Abstract
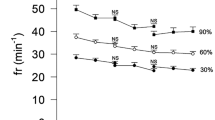
The influences of sex, age, exercise intensity, and end-tidal CO2 on the inspiratory drive ([V T kg−1]·T i −1) and respiratory timing (T i·T tot −1) components of ventilation were examined in 295 youth (138 females, 157 males); similarly distributed 8–18 years of age. Ventilatory and metabolic measures were collected breath-by-breath at rest and during a slow walk (4.0 km h−1), fast walk (5.6 km h−1) and run (8.0 km h−1). Regression modeling for drive (age, sex, and PETCO2) found that sex was significant (R 2 < 0.017; P < 0.05) for rest and running, but not walking. Compared to rest, drive increased by 120% for the slow walk, 217% for the fast walk and 258% for the run (P < 0.0001). Drive decreased with age (P < 0.0001): rest = 0.41 ml kg−1 s−1 year−1; slow walk = 0.90 ml kg−1 s−1 year−1; fast walk = 1.30 ml kg−1 s−1 year−1; and run = 1.47 ml kg−1 s−1 year−1. In the regression models for timing, sex provided ∼ 1% of the variance during the run, but was not significant during rest or walking. Timing increased with exercise intensity by approximately 0.02 units (P < 0.001), but decreased by ∼ 0.002 units year−1 with age for all conditions (P < 0.003). Changes in drive and timing were marginally related to end-tidal CO2 (exercise R 2 < 0.063 for all models). These results suggest that in the control of inspiratory drive and timing during exercise in youth, sex is of minor importance but there are age-related changes which are marginally associated with CO2.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken ML, Franklin JL, Pierson DJ, Schoene RB (1986) Influence of body size and gender on control of ventilation. J Appl Physiol 60(6):1894–1899
Armon Y, Cooper DM, Zanconato S (1991) Maturation of ventilatory responses to 1-minute exercise. Pediatr Res 29:362–368
Askanazi J, Milic-Emili J, Broell JR, Hyman AI, Kinney JM (1979) Influence of exercise and CO2 on breathing pattern of normal man. J Appl Physiol 47(1):192–196
Bainton CR (1972) Effect of speed vs. grade and shivering on ventilation in dogs during active exercise. J Appl Physiol 33(6):778–787
Boule M, Gaultier C, Girard F (1989) Breathing pattern during exercise in untrained children. Respir Physiol 75:225–234
Cooke CB, McDonagh MJN, Nevill AM, Davies CTM (1991) Effects of load on oxygen intake in trained boys and men during treadmill running. J Appl Physiol 71(4):1237–1244
Cooper DM, Kaplan MR, Baumgarten L, Weiler-Ravell D, Whipp BJ, Wasserman K (1987) Coupling of ventilation and CO2 production during exercise in children. Pediatr Res 21:568–572
Das TK (1998) Effects of the menstrual cycle on timing and depth of breathing at rest. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 42(4):498–502
Dombovy ML, Bonekat HW, Williams TJ, Staats BA (1987) Exercise performance and ventilatory response in the menstrual cycle. Med Sci Sports Exerc 19(2):111–117
Eldridge FL (1994) Central integration of mechanisms in exercise hyperpnea. Med Sci Sports Exerc 26(3):319–327
Gaultier C, Perret L, Boule M, Buvry A, Girard F (1981) Occlusion pressure and breathing pattern in healthy children. Respir Physiol 46:71–80
Gratas-Delamarche A, Mercier J, Ramonatxo M, Dassonville J, Prefaut C (1993) Ventilatory response of prepubertal boys and adults to carbon dioxide at rest and during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 66:25–30
Grunstein MM, Derenne JP, Milic-Emili J (1975) Control of depth and frequency of breathing during baroreceptor stimulation in cats. J Appl Physiol 39(3):395–404
Harrell JS, McMurray RG, Baggett CD, Pennell ML, Pearce PF, Bangdiwala SI (2005) Energy costs of physical activities in children and adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37(2):329–336
Jurkowski JEH, Jones NL, Toews CJ, Sutton JR (1981) Effects of menstrual cycle on blood lactate, O2 delivery, and performance during exercise. J Appl Physiol 51(6):1493–1499
Lanteri CJ, Sly PD (1993) Changes in respiratory mechanics with age. J Appl Physiol 74(1):369–378
Lebrun CM, McKenzie DC, Prior JC, Taunton JE (1995) Effects of menstrual cycle phase on athletic performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27(3):437–444
Martin BJ, Weil JV (1979) CO2 and exercise tidal volume. J Appl Physiol 46(2):322–325
Matsuo H, Katayama K, Ishida K, Muramatsu T, Miyamura M (2003) Effect of menstrual cycle and gender on ventilatory and heart rate responses at the onset of exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:100–108
McMurray RG, Ahlborn SW (1982) Respiratory responses to running and walking at the same metabolic rate. Respira Physiol 47:257–265
McMurray RG, Baggett C, Pennell M, Bangdiwala S, Harrell J (2003) Gender differences in ventilatory responses of youth are related to exercise intensity. Port J Sport Sci 3:101–102
Mercier J, Varray A, Ramonatxo M, Mercier B, Prefaut C (1991) Influence of anthropometric characteristics on changes in maximal exercise ventilation and breathing pattern during growth in boys. Eur J Appl Physiol 63:235–241
Milic-Emili J (1982) Recent advances in clinical assessment of control of breathing. Lung 160:1–17
Milic-Emili J, Grunstein MM (1976) Drive and timing components of ventilation. Chest 70(1 Suppl):131–133
Nagano Y, Baba R, Kuraishi K, Yasuda T, Ikoma M, Nishibata K, Yokota M, Nagashima M (1998) Ventilatory control during exercise in normal children. Pediatr Res 43:704–707
Robinson S (1938) Experimental studies of physical fitness in relation to age. Arbeitsphysiologie 10:251–323
Rowland TW (1996) Response to endurance exercise: ventilation. In: Gilly H, Johnson C, Blakley J, Hooper L (eds) Developmental exercise physiology. Human Kinetics, Champaign, pp 141–157
Rowland TW, Cunningham LN (1997) Development of ventilatory responses to exercise in normal white children. Chest 111:327–332
Sato Y, Katayama K, Ishida K, Miyamura M (2000) Ventilatory and circulatory responses at the onset of voluntary exercise and passive movement in children. Eur J Appl Physiol 83:516–523
White DP, Douglas NJ, Pickett CK, Weil JV, Zwillich CW (1983) Sexual influence on the control of breathing. J Appl Physiol 54(4):874–879
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by NINR Grant # NR04564.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ondrak, K.S., McMurray, R.G. Exercise-induced breathing patterns of youth are related to age and intensity. Eur J Appl Physiol 98, 88–96 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-006-0248-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-006-0248-z