Abstract
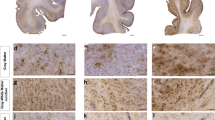
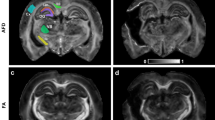
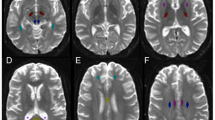
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive degenerative disorder associated with repetitive traumatic brain injury. One of the primary defining neuropathological lesions in CTE, based on the first consensus conference, is the accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau in gray matter sulcal depths. Post-mortem CTE studies have also reported myelin loss, axonal injury and white matter degeneration. Currently, the diagnosis of CTE is restricted to post-mortem neuropathological analysis. We hypothesized that high spatial resolution advanced diffusion MRI might be useful for detecting white matter microstructural changes directly adjacent to gray matter tau pathology. To test this hypothesis, formalin-fixed post-mortem tissue blocks from the superior frontal cortex of ten individuals with an established diagnosis of CTE were obtained from the Veterans Affairs-Boston University-Concussion Legacy Foundation brain bank. Advanced diffusion MRI data was acquired using an 11.74 T MRI scanner at Washington University with 250 × 250 × 500 µm3 spatial resolution. Diffusion tensor imaging, diffusion kurtosis imaging and generalized q-sampling imaging analyses were performed in a blinded fashion. Following MRI acquisition, tissue sections were tested for phosphorylated tau immunoreactivity in gray matter sulcal depths. Axonal disruption in underlying white matter was assessed using two-dimensional Fourier transform analysis of myelin black gold staining. A robust image co-registration method was applied to accurately quantify the relationship between diffusion MRI parameters and histopathology. We found that white matter underlying sulci with high levels of tau pathology had substantially impaired myelin black gold Fourier transform power coherence, indicating axonal microstructural disruption (r = −0.55, p = 0.0015). Using diffusion tensor MRI, we found that fractional anisotropy (FA) was modestly (r = 0.53) but significantly (p = 0.0012) correlated with axonal disruption, where lower FA was associated with greater axonal disruption in white matter directly adjacent to hyperphosphorylated tau positive sulci. In summary, our findings indicate that axonal disruption and tau pathology are closely associated, and high spatial resolution ex vivo diffusion MRI has the potential to detect microstructural alterations observed in CTE tissue. Future studies will be required to determine whether this approach can be applied to living people.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH, Doyle D, Ford I, Gennarelli TA, Graham DI, McLellan DR (1989) Diffuse axonal injury in head injury: definition, diagnosis and grading. Histopathology 15:49–59
Adams JH, Doyle D, Graham DI, Lawrence AE, McLellan DR (1985) Microscopic diffuse axonal injury in cases of head injury. Med Sci Law 25:265–269
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111:209–219
Calabrese E, Badea A, Coe CL, Lubach GR, Styner MA, Johnson GA (2014) Investigating the tradeoffs between spatial resolution and diffusion sampling for brain mapping with diffusion tractography: time well spent? Hum Brain Mapp 35:5667–5685. doi:10.1002/hbm.22578
Cherry JD, Tripodis Y, Alvarez VE, Huber B, Kiernan PT, Daneshvar DH, Mez J, Montenigro PH, Solomon TM, Alosco ML, Stern RA, McKee AC, Stein TD (2016) Microglial neuroinflammation contributes to tau accumulation in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol Commun 4:112. doi:10.1186/s40478-016-0382-8
Cubon VA, Putukian M, Boyer C, Dettwiler A (2011) A diffusion tensor imaging study on the white matter skeleton in individuals with sports-related concussion. J Neurotrauma 28:189–201. doi:10.1089/neu.2010.1430
Currie S, Saleem N, Straiton JA, Macmullen-Price J, Warren DJ, Craven IJ (2016) Imaging assessment of traumatic brain injury. Postgrad Med J 92:41–50. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2014-133211
D’Arceuil H, de Crespigny A (2007) The effects of brain tissue decomposition on diffusion tensor imaging and tractography. NeuroImage 36:64–68. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.039
Dawe RJ, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Vasireddi SK, Arfanakis K (2009) Postmortem MRI of human brain hemispheres: T2 relaxation times during formaldehyde fixation. Magn Reson Med 61:810–818. doi:10.1002/mrm.21909
Gajawelli N, Lao Y, Apuzzo ML, Romano R, Liu C, Tsao S, Hwang D, Wilkins B, Lepore N, Law M (2013) Neuroimaging changes in the brain in contact versus noncontact sport athletes using diffusion tensor imaging. World Neurosurg 80:824–828. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2013.10.020
Gangolli M, Kim J, Holleran L, Stein T, Alvarez V, McKee A, Brody D (2016) Development of Methods to Perform Radiological-Pathological Correlations in Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy. In: National Neurotrauma Society Symposium, Lexington, Kentucky
Ghajari M, Hellyer PJ, Sharp DJ (2017) Computational modelling of traumatic brain injury predicts the location of chronic traumatic encephalopathy pathology. Brain 140:333–343. doi:10.1093/brain/aww317
Goldstein LE, Fisher AM, Tagge CA, Zhang XL, Velisek L, Sullivan JA, Upreti C, Kracht JM, Ericsson M, Wojnarowicz MW, Goletiani CJ, Maglakelidze GM, Casey N, Moncaster JA, Minaeva O, Moir RD, Nowinski CJ, Stern RA, Cantu RC, Geiling J, Blusztajn JK, Wolozin BL, Ikezu T, Stein TD, Budson AE, Kowall NW, Chargin D, Sharon A, Saman S, Hall GF, Moss WC, Cleveland RO, Tanzi RE, Stanton PK, McKee AC (2012) Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in blast-exposed military veterans and a blast neurotrauma mouse model. Sci Transl Med 4:134–160. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003716
Goubran M, Crukley C, de Ribaupierre S, Peters TM, Khan AR (2013) Image registration of ex vivo MRI to sparsely sectioned histology of hippocampal and neocortical temporal lobe specimens. NeuroImage 83:770–781. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.07.053
Goubran M, de Ribaupierre S, Hammond RR, Currie C, Burneo JG, Parrent AG, Peters TM, Khan AR (2015) Registration of in vivo to ex vivo MRI of surgically resected specimens: a pipeline for histology to in vivo registration. J Neurosci Methods 241:53–65. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.12.005
Hasan KM, Narayana PA (2003) Computation of the fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity maps without tensor decoding and diagonalization: theoretical analysis and validation. Magn Reson Med 50:589–598. doi:10.1002/mrm.10552
Hasan KM, Narayana PA (2006) Retrospective measurement of the diffusion tensor eigenvalues from diffusion anisotropy and mean diffusivity in DTI. Magn Reson Med 56:130–137. doi:10.1002/mrm.20935
Henry LC, Tremblay J, Tremblay S, Lee A, Brun C, Lepore N, Theoret H, Ellemberg D, Lassonde M (2011) Acute and chronic changes in diffusivity measures after sports concussion. J Neurotrauma 28:2049–2059. doi:10.1089/neu.2011.1836
Ilvesmaki T, Luoto TM, Hakulinen U, Brander A, Ryymin P, Eskola H, Iverson GL, Ohman J (2014) Acute mild traumatic brain injury is not associated with white matter change on diffusion tensor imaging. Brain 137:1876–1882. doi:10.1093/brain/awu095
Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K (2005) Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 53:1432–1440. doi:10.1002/mrm.20508
Jones DK, Horsfield MA, Simmons A (1999) Optimal strategies for measuring diffusion in anisotropic systems by magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 42:515–525
Kamnaksh A, Budde MD, Kovesdi E, Long JB, Frank JA, Agoston DV (2014) Diffusion tensor imaging reveals acute subcortical changes after mild blast-induced traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep 4:4809. doi:10.1038/srep04809
Karperien A, Ahammer H, Jelinek HF (2013) Quantitating the subtleties of microglial morphology with fractal analysis. Front Cell Neurosci 7:3. doi:10.3389/fncel.2013.00003
Koay CG, Chang LC, Carew JD, Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (2006) A unifying theoretical and algorithmic framework for least squares methods of estimation in diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson 182:115–125. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2006.06.020
Lawrenz M, Finsterbusch J (2015) Mapping measures of microscopic diffusion anisotropy in human brain white matter in vivo with double-wave-vector diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med 73:773–783. doi:10.1002/mrm.25140
Le Bihan D, Johansen-Berg H (2012) Diffusion MRI at 25: exploring brain tissue structure and function. NeuroImage 61:324–341. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.11.006
Lee B, Newberg A (2005) Neuroimaging in traumatic brain imaging. NeuroRx 2:372–383. doi:10.1602/neurorx.2.2.372
Mac Donald CL, Dikranian K, Song SK, Bayly PV, Holtzman DM, Brody DL (2007) Detection of traumatic axonal injury with diffusion tensor imaging in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 205:116–131. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.01.035
Mac Donald CL, Johnson AM, Cooper D, Nelson EC, Werner NJ, Shimony JS, Snyder AZ, Raichle ME, Witherow JR, Fang R, Flaherty SF, Brody DL (2011) Detection of blast-related traumatic brain injury in US military personnel. N Engl J Med 364:2091–2100. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1008069
Mandelkow EM, Stamer K, Vogel R, Thies E, Mandelkow E (2003) Clogging of axons by tau, inhibition of axonal traffic and starvation of synapses. Neurobiol Aging 24:1079–1085. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.04.007
McKee AC, Cairns NJ, Dickson DW, Folkerth RD, Keene CD, Litvan I, Perl DP, Stein TD, Vonsattel JP, Stewart W, Tripodis Y, Crary JF, Bieniek KF, Dams-O’Connor K, Alvarez VE, Gordon WA, Group TC (2016) The first NINDS/NIBIB consensus meeting to define neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 131:75–86. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1515-z
McKee AC, Cantu RC, Nowinski CJ, Hedley-Whyte ET, Gavett BE, Budson AE, Santini VE, Lee HS, Kubilus CA, Stern RA (2009) Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in athletes: progressive tauopathy after repetitive head injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:709–735. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181a9d503
McKee AC, Daneshvar DH (2015) The neuropathology of traumatic brain injury. Handb Clin Neurol 127:45–66. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-52892-6.00004-0
McKee AC, Stein TD, Kiernan PT, Alvarez VE (2015) The neuropathology of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain Pathol 25:350–364. doi:10.1111/bpa.12248
McKee AC, Stern RA, Nowinski CJ, Stein TD, Alvarez VE, Daneshvar DH, Lee HS, Wojtowicz SM, Hall G, Baugh CM, Riley DO, Kubilus CA, Cormier KA, Jacobs MA, Martin BR, Abraham CR, Ikezu T, Reichard RR, Wolozin BL, Budson AE, Goldstein LE, Kowall NW, Cantu RC (2013) The spectrum of disease in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain 136:43–64. doi:10.1093/brain/aws307
Millspaugh J (1937) Dementia pugilistica. US Naval Med Bull 35:297–303
Namjoshi DR, Cheng WH, McInnes KA, Martens KM, Carr M, Wilkinson A, Fan J, Robert J, Hayat A, Cripton PA, Wellington CL (2014) Merging pathology with biomechanics using CHIMERA (Closed-Head Impact Model of Engineered Rotational Acceleration): a novel, surgery-free model of traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurodegener 9:55. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-9-55
Robinson S, Berglass JB, Denson JL, Berkner J, Anstine CV, Winer JL, Maxwell JR, Qiu J, Yang Y, Sillerud LO, Meehan WP 3rd, Mannix R, Jantzie LL (2016) Microstructural and microglial changes after repetitive mild traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurosci Res 95:1025–1035. doi:10.1002/jnr.23848
Shahim P, Linemann T, Inekci D, Karsdal MA, Blennow K, Tegner Y, Zetterberg H, Henriksen K (2016) Serum tau fragments predict return to play in concussed professional ice hockey players. J Neurotrauma 33:1995–1999. doi:10.1089/neu.2014.3741
Shahim P, Mattsson N, Macy EM, Crimmins DL, Ladenson JH, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Tegner Y (2015) Serum visinin-like protein-1 in concussed professional ice hockey players. Brain Inj 29:872–876. doi:10.3109/02699052.2015.1018324
Shahim P, Tegner Y, Wilson DH, Randall J, Skillback T, Pazooki D, Kallberg B, Blennow K, Zetterberg H (2014) Blood biomarkers for brain injury in concussed professional ice hockey players. JAMA Neurol 71:684–692. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.367
Shively SB, Edgerton SL, Iacono D, Purohit DP, Qu BX, Haroutunian V, Davis KL, Diaz-Arrastia R, Perl DP (2016) Localized cortical chronic traumatic encephalopathy pathology after single, severe axonal injury in human brain. Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-016-1649-7
Shively SB, Horkayne-Szakaly I, Jones RV, Kelly JP, Armstrong RC, Perl DP (2016) Characterisation of interface astroglial scarring in the human brain after blast exposure: a post-mortem case series. Lancet Neurol 15:944–953. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30057-6
Siman R, Shahim P, Tegner Y, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Smith DH (2015) Serum SNTF increases in concussed professional ice hockey players and relates to the severity of postconcussion symptoms. J Neurotrauma 32:1294–1300. doi:10.1089/neu.2014.3698
Smith DH, Hicks R, Povlishock JT (2013) Therapy development for diffuse axonal injury. J Neurotrauma 30:307–323. doi:10.1089/neu.2012.2825
Smith DH, Meaney DF, Shull WH (2003) Diffuse axonal injury in head trauma. J Head Trauma Rehabil 18:307–316
Stein TD, Alvarez VE, McKee AC (2014) Chronic traumatic encephalopathy: a spectrum of neuropathological changes following repetitive brain trauma in athletes and military personnel. Alzheimers Res Ther 6:4. doi:10.1186/alzrt234
Stein TD, Alvarez VE, McKee AC (2015) Concussion in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Curr Pain Headache Rep 19:522. doi:10.1007/s11916-015-0522-z
Tremblay S, Henry LC, Bedetti C, Larson-Dupuis C, Gagnon JF, Evans AC, Theoret H, Lassonde M, De Beaumont L (2014) Diffuse white matter tract abnormalities in clinically normal ageing retired athletes with a history of sports-related concussions. Brain 137:2997–3011. doi:10.1093/brain/awu236
Wang Y, Sun P, Wang Q, Trinkaus K, Schmidt RE, Naismith RT, Cross AH, Song SK (2015) Differentiation and quantification of inflammation, demyelination and axon injury or loss in multiple sclerosis. Brain 138:1223–1238. doi:10.1093/brain/awv046
Wansapura JP, Holland SK, Dunn RS, Ball Jr WS (1999) NMR relaxation times in the human brain at 3.0 tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging JMRI 9:531–538
Weiss M, Alkemade A, Keuken MC, Muller-Axt C, Geyer S, Turner R, Forstmann BU (2015) Spatial normalization of ultrahigh resolution 7 T magnetic resonance imaging data of the postmortem human subthalamic nucleus: a multistage approach. Brain Struct Funct 220:1695–1703. doi:10.1007/s00429-014-0754-4
Yeh FC, Wedeen VJ, Tseng WY (2010) Generalized q-sampling imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29:1626–1635. doi:10.1109/TMI.2010.2045126
Yeh FC, Wedeen VJ, Tseng WY (2011) Estimation of fiber orientation and spin density distribution by diffusion deconvolution. NeuroImage 55:1054–1062. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.11.087
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the donors and their families for the generous brain donation which made this research possible. We would also like to thank the Boston University CTE Center for sample procurement. The studies presented in this work were carried out, in part, using Small-Animal MR Facility of the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, and the Hope Center Alafi Neuroimaging Lab, Washington University in St. Louis. This research was funded by the National Institute of Health, and the views expressed are those of the authors. NIH UO1 NS086659-02 (Overall PI: A. McKee, Subproject 3 PI: Brody).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
NIH UO1 NS086659-02 (Overall PI: A. McKee, Subproject 3 PI: Brody).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holleran, L., Kim, J.H., Gangolli, M. et al. Axonal disruption in white matter underlying cortical sulcus tau pathology in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 133, 367–380 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1686-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1686-x