Abstract
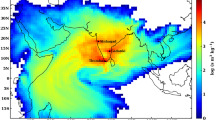
We used the global atmospheric chemical transport model, GEOS-Chem, to simulate the spatial distribution and seasonal variation of surface-layer methane (CH4) in 2004, and quantify the impacts of individual domestic sources and foreign transport on CH4 concentrations over China. Simulated surface-layer CH4 concentrations over China exhibit maximum concentrations in summer and minimum concentrations in spring. The annual mean CH4 concentrations range from 1800 ppb over western China to 2300 ppb over the more populated eastern China. Foreign emissions were found to have large impacts on CH4 concentrations over China, contributing to about 85% of the CH4 concentrations over western China and about 80% of those over eastern China. The tagged simulation results showed that coal mining, livestock, and waste are the dominant domestic contributors to CH4 concentrations over China, accounting for 36%, 18%, and 16%, respectively, of the annual and national mean increase in CH4 concentration from all domestic emissions. Emissions from rice cultivation were found to make the largest contributions to CH4 concentrations over China in the summer, which is the key factor that leads to the maximum seasonal mean CH4 concentrations in summer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding, W. X., Z. C. Cai, and D. X. Wang, 2004: Preliminary budget of methane emissions from natural wetlands in China. Atmos. Environ., 38, 751–759.
Dlugokencky, E. J., P. M. Lang, A. M. Crotwell, and K. A. Masarie, 2012: Atmospheric methane dry air mole fractions from the NOAA/ESRL carbon cycle cooperative global air sampling network, 1983–2011. Version: 2012-09-24. [Available online at ftp://ftp.cmdl.noaa.gov/ccg/ch4/flask/ event/.]
Duncan, B., D. Portman, I. Bey, and C. Spivakovsky, 2000: Parameterization of OH for efficient computation in chemical tracer models. J. Geophys. Res., 105, 12259–12262.
EDGAR v4.0, 2009: European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC)/Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (PBL). Emission Database for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR), release version 4.0. [Available online at http://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu.]
Fang, S. X., L. X. Zhou, L. Xu, B. Yao, L. X. Liu, L. J. Xia, and H. Y. Wang, 2012: CH4 concentrations and the variation characteristics at the four WMO/GAW background stations in China. Environmental Science, 33(9), 2917–2923. (in Chinese)
Fiore, A. M., D. J. Jacob, B. D. Field, D. G. Streets, S. D. Fernandes, and C. Jang, 2002: Linking ozone pollution and climate change: The case for controlling methane. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29(19), 1919, doi: 10.1029/2002GL015601.
Fiore, A. M., D. J. Jacob, H. Liu, R. M. Yantosca, T. D. Fairlie, and Q. Li, 2003: Variability in surface ozone background over the United States: Implications for air quality policy. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D24), 4787, doi: 10.1029/2003JD003855.
Frankenberg, C., and Coauthors, 2006: Satellite chartography of atmospheric methane from SCIAMACHY on board ENVISAT: Analysis of the years 2003 and 2004. J. Geophys. Res., 111, D07303, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006235.
Fraser, A., C. C. Miller, P. I. Palmer, N. M. Deutscher, N. B. Jones, and D. W. T. Griffith, 2011: The Australian methane budget: Interpreting surface and train-borne measurements using a chemistry transport model. J. Geophys. Res., 116, D20306, doi: 10.1029/2011JD015964.
Fung, I., J. John, J. Lerner, E. Matthews, M. Prather, L. P. Steele, and P. J. Fraser, 1991: Three-dimensional model synthesis of the global methane cycle. J. Geophys. Res., 96(D7), 13033–13065, doi: 10.1029/91JD01247.
Holzer, M., T. M. Hall, and R. B. Stull, 2005: Seasonality and weather-driven variability of transpacific transport. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D23103, doi: 10.1029/2005jd006261.
IPCC, 2007: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Solomon et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 996 pp.
Jacob, D. J., and Coauthors, 2003: Transport and Chemical Evolution over the Pacific (TRACE-P) aircraft mission: Design, execution, and first results. J. Geophys. Res., 108, D209000, doi: 10.1029/2002JD003276.
Ji, X. Y., L. Y. Yang, Y. S. Wang, and G. B. Cui, 2006: Background density characteristic of the main greenhouse gas near-surface in Tai Lake basin. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 18(3), 11–15. (in Chinese)
Liu, L. X., L. X. Zhou, M. Wen, F. Zhang, S. X. Fang, and B. Yao, 2009: Characteristics of atmospheric CH4concentration variations at four national baseline observatories in China. Advances in Climate Change Research, 5(5), 285–290.
Pickett-Heaps, C. A., and Coauthors, 2011: Magnitude and seasonality of wetland methane emissions from the Hudson Bay Lowlands (Canada). Atmos. Chem. Phys., 11, 3773–3779, doi: 10.5194/acp-11-3773-2011.
Prinn, R. G., and Coauthors, 2005: Evidence for variability of atmospheric hydroxyl radicals over the past quarter century. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L07809, doi: 10.1029/2004GL022228.
Schneising, O., M. Buchwitz, J. P. Burrows, H. Bovensmann, P. Bergamaschi, and W. Peters, 2009: Three years of greenhouse gas column-averaged dry air mole fractions retrieved from satellite—Part 2: Methane. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 443–465, doi: 10.5194/acp-9-443-2009.
Shangguan, X. J., M. X. Wang, D. Z. Chen, and R. X. Shen, 1993: The transport of methane in the rice paddy fields. Adv. Earth Sci., 8(5), 13–22. (in Chinese)
Streets, D. G., and Coauthors, 2003: An inventory of gaseous and primary aerosol emissions in Asia in the year 2000. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D21), 8809, doi: 10.1029/2002JD003093.
Su, M. F., Y. P. Lin, X. Q. Fan, L. Peng, and C. S. Zhao, 2012: Impacts of global emissions of CO, NOx, and CH4 on China tropospheric hydroxyl free radicals. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 29(4), 838–854, doi:10.1007/s00376-012-1229-2.
van der Werf, G. R., J. T. Randerson, L. Giglio, G. J. Collatz, P. S. Kasibhatla, and A. F. Arellano Jr., 2006: Interannual variability in global biomass burning emissions from 1997 to 2004. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6, 3423–3441, doi: 10.5194/acp-6-3423-2006.
Wang, J. S., J. A. Logan, M. B. McElroy, B. N. Duncan, I. A. Megretskaia, and R. M. Yantosca, 2004: A 3-D model analysis of the slowdown and interannual variability in the methane growth rate from 1988 to 1997. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 18, GB3011, doi: 10.1029/2003GB002180.
Wang, Y. S., and M. X. Wang, 2000: Seasonal variation and trend of atmospheric methane in Beijing. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 24(2), 157–164. (in Chinese)
Wang, Y. S., and Y. H. Wang, 2003: Quick measurement of CH4, CO2 and N2O emissions from a short-plant ecosystem. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20(5), 842–844.
Xiao, Y. P., and Coauthors, 2004: Constraints on Asian and European sources of methane from CH4-C2H6-CO correlations in Asian outflow. J. Geophys. Res., 109, D15S16, doi: 10.1029/2003JD004475.
Xiong X., S. Houweling, J. Wei, E. Maddy, F. Sun, and C. Barnet, 2009: Methane plume over south Asia during the monsoon season: Satellite observation and model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 783–794.
Yan, X. Y., Z. C. Cai, T. Ohara, and H. Akimoto, 2003: Methane emission from rice fields in mainland China: Amount and seasonal and spatial distribution. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D16), 4505, doi: 10.1029/2002JD003182.
Yevich, R., and J. A. Logan, 2003: An assessment of biofuel use and burning of agricultural waste in the developing world. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 17(4), 1095, doi: 10.1029/2002GB001952.
Zhang, B., and G. Q. Chen, 2010: Methane emissions by Chinese economy: Inventory and embodiment analysis. Energy Policy, 38, 4304–4316.
Zhang, X. Y., W. G. Bai, P. Zhang, and W. H. Wang, 2011a: Spatiotemporal variations in mid-upper tropospheric methane over China from satellite observations. Chinese Sci. Bull., 56, 2804–2811. (in Chinese)
Zhang, X. Y, H. Jiang, Y. Q. Wang, Y. Han, M. Buchwitz, O. Schneising, and J. P. Burrows, 2011b: Spatial variations of atmospheric methane concentrations in China. Inter. J. Remote Sens., 32(3), 833–847.
Zheng, X. Y., C. D. Liu, F. H. Zhao, F. K. Duan, T. Yu, and H. Cachier, 2005: Seasonal characterizers of contributions from biomass burning emissions to atmospheric particles in Beijing. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 35(4), 346–352. (in Chinese)
Zhou, J. B., M. M. Jiang, and G. Q. Chen, 2007a: Estimation of methane and nitrous oxide emission from livestock and poultry in China during 1949–2003. Energy Policy, 35(7), 3759–3767.
Zhou, L. X., D. E. J. Worthy, P. M. Lang, M. K. Ernst, X. C. Zhang, Y. P. Wen, and J. L. Li, 2004: Ten years of atmospheric methane observations at a high elevation site in Western China. Atmos. Environ., 38(40), 7041–7054.
Zhou, L. X., X. J. Zhou, X. C. Zhang, Y. P. Wen, and P. Yan, 2007b: Progress in the study of background greenhouse gases at Waliguan observatory. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 65(3), 458–468. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Liao, H. & Wang, Y. Simulated spatial distribution and seasonal variation of atmospheric methane over China: Contributions from key sources. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 31, 283–292 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-013-3018-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-013-3018-y