Abstract
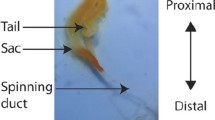
The diversity in function and mechanical behavior of spider silks, and the ability to produce these silks recombinantly, have tremendous potential in creating a new class of biomimetic materials. Here we investigate the structural and mechanical properties of pyriform silks from the golden orb-weaver, Nephila clavipes. Nanoscale indentation measurements using atomic force microscopy on natural pyriform silk suggests that this biomaterial has high toughness that may be suitable for dissipating high amounts of mechanical energy. We also observed the occurrence of highly organized nanocrystals within the pyriform silk fibers that may contribute to the remarkable energy dissipation capability of these silks. It has been demonstrated that poly-(Gly–Ala) and poly-Ala stretches within the internal block repeat modules of dragline silk fibroins form nanocrystals, and these nanocrystalline structures may be responsible for the high extensibility of the dragline silks. In contrast, amino acid sequence analysis shows that PySp2 does not contain the same motifs. In the absence of poly-(Gly–Ala) and poly-Ala repeats, we hypothesized that PySp2 contains new protein motifs sufficient to polymerize into functional structures. To investigate the functional contributions of these novel motifs during pyriform fiber formation, we expressed different recombinant PySp2 fibroins with various segments spanning its block repeat units. We demonstrate that PySp2 recombinant proteins with the Pro-rich sub-block domain (PXP motifs, where X= sub-set of the amino acids A, L, or R) and/or the Ser + Gln + Ala-rich sub-block domain (QQSSVAQS motifs) are sufficient for artificial fiber formation. Moreover, we show that recombinant PySp2 proteins that contain a single block repeat unit can self-assemble into foam-like nanostructures. Collectively, our findings support the use of PySp2 recombinant proteins for a wide range of biomimetic materials with morphologies ranging from fibers to porous structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Xu, R.V. Lewis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 7120 (1990)
M.B. Hinman, R.V. Lewis, J. Biol. Chem. 267, 19320 (1992)
A. Sponner, B. Schlott, F. Vollrath, E. Unger, F. Grosse, K. Weisshart, Biochemistry 44, 4727 (2005)
X. Hu, K. Kohler, A.M. Falick, A.M. Moore, P.R. Jones, C. Vierra, Biochemistry 45, 3506 (2006)
R.V. Lewis, C.Y. Hayashi, Science 287, 1477 (2000)
A. Sponner, E. Unger, F. Grosse, K. Weisshart, Biomacromolecules 5, 840 (2004)
A. Rising, G. Hjalm, W. Engstrom, J. Johansson, Biomacromolecules 7, 3120 (2006)
P. Geurts, L. Zhao, Y. Hsia, E. Gnesa, S. Tang, F. Jeffery, C.L. Mattina, A. Franz, L. Larkin, C. Vierra, Biomacromolecules 11, 3495 (2010)
R. Foelix, Biology of Spiders (Oxford University Press, New York, 1996)
B. Swanson, T. Blackledge, J. Beltran, C. Hayashi, Appl. Phys. A 82, 213 (2006)
J.D. van Beek, S. Hess, F. Vollrath, B.H. Meier, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 10266 (2002)
B.L. Thiel, K.B. Guess, C. Viney, Biopolymers 41, 703 (1997)
T. Lefevre, M.E. Rousseau, M. Pezolet, Biophys. J. 92, 2885 (2007)
S. Keten, Z. Xu, B. Ihle, M.J. Buehler, Nat. Mater. 9, 359 (2010)
A. Simmons, E. Ray, L.W. Jelinski, Macromolecules 27, 5235 (1994)
W. Oliver, G. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004)
S. Tang, P. Mathews, C. Randall, E. Yurtsev, K. Fields, A. Wong, A. Kuo, A. Alliston, P. Hansma, Polym. Test. 29, 159 (2009)
X. Hu, B. Lawrence, K. Kohler, A.M. Falick, A.M. Moore, E. McMullen, P.R. Jones, C. Vierra, Biochemistry 44, 10020 (2005)
M. Tian, R.V. Lewis, Biochemistry 44, 8006 (2005)
N.A. Ayoub, J.E. Garb, R.M. Tinghitella, M.A. Collin, C.Y. Hayashi, PLoS ONE 2, e514 (2007)
D.J. Perry, D. Bittencourt, J. Siltberg-Liberles, E.L. Rech, R.V. Lewis, Biomacromolecules 18, 3000 (2010)
F. Hagn, L. Eisoldt, J.G. Hardy, C. Vendrely, M. Coles, T. Scheibel, H. Kessler, Nature 465, 239 (2010)
F. Teule, A.R. Cooper, W.A. Furin, D. Bittencourt, E.L. Rech, A. Brooks, R.V. Lewis, Nat. Protoc. 4, 341 (2009)
S.A. Anthoula Lazaris, Y. Huang, J.-F. Zhou, F. Duguay, N. Chretien, E.A. Welsh, J.W. Soares, C.N. Karatzas, Science 295, 472 (2002)
X.X. Xia, Z.G. Qian, C.S. Ki, Y.H. Park, D.L. Kaplan, S.Y. Lee, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 14059 (2010)
D. Huemmerich, U. Slotta, T. Scheibel, Appl. Phys. A 82, 219 (2006)
K. Spiess, A. Lammel, T. Scheibel, Macromol. Biosci. 10, 998 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsia, Y., Gnesa, E., Tang, S. et al. Identification and synthesis of novel biomaterials based on spider structural silk fibers. Appl. Phys. A 105, 301–309 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6621-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6621-8