Abstract.
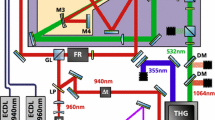
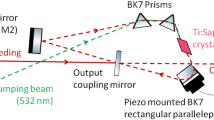
We demonstrate third-harmonic microscopy of thin biological objects using a Ti:sapphire laser source. A very simple modification to the collection and detection systems of the microscope allows for the detection of the third-harmonic signal near 270 nm. We show that, using a Ti:sapphire laser, we can combine third-harmonic imaging with two-photon excitation fluorescence simultaneously. Compared to other possible laser sources for third-harmonic microscopy, the Ti:sapphire laser provides better optical resolution, better power availability, and is less absorbed in water. We find that the Ti:sapphire laser is the most suitable laser source for third-harmonic microscopy for thin biological specimens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 September 2001 / Revised version: 29 October 2001 / Published online: 27 June 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yelin, D., Oron, D., Korkotian, E. et al. Third-harmonic microscopy with a titanium–sapphire laser. Appl Phys B 74 (Suppl 1), s97–s101 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-0884-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-0884-x