Purpose
The pediatric appendicitis score (PAS) has been used as a diagnostic tool for the assessment of acute abdominal pain. Our institution has utilized this scoring system as part of a clinical pathway for acute appendicitis. We sought to discover if the PAS could also serve as a prognostic indicator.
Methods
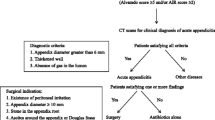
Patients treated within the clinical pathway were divided into three groups (A, B, and C) based on the PAS assigned on admission. Data pertaining to intraoperative findings and length of hospital stay were collected prospectively.
Results
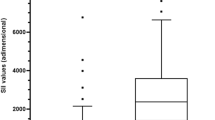
In 4 months, 112 patients were enrolled in the study (median age 10.5, range 1–18). 69 of these patients underwent early laparoscopic appendectomy. For group A, 75% had simple appendicitis and 5% were complex. For group B, 68.4% patients had simple appendicitis and 26.3% were complex. For group C, 27.3% were simple and 63.6% were complex. Mean length of hospital stay increased from 1.63 ± 0.34 for patients in group A to 5.9 ± 1.37 for patients in group C.
Conclusion
Our observational data suggests that the PAS may be a prognostic tool for acute appendicitis. It thereby may impact on preoperative management and postoperative clinical pathways. A larger cohort is necessary to validate our findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samuel M (2002) Pediatric appendicitis score. J Pediatr Surg 37(6):877–881. doi:S0022346802397938[pii]
Partrick DA (2006) Prospective evaluation of a primary laparoscopic approach for children presenting with simple or complicated appendicitis. Am J Surg 192(6):750–755. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.08.039
Pearl RH, Hale DA, Molloy M, Schutt DC, Jaques DP (1995) Pediatric appendectomy. J Pediatr Surg 30(2):173–178 (discussion 178–181)
Dado G, Anania G, Baccarani U, Marcotti E, Donini A, Risaliti A, Pasqualucci A, Bresadola F (2000) Application of a clinical score for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in childhood: a retrospective analysis of 197 patients. J Pediatr Surg 35(9):1320–1322. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2000.9316
Lintula H, Pesonen E, Kokki H, Vanamo K, Eskelinen M (2005) A diagnostic score for children with suspected appendicitis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 390(2):164–170. doi:10.1007/s00423-005-0545-8
Hsiao KH, Lin LH, Chen DF (2005) Application of the mantrels scoring system in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. Acta Paediatr Taiwan 46(3):128–131
Bhatt M, Joseph L, Ducharme FM, Dougherty G, McGillivray D (2009) Prospective validation of the pediatric appendicitis score in a Canadian pediatric emergency department. Acad Emerg Med 16(7):591–596. doi:10.1111/j.1553-2712.2009.00445.x
Goldman RD, Carter S, Stephens D, Antoon R, Mounstephen W, Langer JC (2008) Prospective validation of the pediatric appendicitis score. J Pediatr 153(2):278–282. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.01.033
Gurleyik G, Emir S, Kilicoglu G, Arman A, Saglam A (2005) Computed tomography severity index, APACHE II score, and serum CRP concentration for predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. JOP 6(6):562–567
Beltran MA, Almonacid J, Vicencio A, Gutierrez J, Cruces KS, Cumsille MA (2007) Predictive value of white blood cell count and C-reactive protein in children with appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg 42(7):1208–1214. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.02.010
Wang LT, Prentiss KA, Simon JZ, Doody DP, Ryan DP (2007) The use of white blood cell count and left shift in the diagnosis of appendicitis in children. Pediatr Emerg Care 23(2):69–76. doi:10.1097/PEC.0b013e31802d1716
Shalak F, Almulhim SI, Ghantous S, Yazbeck S (2009) Laparoscopic appendectomy: burden or benefit? A single-center experience. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 19(3):427–429. doi:10.1089/lap.2008.0109
Pham VA, Pham HN, Ho TH (2009) Laparoscopic appendectomy: an efficacious alternative for complicated appendicitis in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg 19(3):157–159. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1202247
Mallick MS, Al-Qahtani A, Al-Bassam A (2007) Laparoscopic appendectomy is a favorable alternative for complicated appendicitis in children. Pediatr Surg Int 23(3):257–259. doi:10.1007/s00383-006-1833-2
Fraser JD, Aguayo P, Sharp SW, Snyder CL, Holcomb 3rd GW, Ostlie DJ, St Peter SD (2009) Physiologic predictors of postoperative abscess in children with perforated appendicitis: subset analysis from a prospective randomized trial. Surgery. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2009.10.057
St Peter SD, Sharp SW, Holcomb GW 3rd, Ostlie DJ (2008) An evidence-based definition for perforated appendicitis derived from a prospective randomized trial. J Pediatr Surg 43(12):2242–2245. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2008.08.051
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adibe, O.O., Muensterer, O.J., Georgeson, K.E. et al. Severity of appendicitis correlates with the pediatric appendicitis score. Pediatr Surg Int 27, 655–658 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-010-2744-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-010-2744-9