Abstract
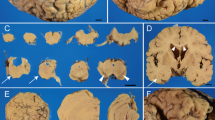
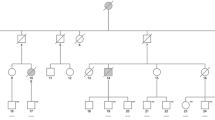
Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids (HDLS) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by cerebral white matter degeneration with axonal spheroids leading to progressive cognitive and motor dysfunction. We report clinical and pathological features, as well as molecular genetic analysis, of a family with HDLS. A pedigree consisting of 27 persons in 5 generations contained 6 affected individuals. Dementia and depression were common; two individuals presented with a syndrome resembling corticobasal degeneration (CBD). Postmortem neuropathologic evaluation of three affected individuals revealed enlargement of the lateral ventricles and marked attenuation of cerebral white matter, but preservation of white matter in brainstem and cerebellum, except for the corticospinal tract. Histopathologic studies showed a loss of myelinated fibers, lipid-laden macrophages and bizarre astrocytes, as well as abundant axonal spheroids that were immunoreactive for phosphorylated neurofilament protein and amyloid precursor protein (APP), but not αB-crystallin and variably with ubiquitin. By electron microscopy, axonal spheroids contained aggregates of intermediate filaments or of organelles that were predominantly vesicular and lamellar. The cerebral cortex had focal neuronal degeneration with αB-crystallin-immunoreactive ballooned neurons. In summary, the present report describes a previously unreported kindred with HDLS with individuals presenting as CBD. Immunohistochemistry for APP and αB-crystallin demonstrates distinctive neurodegeneration in cerebral axons and perikarya.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HDLS:
-
Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids
- eIF2B:
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B
- MMSE:
-
Mini-Mental Status Examination
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- LFB–PAS:
-
Luxol fast blue–periodic acid Schiff
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- MAPT:
-
Microtubule associated protein tau
- FTDP-17:
-
Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome
- CBD:
-
Corticobasal degeneration
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
- CT:
-
Computed tomogram
References
Adolfsson R, Forsell A, Johansson G (1978) Hereditary polycystic osteodysplasia with progressive dementia in Sweden. Lancet 1:1209–1210
Axelsson R, Roytta M, Sourander P, Akesson HO, Andersen O (1984) Hereditary diffuse leucoencephalopathy with spheroids. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 314:1–65
Browne L, Sweeney BJ, Farrell MA (2003) Late-onset neuroaxonal leucoencephalopathy with spheroids and vascular amyloid. Eur Neurol 50:85–90
Dickson DW, Bergeron C, Chin SS, Duyckaerts C, Horoupian D, Ikeda K, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, Lippa CF, Mirra SS, Tabaton M, Vonsattel JP, Wakabayashi K, Litvan I (2002) Office of rare diseases neuropathologic criteria for corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:935–946
Eldridge R, Anayiotos CP, Schlesinger S, Cowen D, Bever C, Patronas N, McFarland H (1984) Hereditary adult-onset leukodystrophy simulating chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 311:948–953
Goodman LE, Dickson DW (1995) Nonhereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids presenting as early-onset, rapidly progressive dementia [abstract]. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54:471
Gwinn-Hardy K, Mehta ND, Farrer M, Maraganore D, Muenter M, Yen SH, Hardy J, Dickson DW (2000) Distinctive neuropathology revealed by α-synuclein antibodies in hereditary parkinsonism and dementia linked to chromosome 4p. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 99:663–672
Hancock N, Poon M, Taylor B, McLean C (2003) Hereditary diffuse leucoencephalopathy with spheroids. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1345–1347
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Petersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaff E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebrand M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski J, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd PR, Hayward N, Kwok JB, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann D, Lynch T, Heutink P (1998) Association of missense and 5’-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393:702–705
Jellinger KA, Duda J (2003) Neuroaxonal dystrophies. In: Dickson DW (eds) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 386–389
Kondo T, Takahashi K, Kohara N, Takahashi Y, Hayashi S, Takahashi H, Matsuo H, Yamazaki M, Inoue K, Miyamoto K, Yamamura T (2002) Heterogeneity of presenile dementia with bone cysts (Nasu–Hakola disease): three genetic forms. Neurology 59:1105–1107
Leegwater PA, Vermeulen G, Konst AA, Naidu S, Mulders J, Visser A, Kersbergen P, Mobach D, Fonds D, van Berkel CG, Lemmers RJ, Frants RR, Oudejans CB, Schutgens RB, Pronk JC, van der Knaap MS (2001) Subunits of the translation initiation factor eIF2B are mutant in leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Nat Genet 29:383–388
Litvan I, Bhatia KP, Burn DJ, Goetz CG, Lang AE, McKeith I, Quinn N, Sethi KD, Shults C, Wenning GK (2003) Movement disorders society scientific issues committee report: SIC task force appraisal of clinical diagnostic criteria for parkinsonian disorders. Mov Disord 18:467–486
Marotti JD, Tobias S, Fratkin JD, Powers JM, Rhodes CH (2004) Adult onset leukodystrophy with neuroaxonal spheroids and pigmented glia: report of a family, historical perspective, and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 107:481–488
Miyazu K, Kobayashi K, Fukutani Y, Nakamura I, Hasegawa H, Yamaguchi N, Saitoh T (1991) Membranous lipodystrophy (Nasu–Hakola disease) with thalamic degeneration: report of an autopsied case. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 82:414–419
Moser HW, Loes DJ, Melhem ER, Raymond GV, Bezman L, Cox CS, Lu SE (2000) X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: overview and prognosis as a function of age and brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormality. A study involving 372 patients. Neuropediatrics 31:227–239
Paloneva J, Autti T, Raininko R, Partanen J, Salonen O, Puranen M, Hakola P, Haltia M (2001) CNS manifestations of Nasu–Hakola disease: a frontal dementia with bone cysts. Neurology 56:1552–1558
Paloneva J, Kestila M, Wu J, Salminen A, Bohling T, Ruotsalainen V, Hakola P, Bakker AB, Phillips JH, Pekkarinen P, Lanier LL, Timonen T, Peltonen L (2000) Loss-of-function mutations in TYROBP (DAP12) result in a presenile dementia with bone cysts. Nat Genet 25:357–361
Prass K, Bruck W, Schroder NW, Bender A, Prass M, Wolf T, Van der Knaap MS, Zschenderlein R (2001) Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter presenting with dementia. Ann Neurol 50:665–668
Racette BA, Perry A, D’Avossa G, Perlmutter JS (2001) Late-onset neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation type 1: expanding the clinical spectrum. Mov Disord 16:1148–1152
Sabbadini G, Francia A, Calandriello L, Di Biasi C, Trasimeni G, Gualdi GF, Palladini G, Manfredi M, Frontali M (1995) Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leucoencephalopathy (CADASIL). Clinical, neuroimaging, pathological and genetic study of a large Italian family. Brain 118:207–215
Terada S, Ishizu H, Yokota O, Ishihara T, Nakashima H, Kugo A, Tanaka Y, Nakashima T, Nakashima Y, Kuroda S (2004) An autopsy case of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids, clinically suspected of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 108:538–545
van der Knaap MS, Kamphorst W, Barth PG, Kraaijeveld CL, Gut E, Valk J (1998) Phenotypic variation in leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Neurology 51:540–547
van der Knaap MS, Leegwater PA, Konst AA, Visser A, Naidu S, Oudejans CB, Schutgens RB, Pronk JC (2002) Mutations in each of the five subunits of translation initiation factor eIF2B can cause leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Ann Neurol 51:264–270
van der Knaap MS, Naidu S, Kleinschmidt-Demasters BK, Kamphorst W, Weinstein HC (2000) Autosomal dominant diffuse leukoencephalopathy with neuroaxonal spheroids. Neurology 54:463–468
Waltz G, Harik SI, Kaufman B (1987) Adult metachromatic leukodystrophy. Value of computed tomographic scanning and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Arch Neurol 44:225–227
Wszolek ZK, Tsuboi Y, Farrer M, Uitti RJ, Hutton ML (2003) Hereditary tauopathies and parkinsonism. Adv Neurol 91:153–163
Yamashita M, Yamamoto T (2002) Neuroaxonal leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids. Eur Neurol 48:20–25
Yazawa I, Nakano I, Yamada H, Oda M (1997) Long tract degeneration in familial sudanophilic leukodystrophy with prominent spheroids. J Neurol Sci 147:185–191
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the members of this kindred for their interest and willingness to cooperate in this study. The study was partially supported by the Morris K. Udall Center for Excellence in Parkinson’s Disease Research (P50 NS40256), VA Research Funds, the Indiana Alzheimer Disease Center (P30 AG10133) and the National Cell Repository for Alzheimer’s Disease (U24 AG21886). YB is a recipient of Robert and Clarice Smith fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baba, Y., Ghetti, B., Baker, M.C. et al. Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids: clinical, pathologic and genetic studies of a new kindred. Acta Neuropathol 111, 300–311 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0046-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0046-z