1999) Localization and age-dependent expression of the inward rectifier K+ channel subunit Kir 5.1 in a mammalian reproductive system. FEBS Lett 449:146–152
Schulze D, Krauter T, Fritzenschaft H, Soom M, Baukrowitz T (2003) Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) modulation of ATP and pH sensitivity in Kir channels. A tale of an active and a silent PIP2 site in the N terminus. J Biol Chem 278:10500–10505
Schwalbe RA, Bianchi L, Accili EA, Brown AM (1998) Functional consequences of ROMK mutants linked to antenatal Bartter’s syndrome and implications for treatment. Hum Mol Genet 7:975–980
Shuck ME, Piser TM, Bock JH, Slightom JL, Lee KS, Bienkowski MJ (1997) Cloning and characterization of two K+ inward rectifier (Kir) 1.1 potassium channel homologs from human kidney (Kir1.2 and Kir1.3). J Biol Chem 272:586–593
Shyng SL, Nichols CG (1997) Octameric stoichiometry of the KATP channel complex. J Gen Physiol 110:655–664
Shyng SL, Cukras CA, Harwood J, Nichols CG (2000) Structural determinants of PIP2 regulation of inward rectifier KATP channels. J Gen Physiol 116:599–608
Simon DB, Karet FE, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Hamdan JH, DiPietro A, Trachtman H, Sanjad SA, Lifton RP (1996) Genetic heterogeneity of Bartter’s syndrome revealed by mutations in the K+ channel, ROMK. Nat Genet 14:152–156
Soom M, Schonherr R, Kubo Y, Kirsch C, Klinger R, Heinemann SH (2001) Multiple PIP2 binding sites in Kir2.1 inwardly rectifying potassium channels. FEBS Lett 490:49–53
Standen NB, Stanfield PR (1978) A potential- and time-dependent blockade of inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres by barium and strontium ions. J Physiol 280:169–191
Stanfield PR, Davies NW, Shelton PA, Khan IA, Brammar WJ, Standen NB, Conley EC (1994) The intrinsic gating of inward rectifier K+ channels expressed from the murine IRK1 gene depends on voltage, K+ and Mg2+. J Physiol 475:1–7
Stanfield PR, Nakajima S, Nakajima Y (2002) Constitutively active and G-protein coupled inward rectifier K+ channels: Kir2.0 and Kir3.0. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 145:47–179
Suh BC, Hille B (2005) Regulation of ion channels by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:370–378
Sui JL, Chan K, Langan MN, Vivaudou M, Logothetis DE (1999) G protein gated potassium channels. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprot Res 33:179–201
Sui JL, Chan KW, Logothetis DE (1996) Na+ activation of the muscarinic K+ channel by a G-protein-independent mechanism. J Gen Physiol 108:381–391
Sui JL, Petit-Jacques J, Logothetis DE (1998) Activation of the atrial KACh channel by the βγ subunits of G proteins or intracellular Na+ ions depends on the presence of phosphatidylinositol phosphates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1307–1312
Takano M, Kuratomi S (2003) Regulation of cardiac inwardly rectifying potassium channels by membrane lipid metabolism. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 81:67–79
Takumi T, Ishii T, Horio Y, Morishige K, Takahashi N, Yamada M, Yamashita T, Kiyama H, Sohmiya K, Nakanishi S (1995) A novel ATP-dependent inward rectifier potassium channel expressed predominantly in glial cells. J Biol Chem 270:16339–16346
Tanemoto M, Kittaka N, Inanobe A, Kurachi Y (2000) In vivo formation of a proton-sensitive K+ channel by heteromeric subunit assembly of Kir5.1 with Kir4.1. J Physiol 525(Pt 3):587–592
Tucker SJ, Imbrici P, Salvatore L, D’Adamo MC, Pessia M (2000) pH dependence of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel, Kir5.1, and localization in renal tubular epithelia. J Biol Chem 275:16404–16407
Vandenberg CA (1987) Inward rectification of a potassium channel in cardiac ventricular cells depends on internal magnesium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2560–2564
Vivaudou M, Chan KW, Sui JL, Jan LY, Reuveny E, Logothetis DE (1997) Probing the G-protein regulation of GIRK1 and GIRK4, the two subunits of the KACh channel, using functional homomeric mutants. J Biol Chem 272:31553–31560
Wang WH, Giebisch G (1991) Dual modulation of renal ATP-sensitive K+ channel by protein kinases A and C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9722–9725
Wible BA, De Biasi M, Majumder K, Taglialatela M, Brown AM (1995) Cloning and functional expression of an inwardly rectifying K+ channel from human atrium. Circ Res 76:343–350
Xiao J, Zhen XG, Yang J (2003) Localization of PIP2 activation gate in inward rectifier K+ channels. Nat Neurosci 6:811–818
Xie LH, John SA, Ribalet B, Weiss JN (2007) Activation of inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) channels by phosphatidylinosital-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2): interaction with other regulatory ligands. Prog Biophys Mol Biol (in press)
Xu H, Cui N, Yang Z, Qu Z, Jiang C (2000) Modulation of Kir4.1 and Kir5.1 by hypercapnia and intracellular acidosis. J Physiol (Lond) 524:725–735
Yan K, Gautam N (1996) A domain on the G protein beta subunit interacts with both adenylyl cyclase 2 and the muscarinic atrial potassium channel. J Biol Chem 271:17597–17600
Yang Z, Xu H, Cui N, Qu Z, Chanchevalap S, Shen W, Jiang C (2000) Biophysical and molecular mechanisms underlying the modulation of heteromeric Kir4.1-Kir5.1 channels by CO2 and pH. J Gen Physiol 116:33–45
Zaritsky JJ, Eckman DM, Wellman GC, Nelson MT, Schwarz TL (2000) Targeted disruption of Kir2.1 and Kir2.2 genes reveals the essential role of the inwardly rectifying K+ current in K+-mediated vasodilation. Circ Res 87:160–166
Zaritsky JJ, Redell JB, Tempel BL, Schwarz TL (2001) The consequences of disrupting cardiac inwardly rectifying K+ current (IK1) as revealed by the targeted deletion of the murine Kir2.1 and Kir2.2 genes. J Physiol 533:697–710
Zeng WZ, Li XJ, Hilgemann DW, Huang CL (2003) Protein kinase C inhibits ROMK1 channel activity via a phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 278:16852–16856
Zeng WZ, Liou HH, Krishna UM, Falck JR, Huang CL (2002) Structural determinants and specificities for ROMK1-phosphoinositide interaction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F826–F834
Zhang H, Craciun LC, Mirshahi T, Rohacs T, Lopes CM, Jin T, Logothetis DE (2003) PIP2 activates KCNQ channels, and its hydrolysis underlies receptor-mediated inhibition of M currents. Neuron 37:963–975
Zhang H, He C, Yan X, Mirshahi T, Logothetis DE (1999) Activation of inwardly rectifying K+ channels by distinct PtdIns(4,5)P2 interactions. Nat Cell Biol 1:183–188
Zhao Q, Yang M, Ting AT, Logothetis DE (2007) PIP2 regulates the ionic current of P2X receptors and P2X7-mediated cell death. Channels 1:46–55
Nichols CG, Lopatin AN (1997) Inward rectifier potassium channels. Annu Rev Physiol 59:171–191
Liou HH, Zhou SS, Huang CL (1999) Regulations of ROMK1 channel by protein kinase A via phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 10:5820–5825
Ishihara K, Mitsuiye T, Noma A, Takano M (1989) The Mg2+ block and intrinsic gating underlying inward rectification of K+ current in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. J Physiol 419:297–320
Shimura M, Yuan Y, Chang JT, Jhang S, Campochiaro PA, Zack DJ, Hughes BA (2001) Expression and permeation properties of the K+ channel Kir 7.1 in the retinal pigment epithelium. J Physiol 531:329–346
Kusaka S, Inanobe A, Fujita A, Makino Y, Tanemoto M, Matsushita K, Tano Y, Kurachi Y (2001) Functional Kir 7.1 channels localized at the root of apical processes in rat retinal pigment epithelium. J Physiol 513:27–36
Yang D, Pan A, Swaminathan A, Kumar G, Hugges BA (2003) Expression and localization of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir7.1 in native bovine retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:3178–3185
Cortes DM, Cuello LG, Perozo E (2001) Molecular architecture of full-length KcsA: role of cytoplasmic domain in ion permeation and activation gating. J Gen Physiol 117:165–180
Jin T, Logothetis DE (2004) Effect of altered channel-PIP2 interactions on single-channel kinetics of inwardly rectifying K+ (Kir) channels. Biophys J 86:439A–440A
Lu Z, MacKinnon R (1994) Electrostatic tuning of Mg2+ affinity in an inward-rectifier K+ channel. Nature 371:243–246
Huang CL, Slesinger PA, Casey PJ, Jan YN, Jan LY (1995) Evidence that direct binding of G βγ to the GIRK1 G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channel is important for channel activation. Neuron 15:1133–1143
Lin YW, Jia T, Weinsoft AM, Shyng SL (2003) Stabilization of the activity of ATP-sensitive potassium channels by ion pairs formed between adjacent Kir6.2 subunits. J Gen Physiol 122:225–237
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank past and present members of the Logothetis lab. Without their dedication and enthusiasm in studying phosphoinositide control of Kir channel activity, this manuscript would not have been possible. This work was supported by NIH grant HL59949 to DEL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Logothetis, D.E., Jin, T., Lupyan, D. et al. Phosphoinositide-mediated gating of inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 455, 83–95 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0276-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0276-5